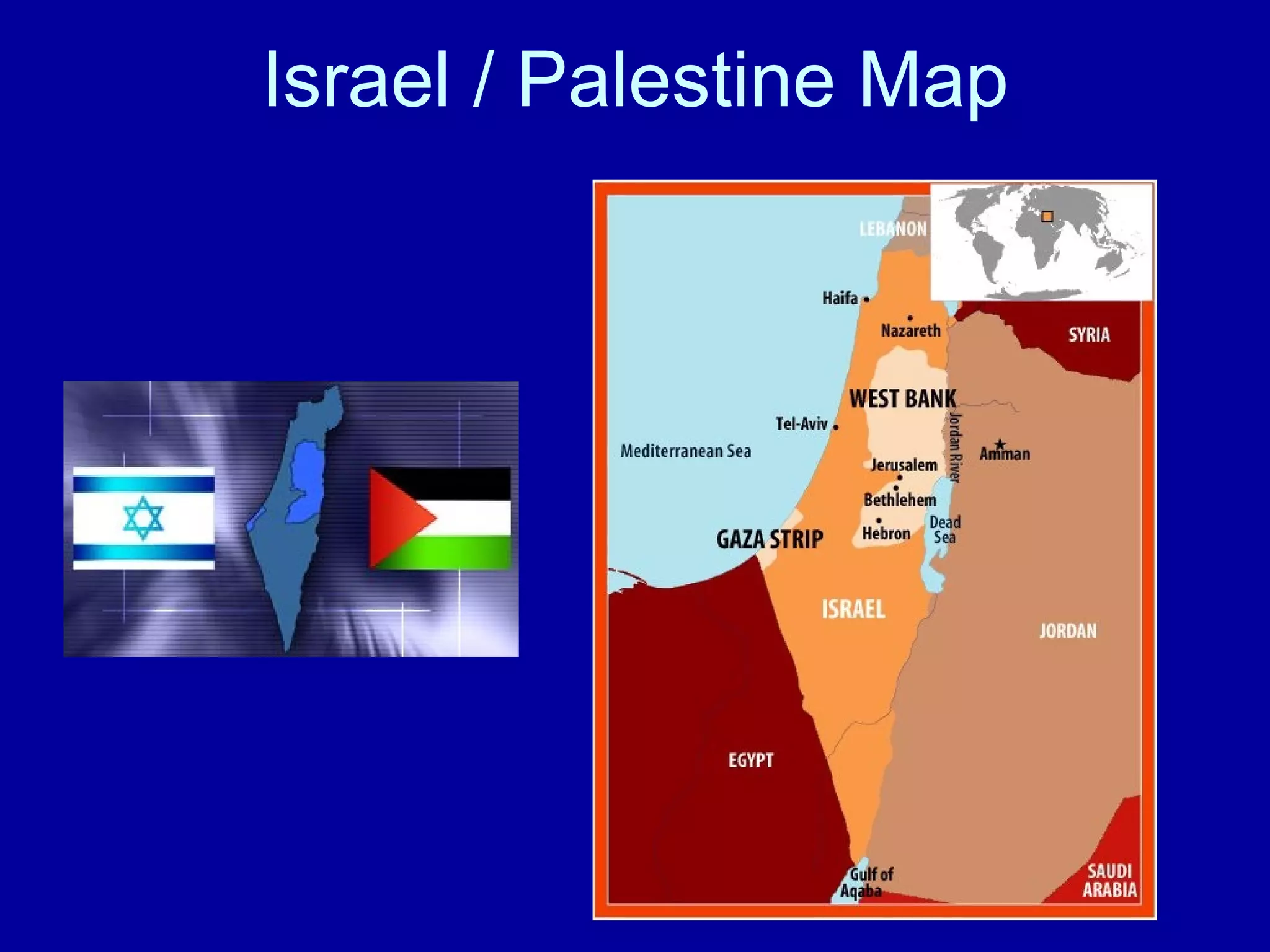
The Middle East region faces significant religious, ethnic, and political divisions that have led to ongoing conflicts. The area contains important natural resources like oil, but limited water supplies that countries disagree over. Governments range from democracies to dictatorships. The Israeli-Palestinian conflict stems from competing claims to the land and Britain's 1917 Balfour Declaration supporting a Jewish homeland. This has resulted in several Arab-Israeli wars over the decades as Palestinians fight for statehood. Civil war has also broken out in Lebanon due to its religious and ethnic diversity. International efforts have pursued a roadmap to peace, but violence continues between Israel and Palestinian groups.