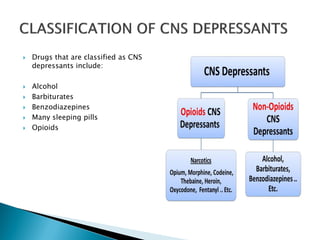
Central nervous system (CNS) depressants are a class of drugs that slow down brain activity and cause muscles to relax. They include benzodiazepines, barbiturates, alcohol, opioids, and some sleeping pills. They work by enhancing the effects of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA at GABAA receptors in the brain, resulting in sedative, hypnotic, anxiolytic, and muscle relaxant effects. While effective for treating conditions like anxiety and insomnia, long-term use can lead to tolerance, addiction, and withdrawal symptoms.






![ MECHANISIM OF ACTION
Barbiturates act as positive allosteric modulators and, at higher doses, as agonists of
GABAA receptors.[18] GABA is the principal inhibitory neurotransmitter in the
mammalian central nervous system (CNS). Barbiturates bind to the GABAA receptor at
multiple homologous transmembrane pockets located at subunit interfaces,[19] which
are binding sites distinct from GABA itself and also distinct from the benzodiazepine
binding site. Like benzodiazepines, barbiturates potentiate the effect of GABA at this
receptor. In addition to this GABAergic effect, barbiturates also block AMPA and kainate
receptors, subtypes of ionotropic glutamate receptor. Glutamate is the principal
excitatory neurotransmitter in the mammalian CNS.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cnsdepressants-200530185849/85/Cns-depressants-10-320.jpg)