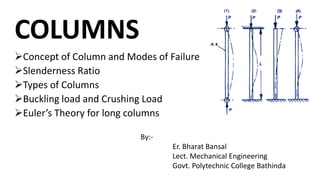
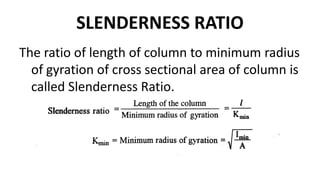
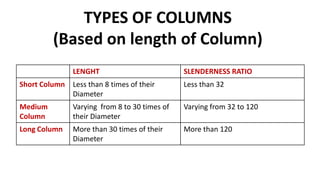
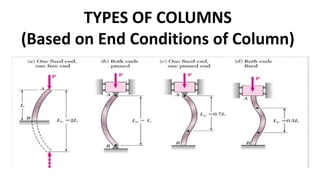
This document discusses columns and column failure. It defines a column as a vertical structural member subjected to axial compressive loads. It describes two main modes of column failure as direct compression and buckling. It also defines key column terms like slenderness ratio, buckling load, crushing load, and Euler's theory for calculating the buckling load of long columns.