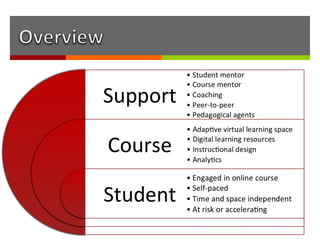
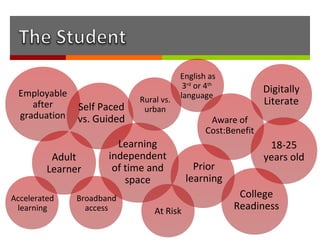
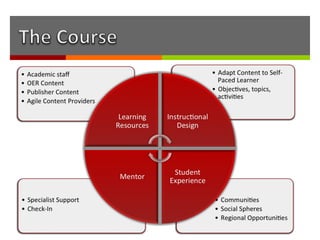
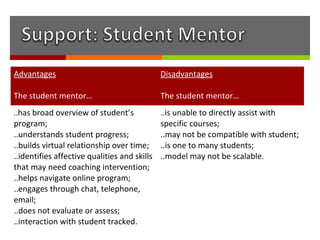
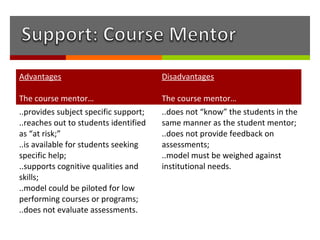
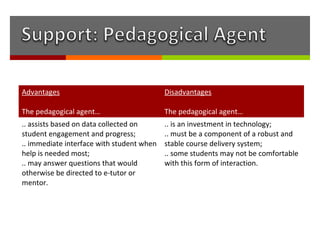
The document discusses how online institutions can support student success through a mentoring model. It outlines different types of mentors like student mentors, course mentors, eCoaches, and peer mentors. It also discusses using pedagogical agents and formative assessments to provide mentors with student progress data. Recommendations include piloting additional support in high risk courses, creating a signature online degree program, and enhancing the existing e-tutor model at UNISA with evidence-based practices from other institutions.