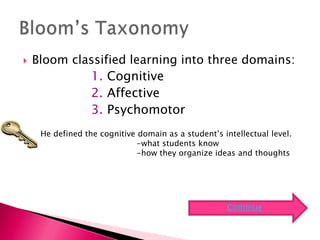
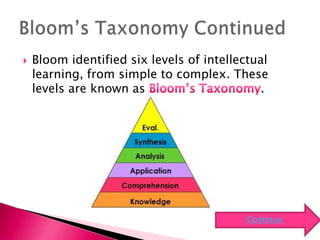
Cognitive psychology studies how people think, perceive, remember, and learn. It emerged in reaction to behaviorism. Learning is not just reactionary. Key contributors include Paivio, Gagne, Gardner, and Bloom. Bloom classified learning into cognitive, affective, and psychomotor domains. He defined cognitive domain as intellectual level, organizing it into six levels of complexity from knowledge to evaluation. Teachers may use alternative assessments and technology to incorporate higher-order thinking. Students may delve deeper into critical thinking and use technology for creative synthesis.