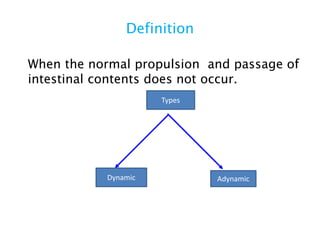
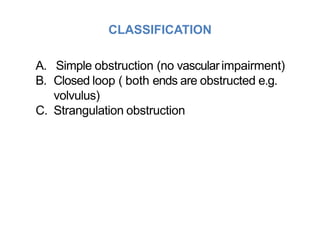
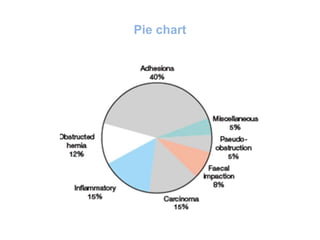
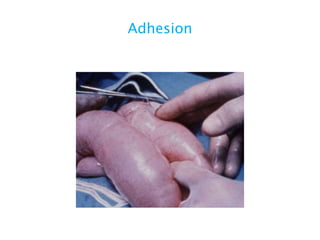
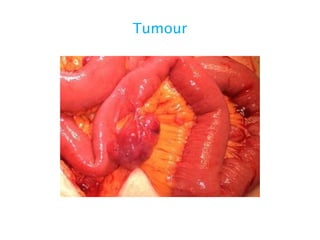
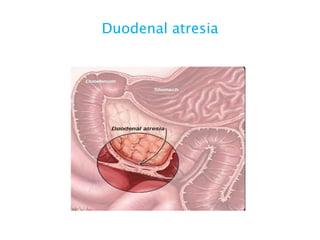
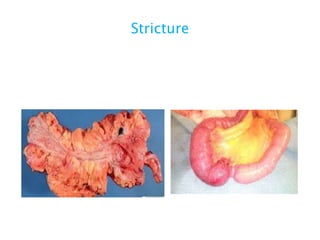
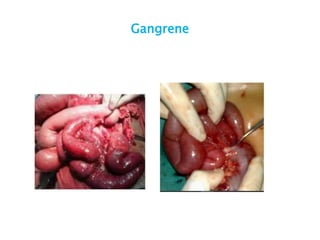
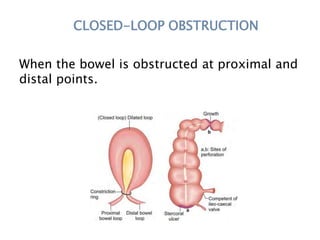
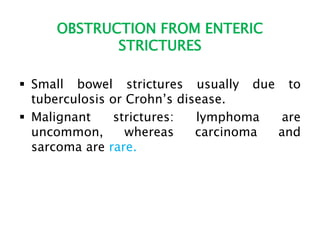
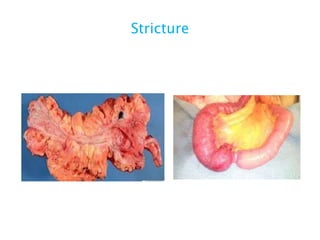
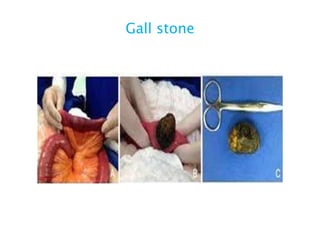
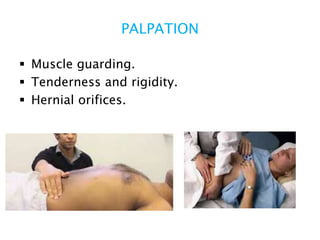
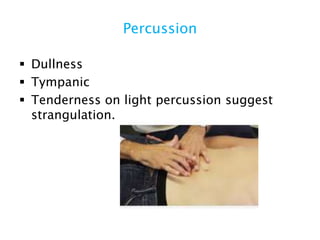
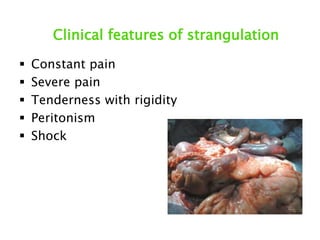
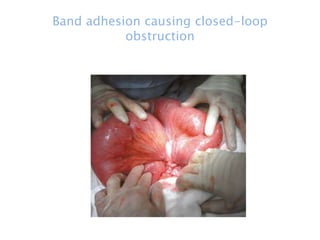
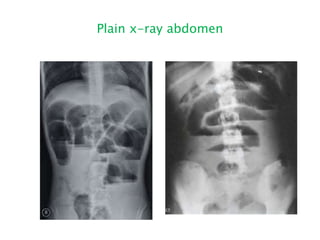
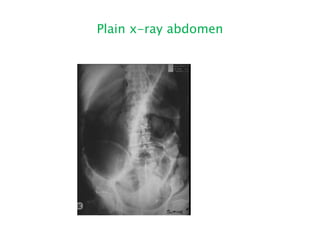
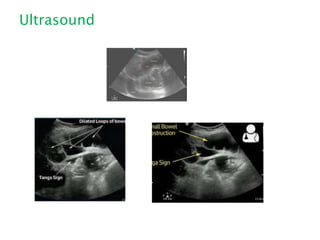
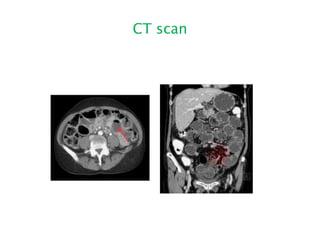
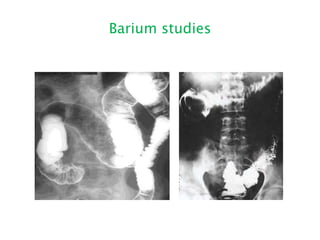
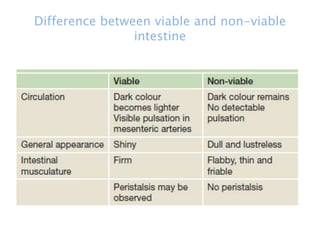
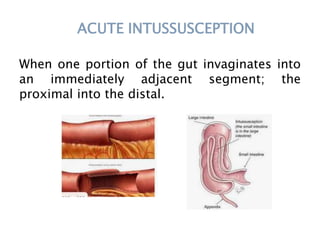
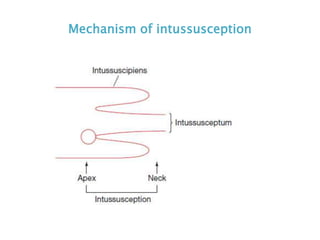
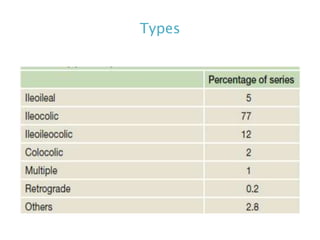
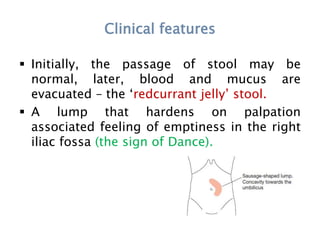
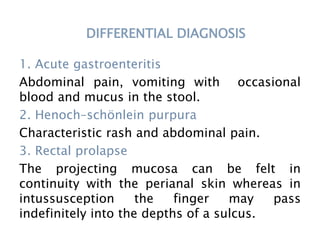
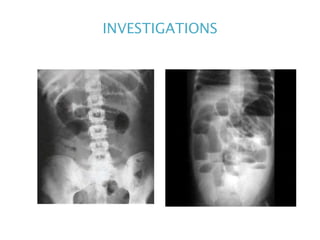
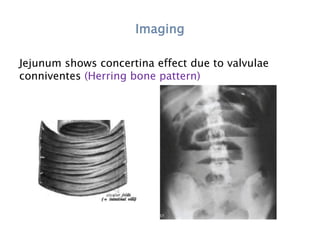
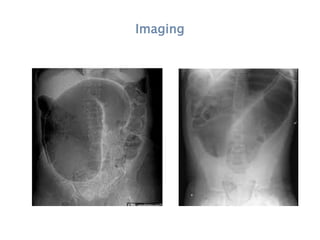
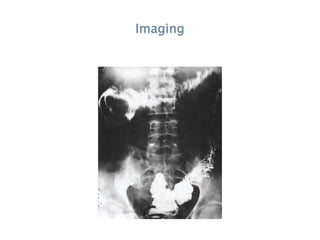
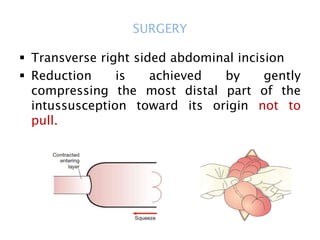
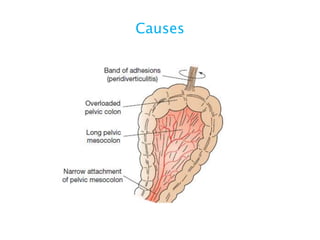
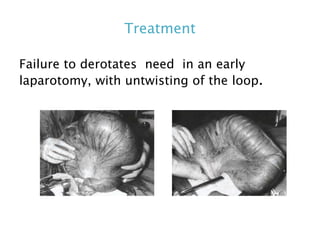
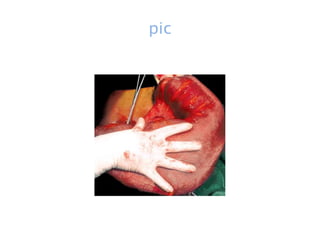
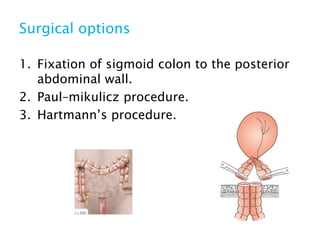
This document discusses intestinal obstruction, including its definition, types, causes, classification, pathophysiology, clinical features, investigations, and treatment. Intestinal obstruction can be dynamic, caused by mechanical blockage, or adynamic, where peristalsis is absent. Common causes include adhesions, tumors, hernias, and fecal impaction. Clinical exam and imaging help evaluate for mechanical obstruction or paralytic ileus. Treatment involves relieving the obstruction through surgery if needed, along with supportive measures like IV fluids and nasogastric decompression.