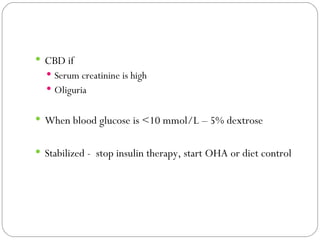
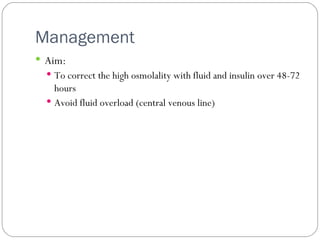
Diabetic coma, also known as hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome, is a serious complication that can occur in people with type 2 diabetes who become ill or stressed. It occurs when blood sugar levels become too high and the body becomes severely dehydrated, with no ketones formed. Early symptoms include increased thirst, urination, weakness, and altered mental state. Treatment involves correcting the high osmolality over 48-72 hours through fluid replacement and insulin, while avoiding fluid overload. Management also includes monitoring sodium levels and stabilizing blood glucose before transitioning to oral medications or diet control.




![Management Manage as for DKA except: Initial resuscitation with colloid 0.9% saline for fluid replacement If [Na+] is > 150 mmol/L, use 5% dextrose Slow correction of Na Start insulin at 3 U/hr Anticoagulate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/comaindiabeticpatient-091102093344-phpapp01/85/Coma-In-Diabetic-Patient-9-320.jpg)