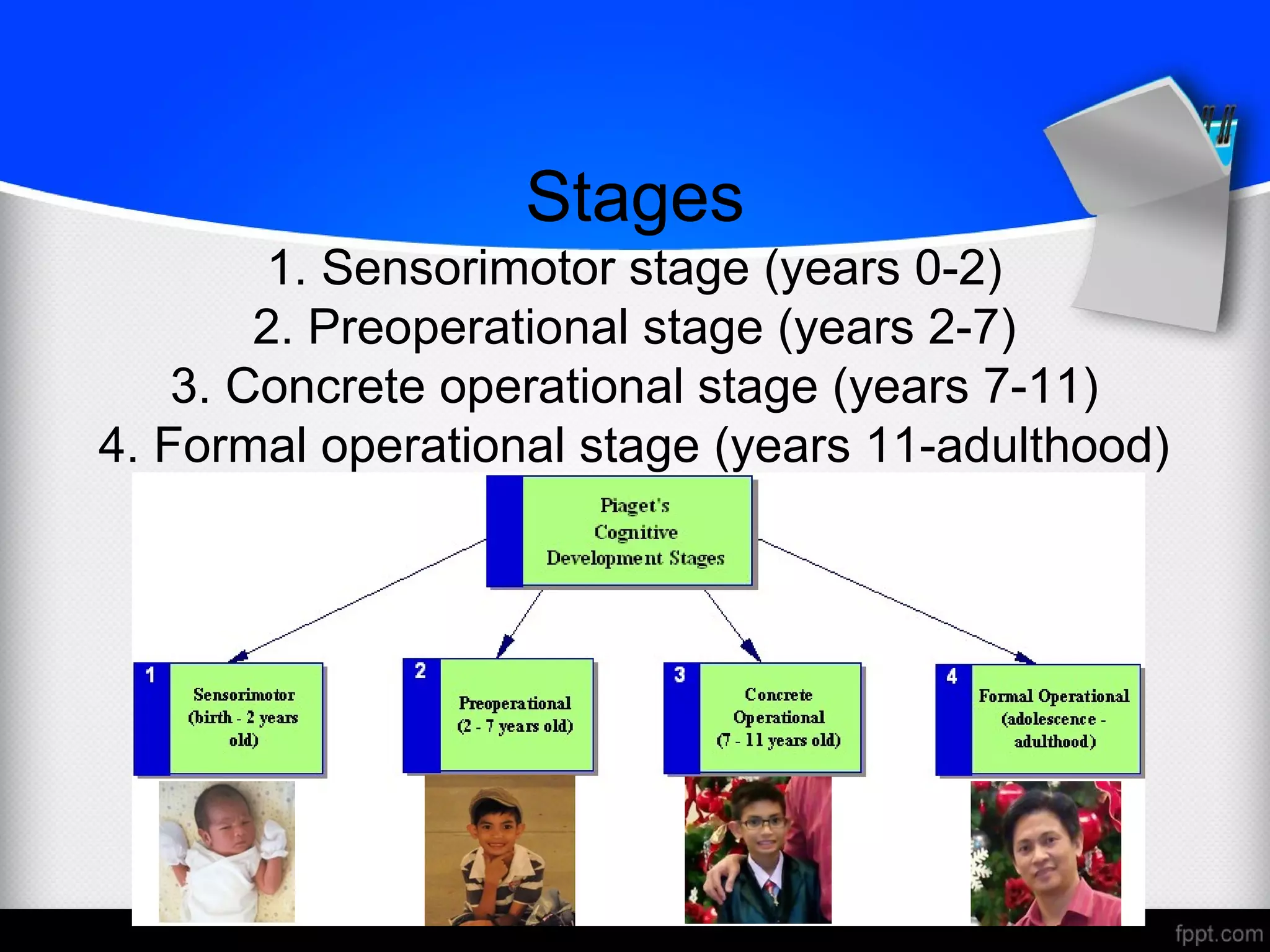
Jean Piaget's theory of cognitive development proposes that children progress through 4 stages of cognitive development - sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational - as their mental abilities advance from birth through adulthood. Each stage is characterized by discoveries and abilities that are appropriate to the child's age and experiences. Piaget's theory suggests that education should provide experiences tailored to students' developmental levels to effectively promote learning and transition between stages.















![Bibliography
“PIAGET'S COGNITIVE STAGES”. Patient Teaching, Loose Leaf
Library
Springhouse Corporation (1990)
<http://honolulu.hawaii.edu/intranet/committees/FacDevCom/guidebk/t
eachtip/piaget.htm>
“Learning and Teaching Piaget’s developmental theory”. [On-line: UK]
10 February 2010
http://www.learningandteaching.info/learning/piaget.htm
http://www.slideshare.net
http://en.wikipedia.org
Images: google.com & fb accounts](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/piagetscognitivedevelopmentstagesandmaslowshierarchyofneeds-151130230749-lva1-app6892/75/Piaget-s-cognitive-development-stages-and-maslow-s-hierarchy-of-needs-20-2048.jpg)