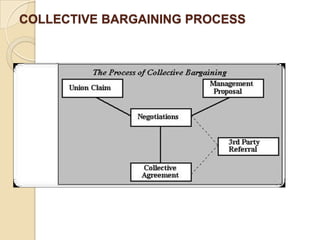
Collective bargaining is a process between employers and employees to reach agreements on work conditions. It aims to reach collective agreements on issues like pay, hours, training, and safety. It involves negotiations between employee representatives and employers to determine employment conditions. The result is a collective bargaining agreement. The collective bargaining process involves five steps - preparing negotiation teams, discussing ground rules, proposing positions, bargaining details, and finalizing a settlement agreement.