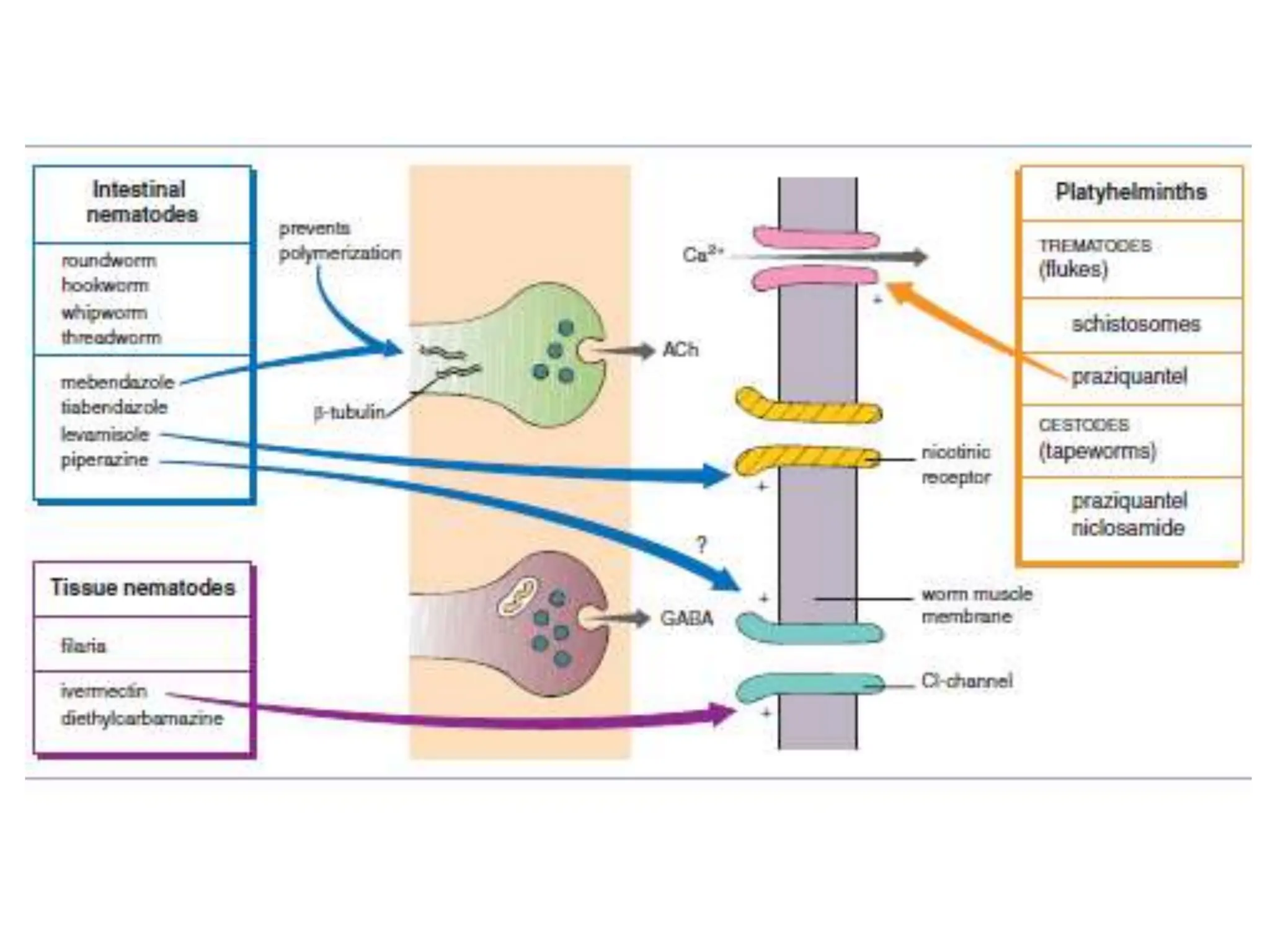
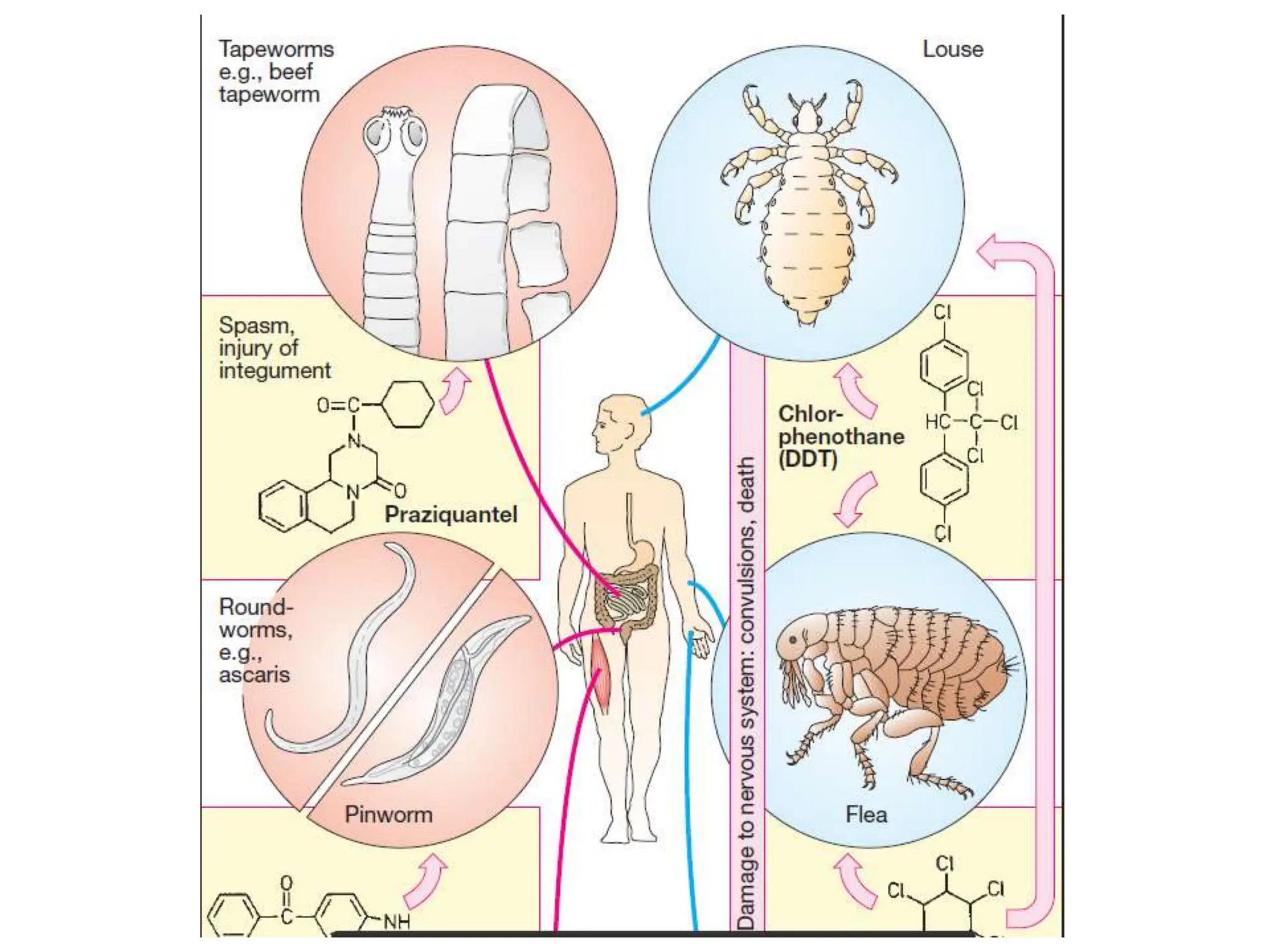
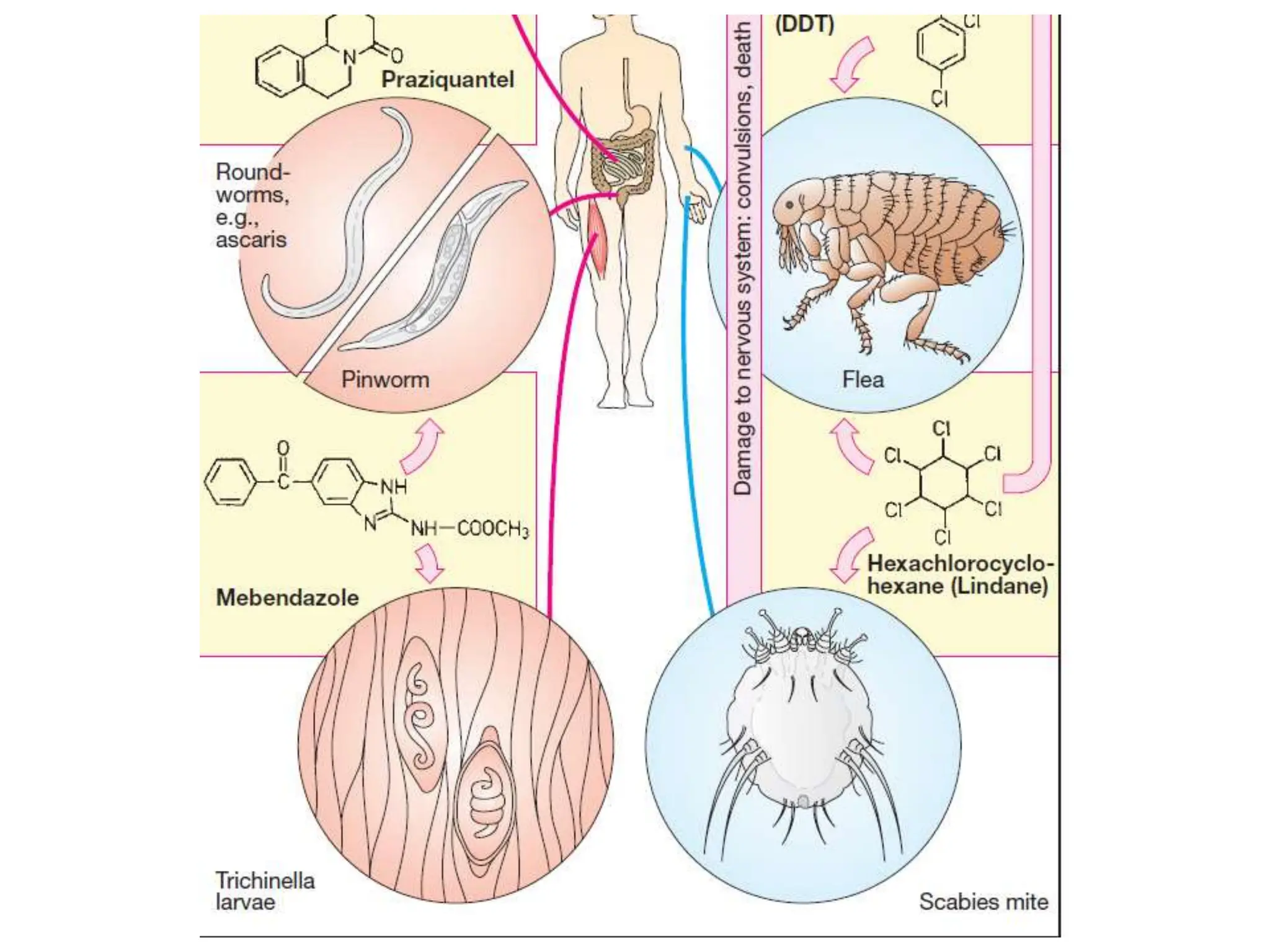
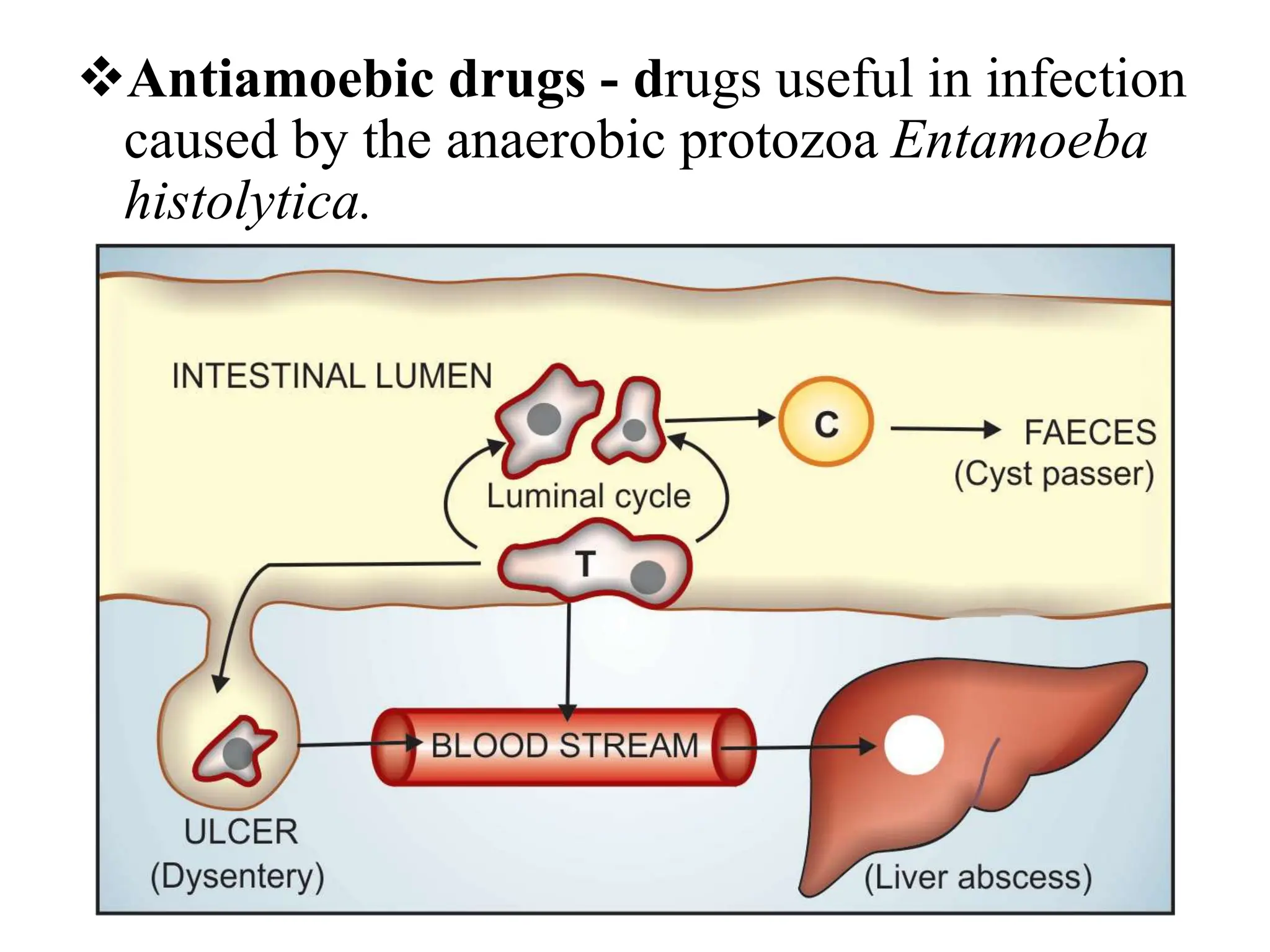
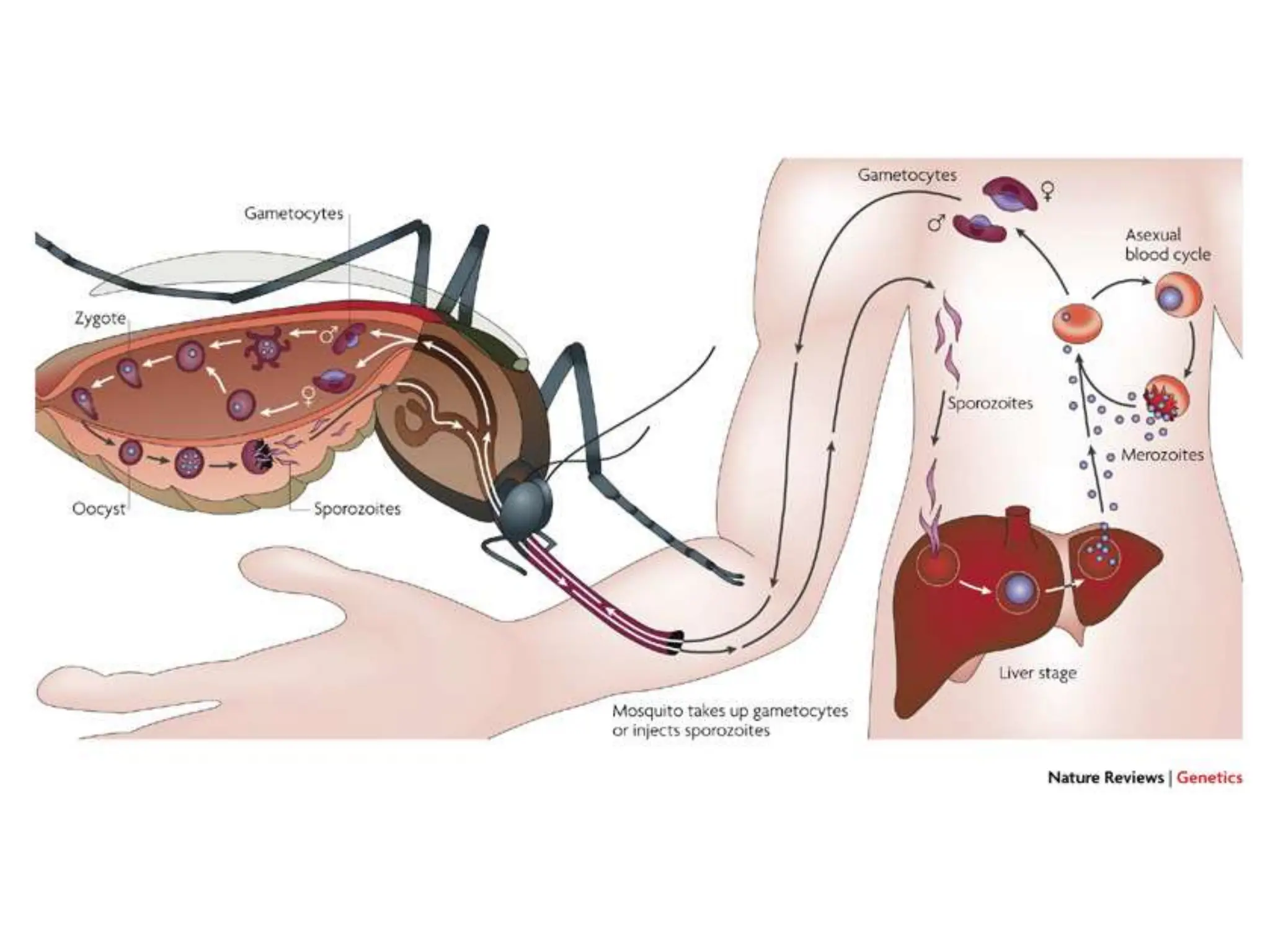
Antihelminthic and antiprotozoal drugs work by killing or expelling parasitic worms and protozoa. Common antihelminthics discussed include mebendazole, albendazole, pyrantel, and levamisole which are used to treat nematode, cestode, and trematode infections. Their mechanisms of action involve inhibiting microtubule assembly, inducing paralysis, or activating nicotinic receptors in the parasites. Common antiprotozoals discussed include metronidazole for amebiasis, giardiasis and trichomoniasis, and drugs for malaria such as chloroquine, primaquine, and antifol combinations. Adverse