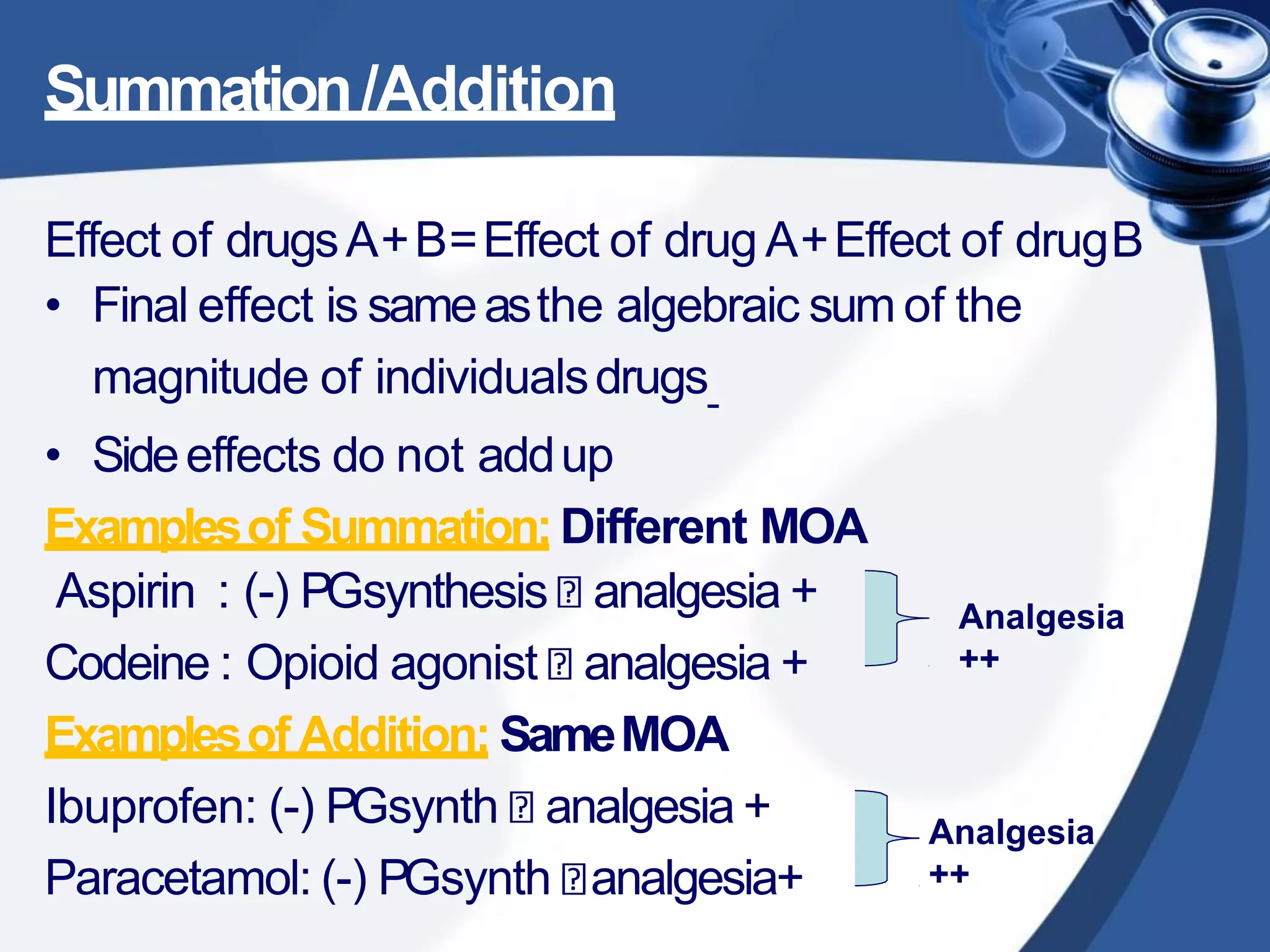
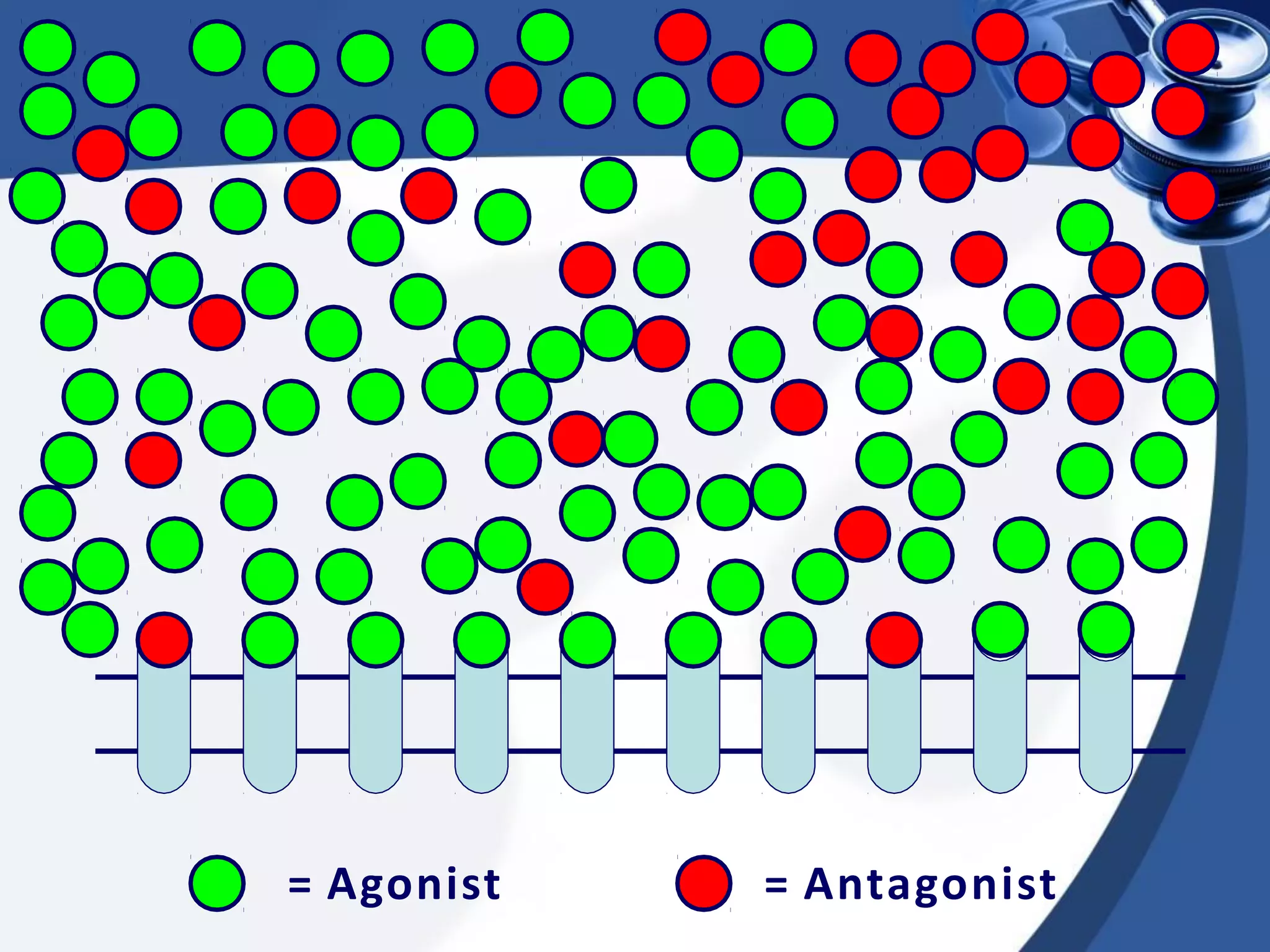
1. Drug combinations can have additive, synergistic, or antagonistic effects depending on how the drugs interact. Additive effects are when the combined effect is equal to the sum of the individual drug effects. Synergistic effects occur when the combined effect is greater than the sum. Antagonistic effects are when the combined effect is less than the sum.
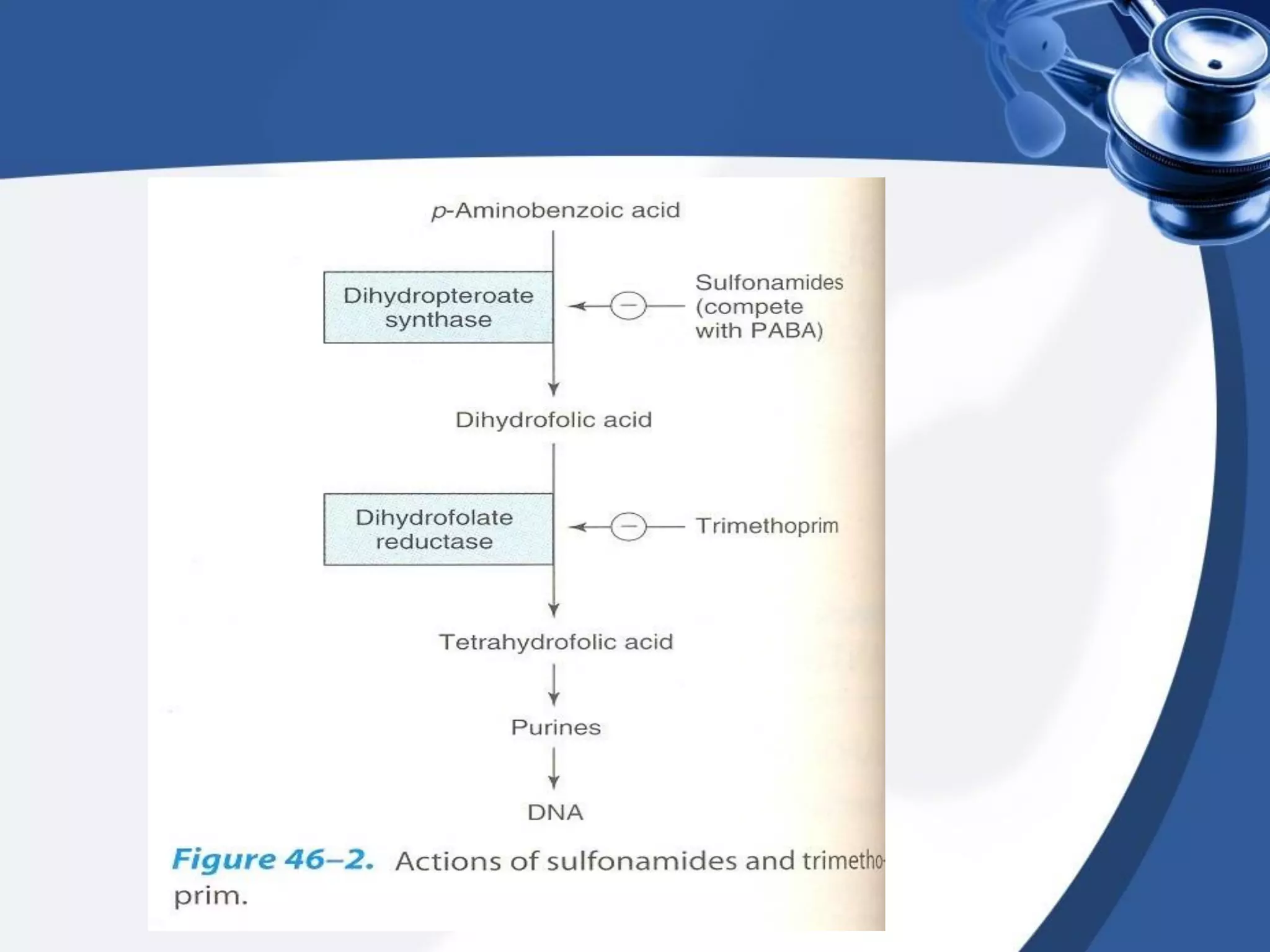
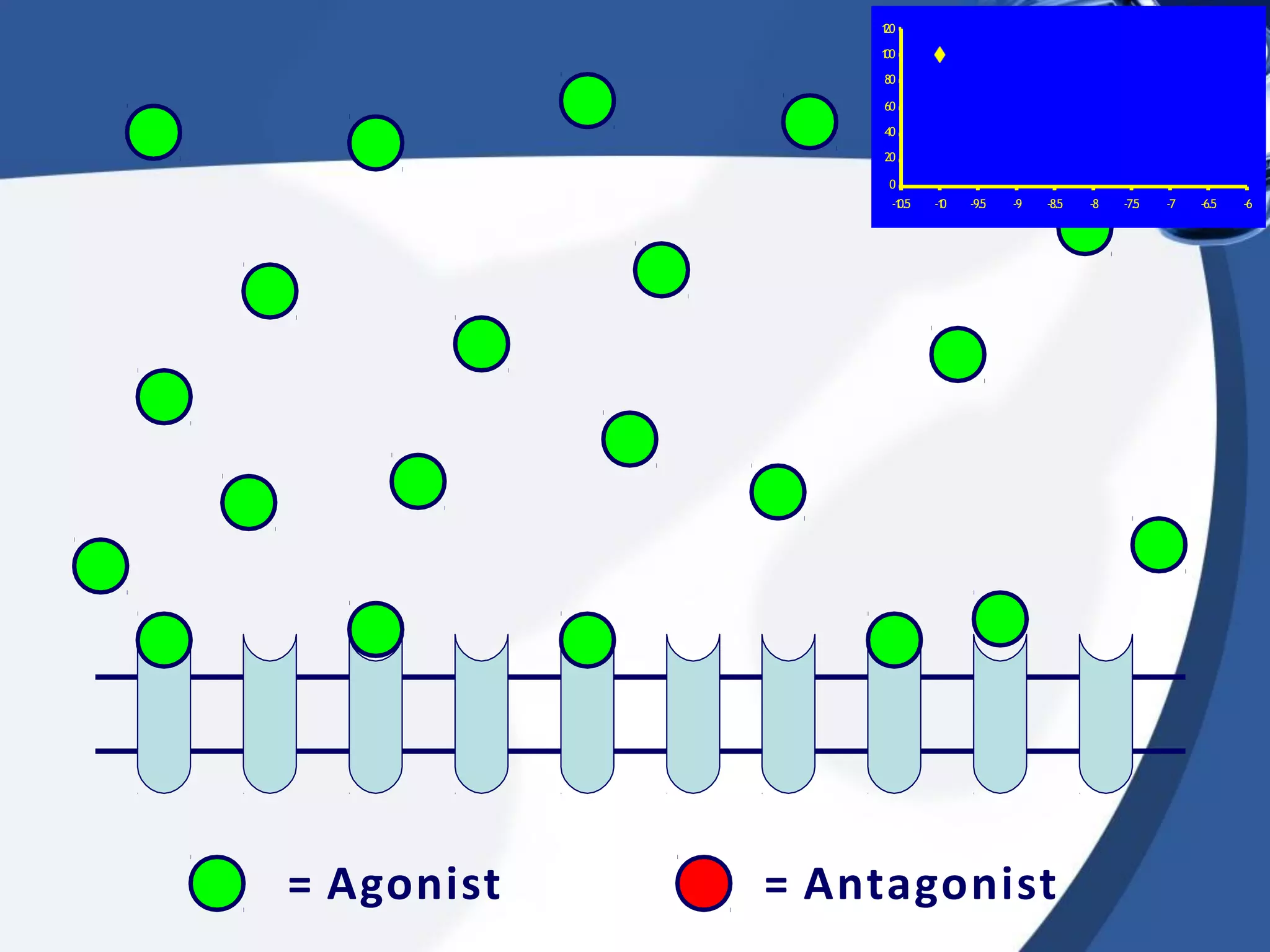
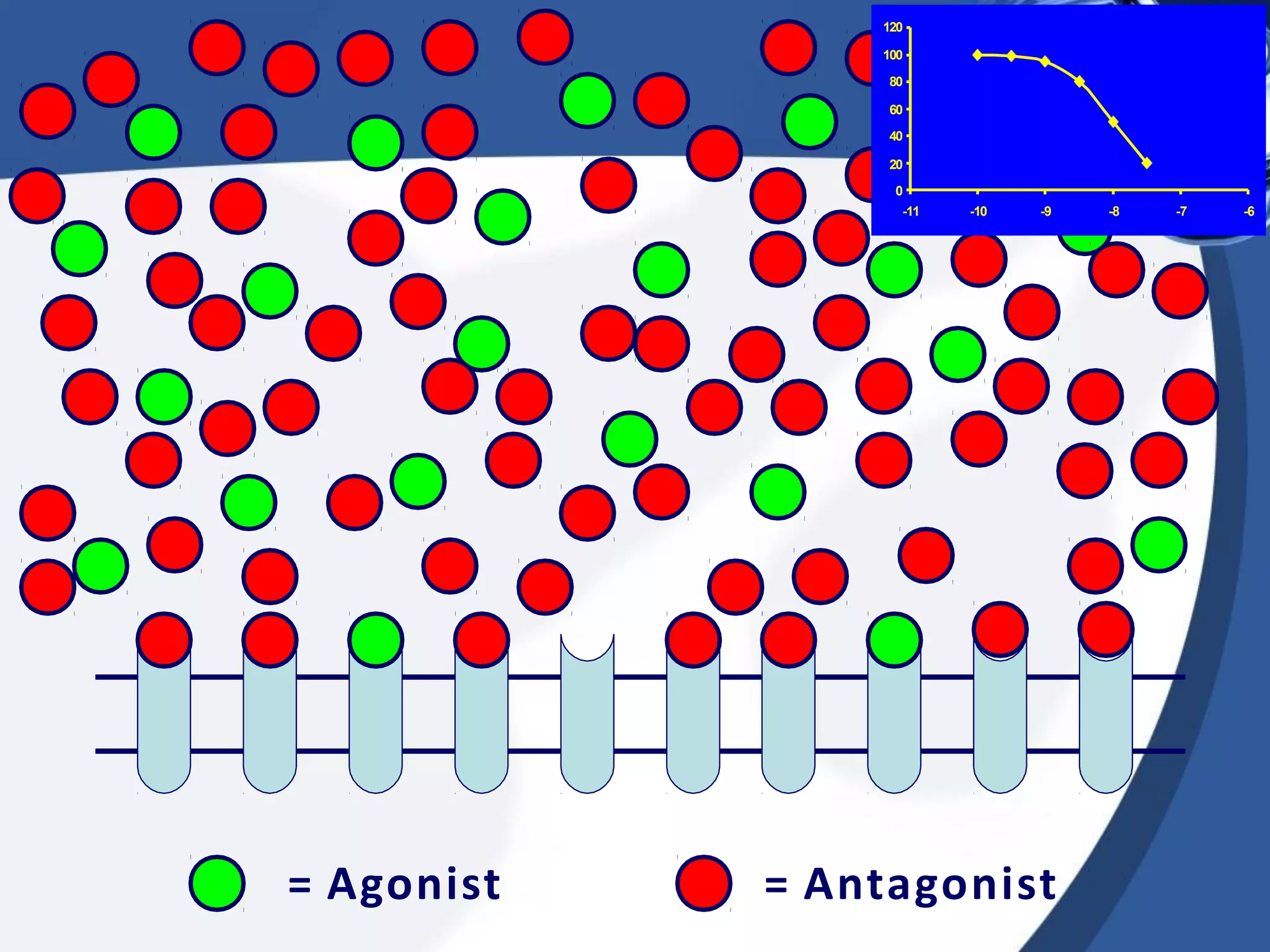
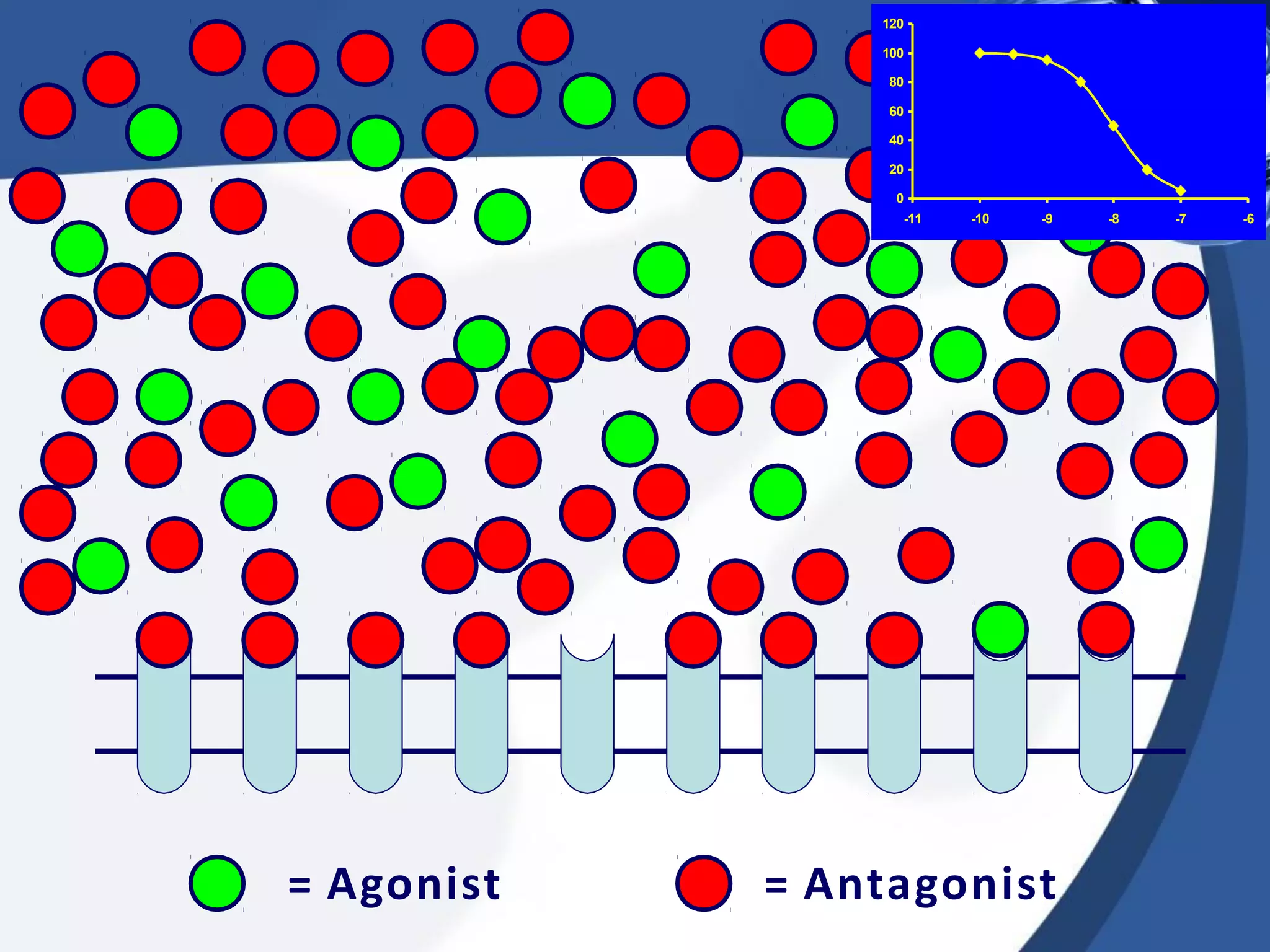
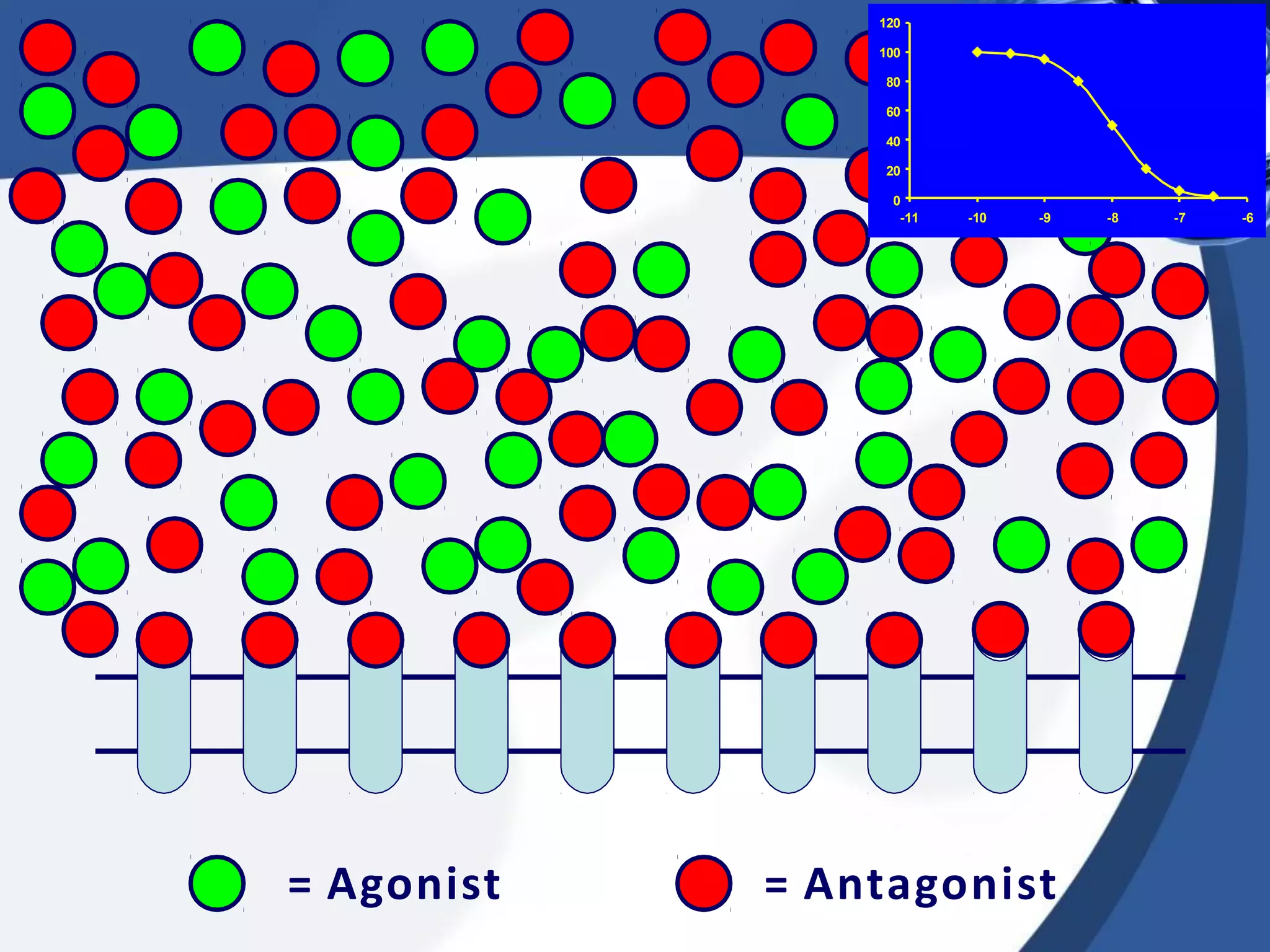
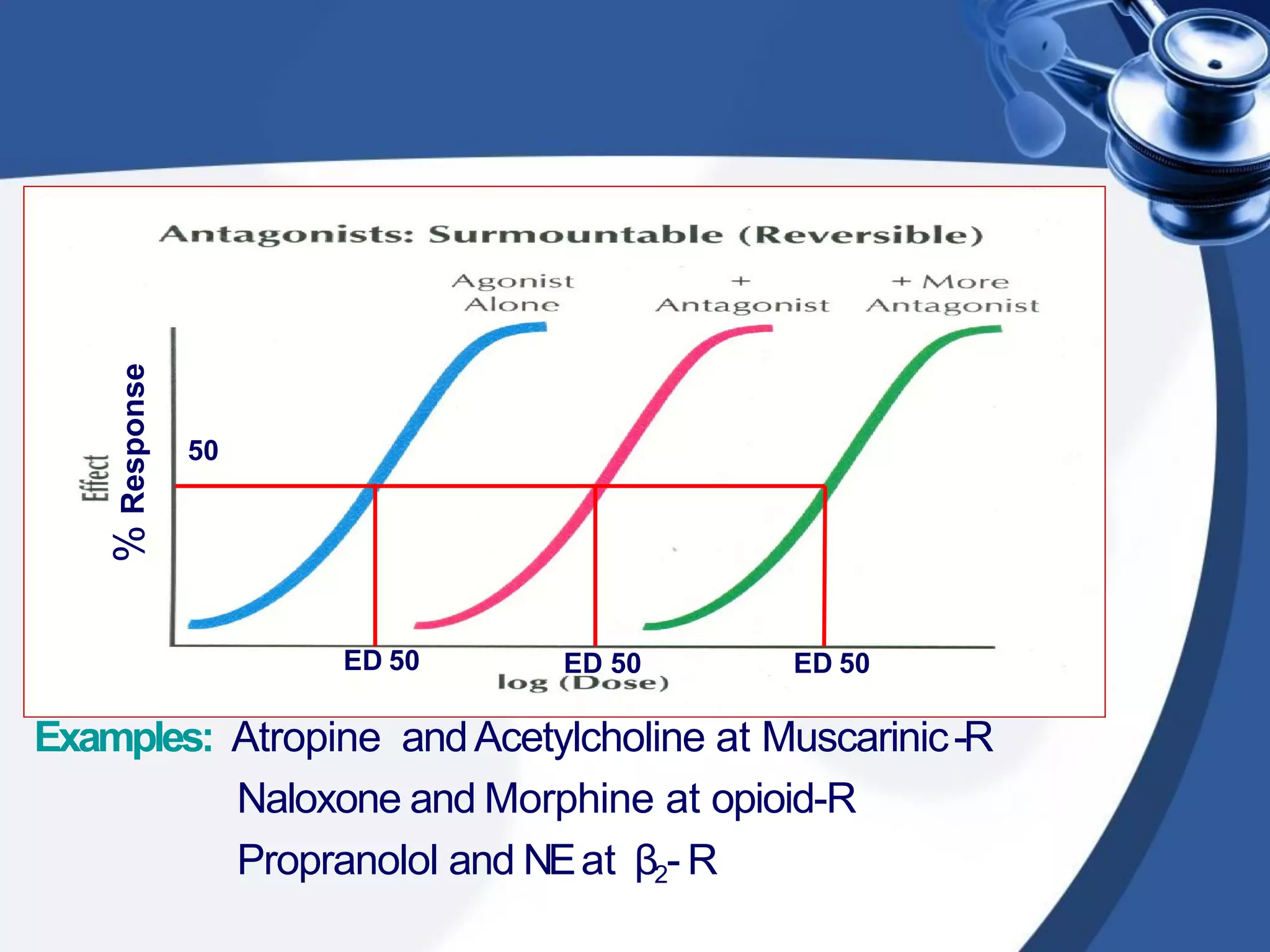
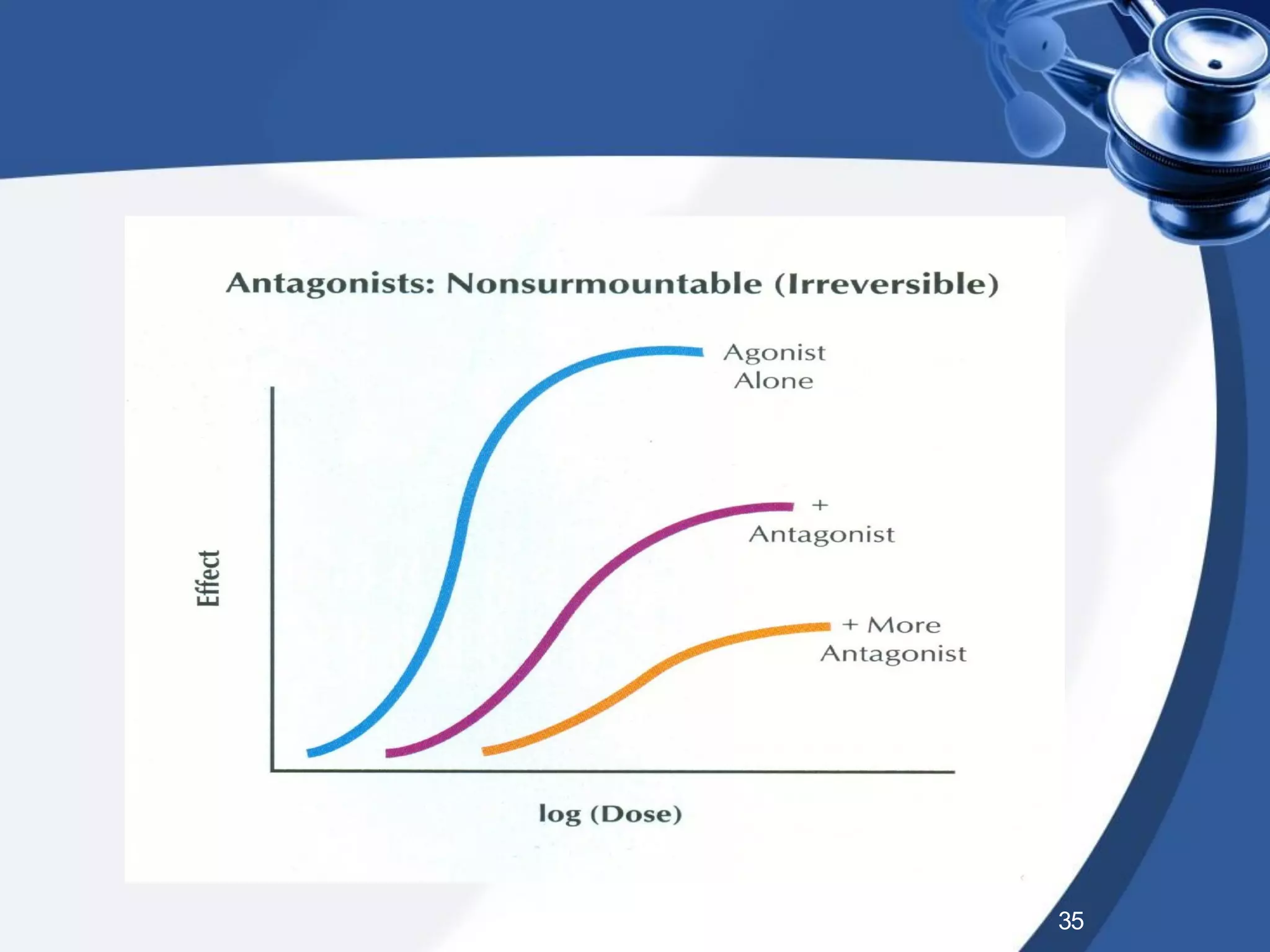
2. There are different types of drug antagonism including competitive (reversible or irreversible), non-competitive, chemical, physiological, and physical. Competitive antagonism occurs when drugs bind to the same receptor site, while non-competitive antagonism involves effects downstream of the receptor.
3. Rightward shifts of dose-response curves indicate competitive antagon