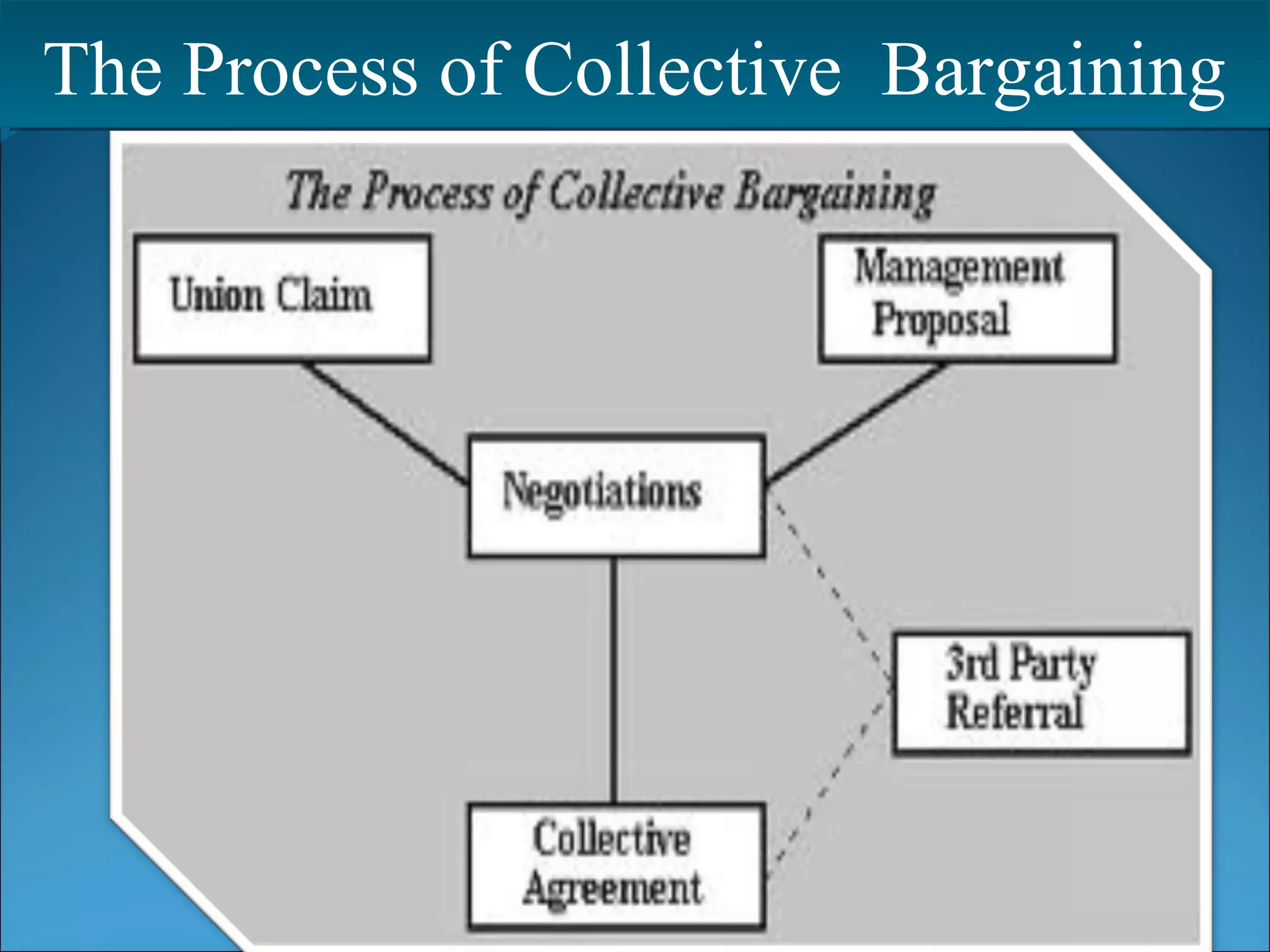
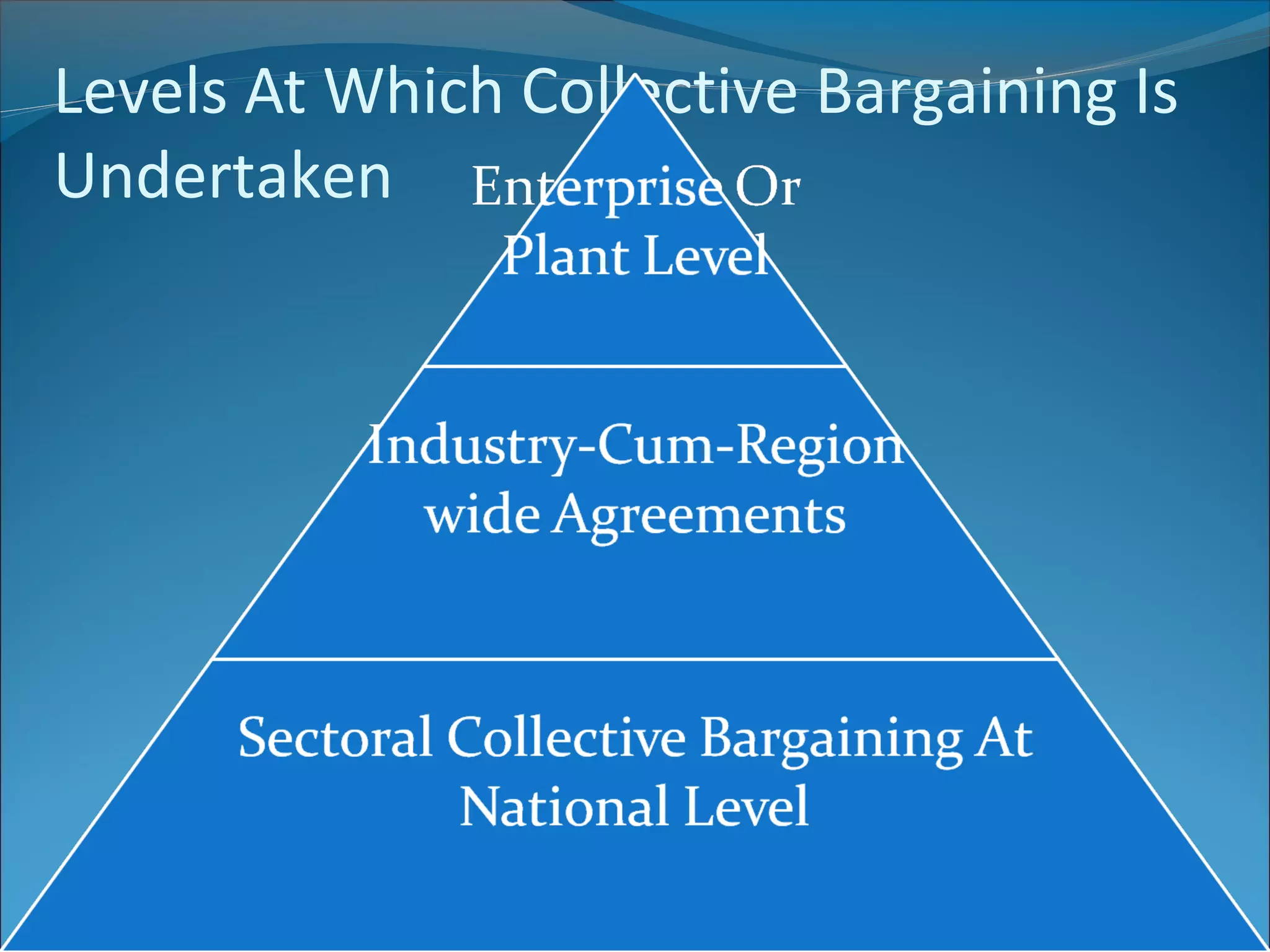
This document discusses collective bargaining, including its definition, evolution, types, process, agreements, levels, conditions for success, trends, and perceptions. Collective bargaining is a negotiation process between labor unions and employers to determine wages, hours, rules and working conditions. It aims to find common ground to reconcile conflicting interests through proposals and counterproposals. Key factors for successful collective bargaining include trade union recognition, good faith efforts, and adherence to reached agreements.