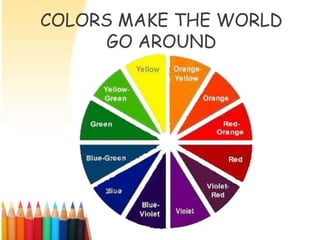
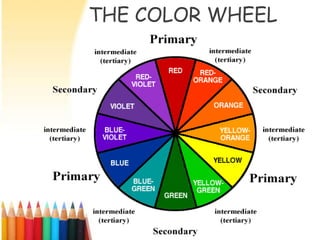
This lesson plan covers basic color theory and hair coloring. It defines key color terms like primary colors, secondary colors, and the color wheel. The plan outlines safety practices for hair coloring and objectives for students to understand color theory, identify different color categories, and perform a color wheel. It also includes examples of primary colors, how to mix secondary and tertiary colors, and uses the level system to identify hair colors.