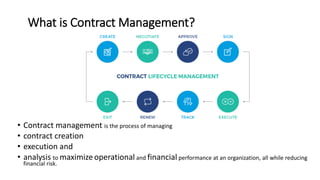
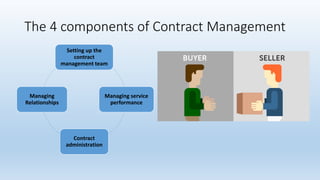
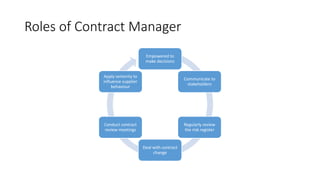
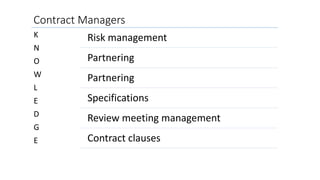
Contract management involves the processes of creating, executing, and analyzing contracts to enhance operational and financial performance while minimizing risks. Key components include managing service performance, administration, and relationships, along with specific responsibilities and skills required for contract managers. Effective contract management leads to benefits such as standardized processes, improved compliance, and reduced spending issues.