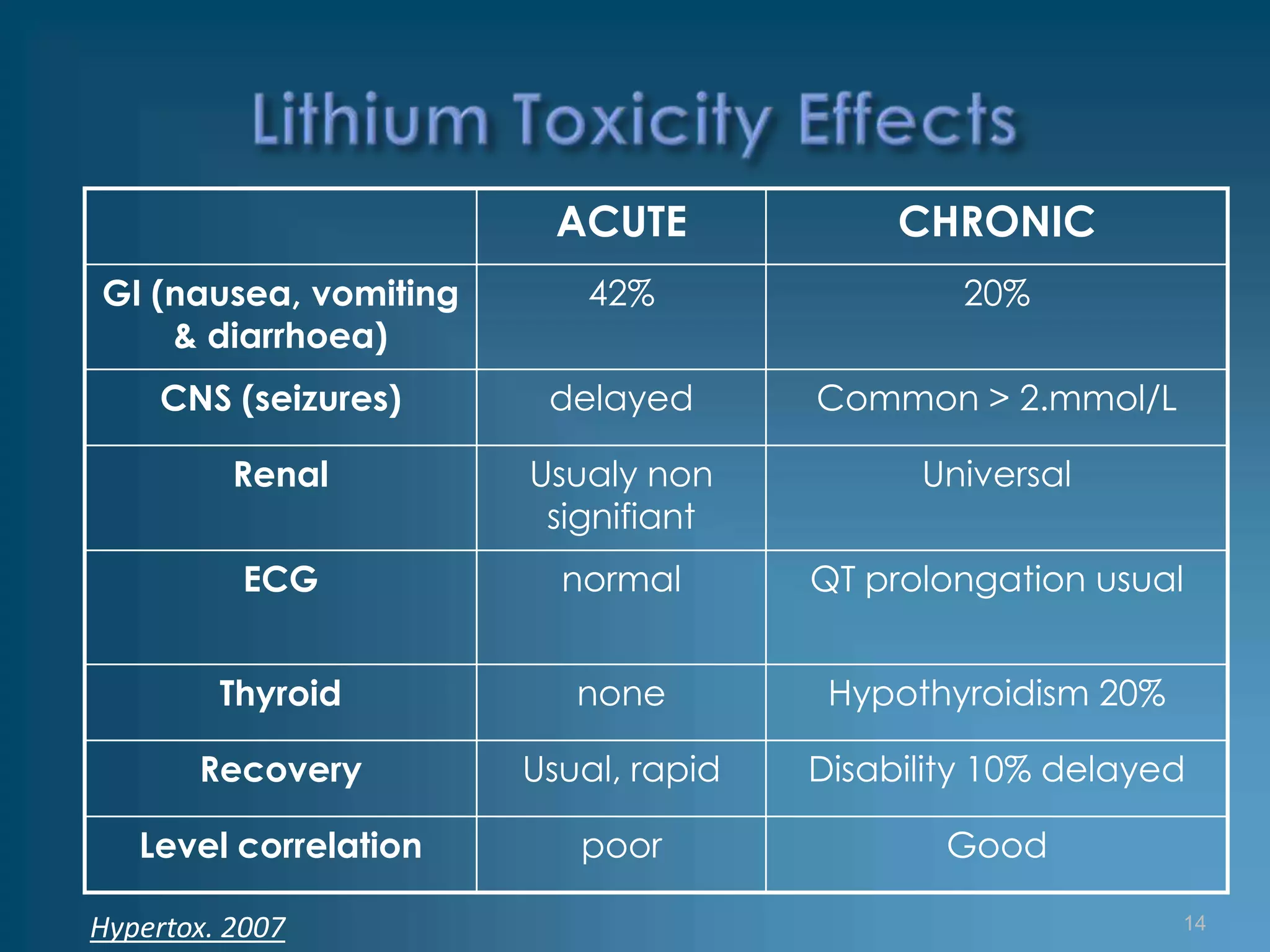
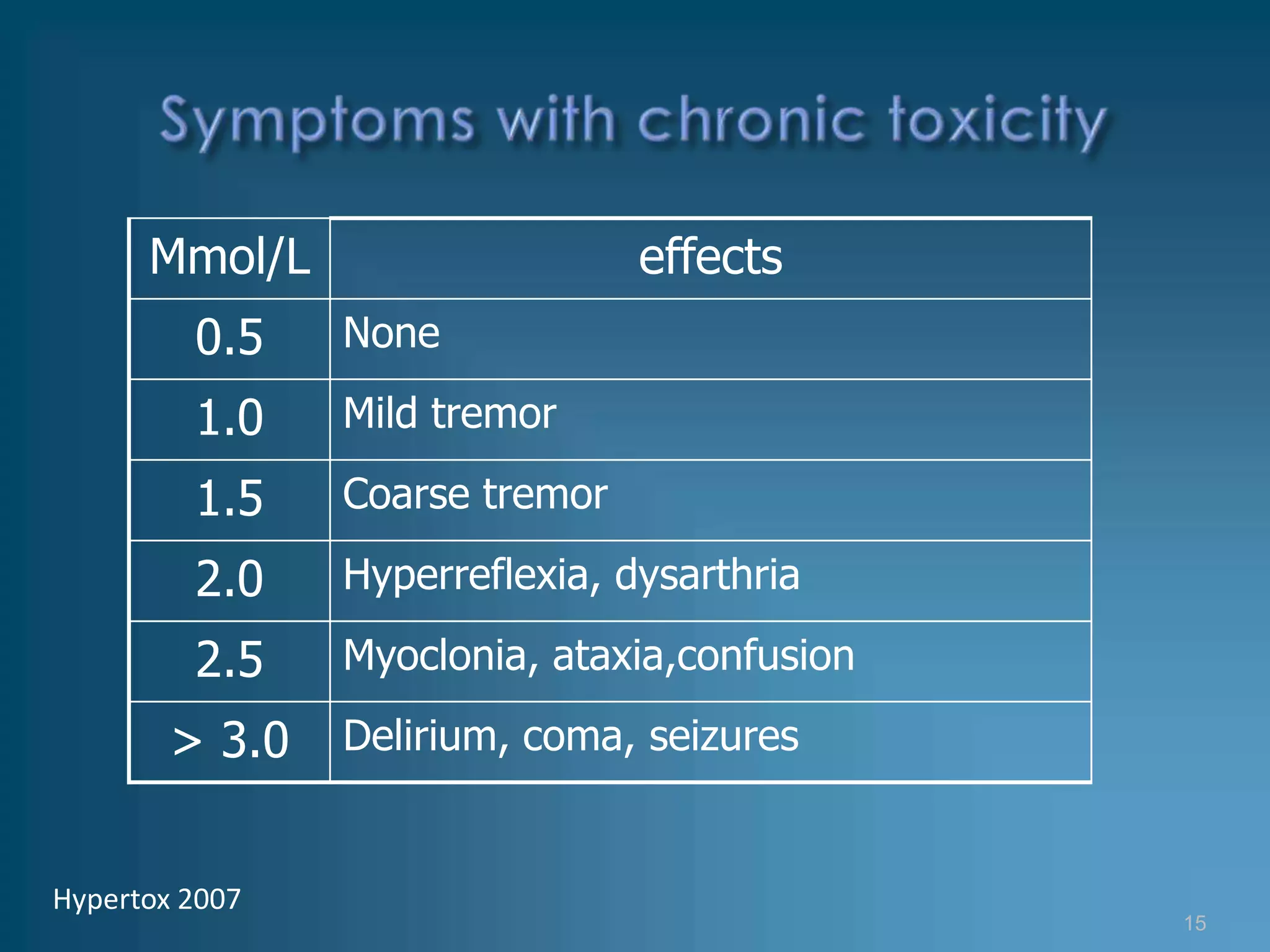
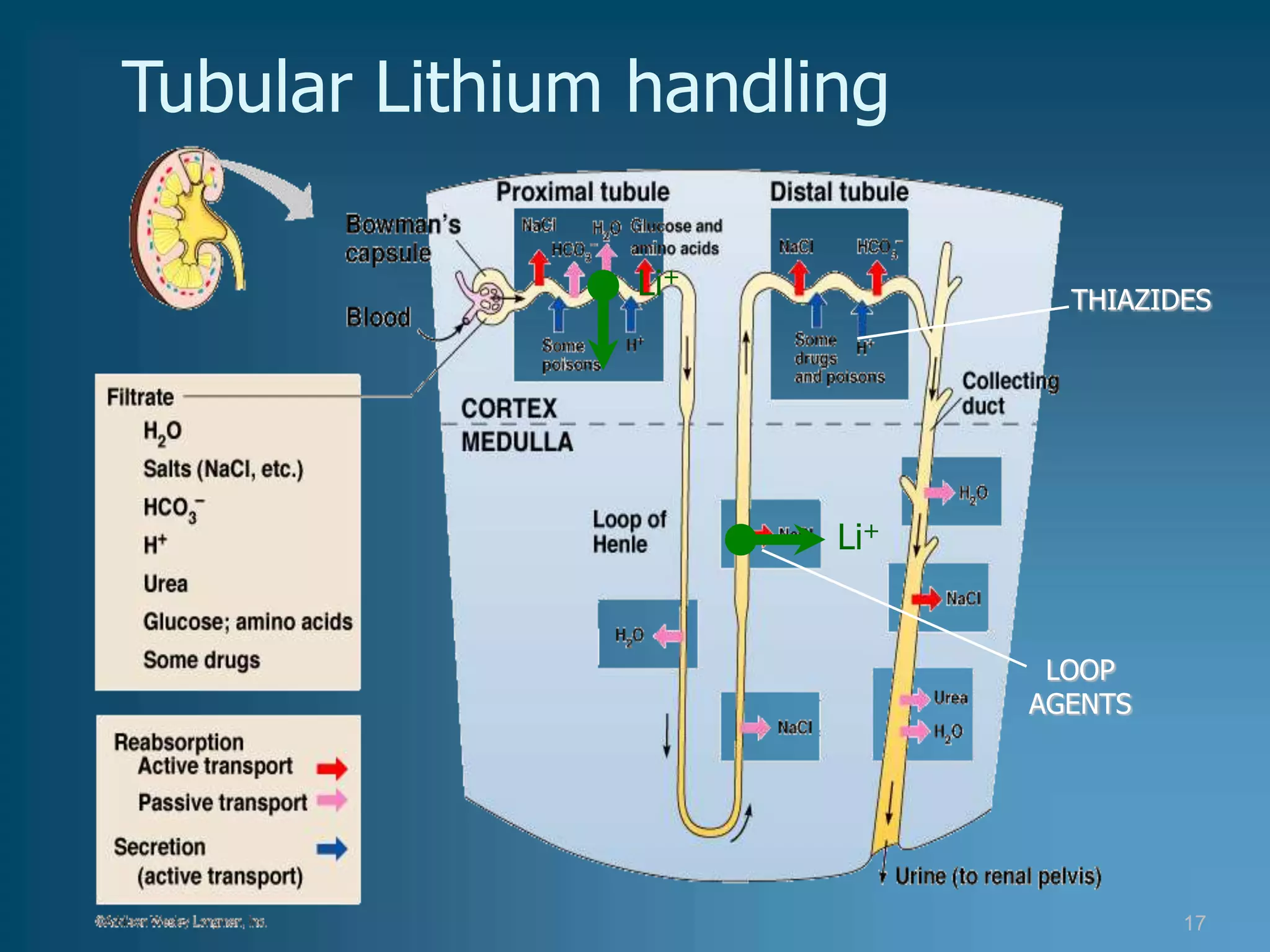
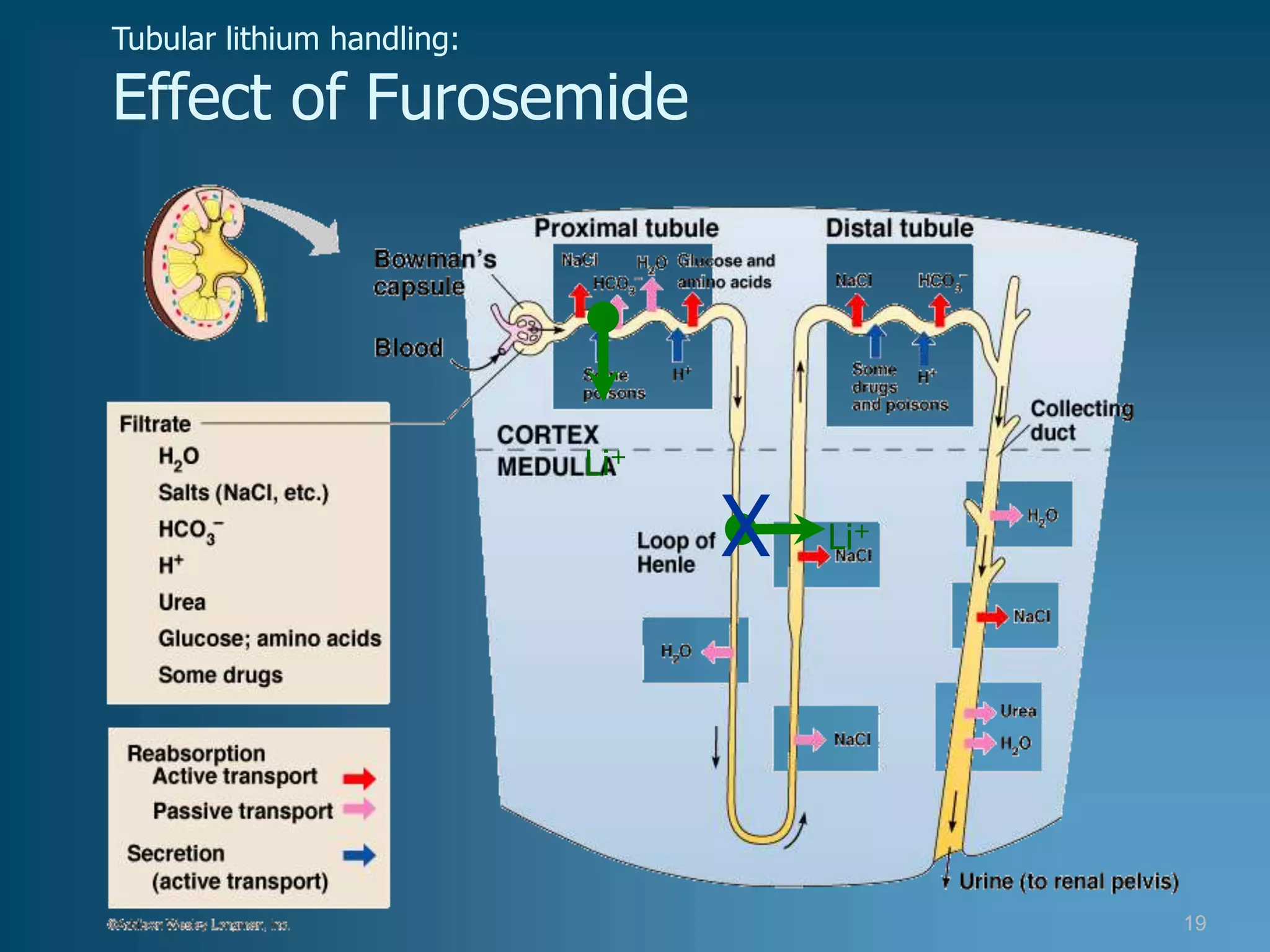
The patient, a 53-year-old man with bipolar disorder treated with lithium carbonate, presented with loose stool, nausea, fatigue, and loss of energy over the past two days. His lithium level was found to be 3.17 mmol/L, above the therapeutic range of 0.50-1.20 mmol/L, indicating lithium toxicity. He was admitted and treated supportively with IV fluids and discontinuation of lithium. His lithium level decreased to 0.68 mmol/L after 4 days and he was discharged to psychiatric care after one week.











![Drugs increase the lithium toxicity
• nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs [NSAIDs],
• diuretics,
• tetracyclines,
• phenytoin,and
• cyclosporine
Symptoms
• Nausea and vomiting
• Diarrhea
• Weakness and fatigue
• Lethargy and confusion
• Tremor
• Seizure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lithiumtoxicity-124514320122-phpapp02/75/Lithium-Toxicity-12-2048.jpg)