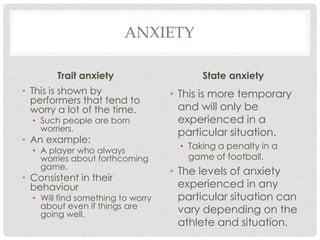
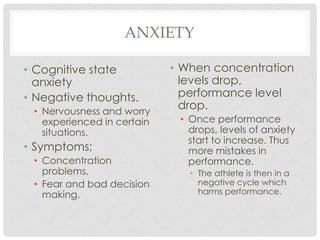
This document discusses the effects of stress and anxiety on sporting performance. It describes how the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems control the body's stress response, known as the "fight or flight" response. The document outlines the symptoms of stress and anxiety, including cognitive and somatic state anxiety. It explains how high levels of anxiety can negatively impact an athlete's concentration, decision making, and coordination, potentially leading to lower performance. However, some symptoms of anxiety may also provide benefits like increased blood flow and breathing rate, depending on the athlete's perception. The key is for athletes to manage anxiety and view it as a positive rather than a negative state.