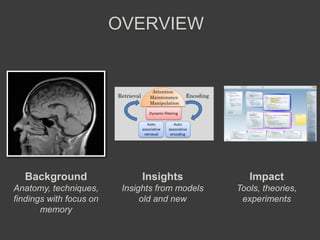
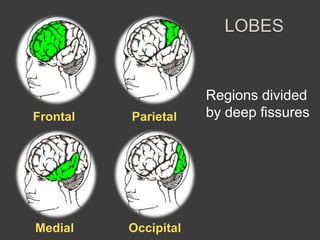
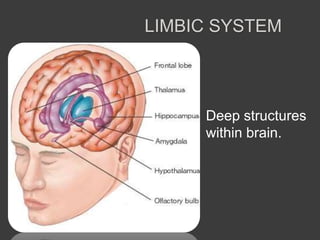
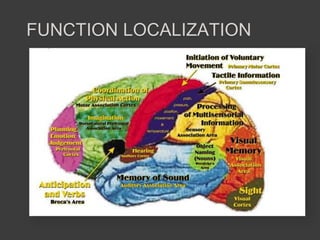
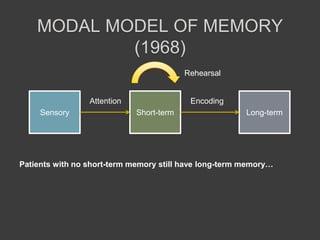
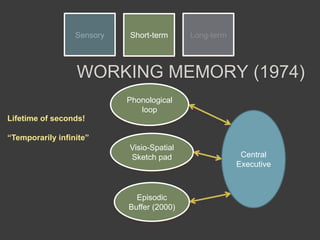
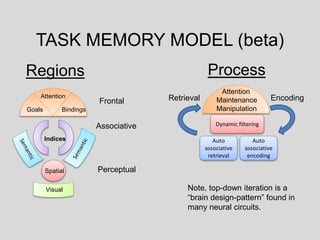
This document discusses cognitive neuroscience perspectives on memory for programming tasks. It provides an overview of memory models and insights from neuroscience research on memory. Some key points include:
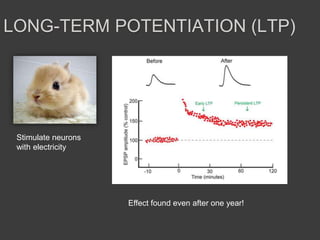
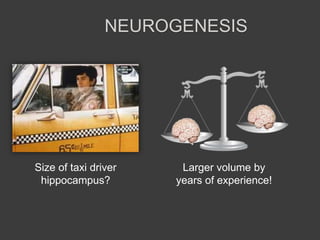
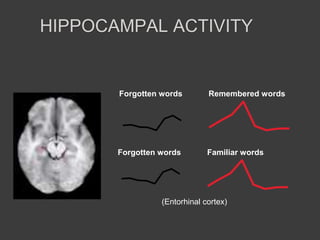
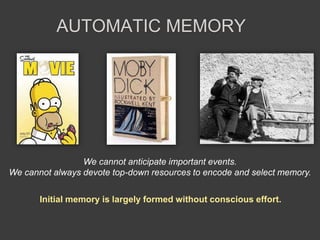
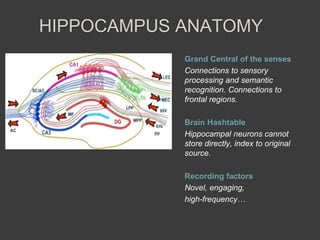
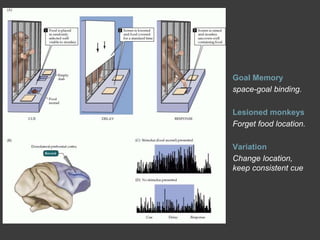
- Memory is formed automatically in the hippocampus through long-term potentiation and is later consolidated and stored in original brain regions.
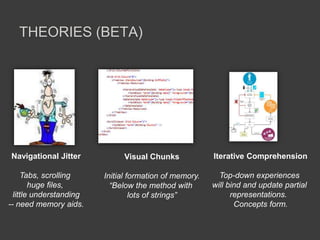
- Tools and theories from cognitive neuroscience could inform the design of programming environments and tools to better support programmers' memory through mechanisms like auto-association and spatial memory cues.
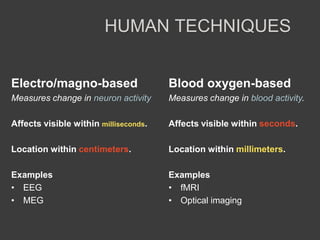
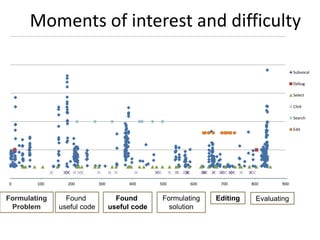
- Experiments studying programmers' brain activity and memory formation could provide insights to improve memory support in integrated development environments.