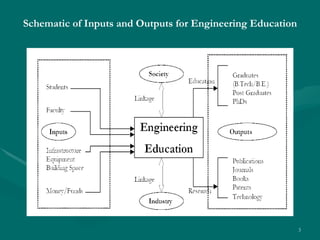
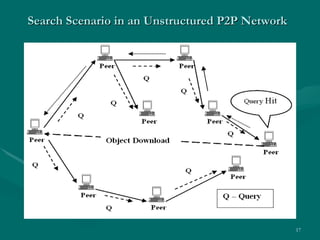
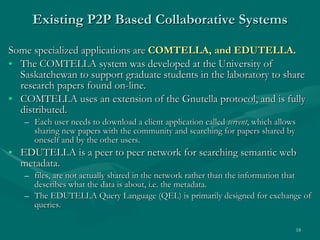
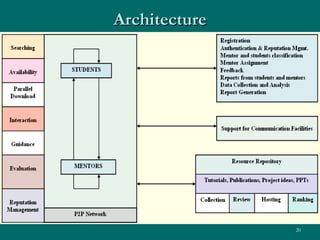
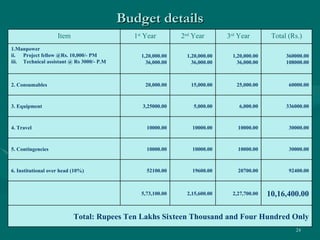
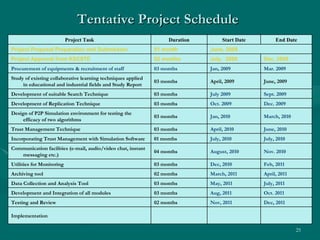
The document proposes developing a peer-to-peer (P2P) network to connect engineering colleges in Kerala, India to improve collaborative learning. Currently, the education system focuses on rote learning and passing exams rather than developing skills. The proposed P2P network would provide resources, communication, and guidance to support collaborative learning. It would involve designing modules for file sharing, communication tools, and monitoring trust and reputation over the P2P network. The goal is to enhance academic quality and research through more interactive, collaborative learning.