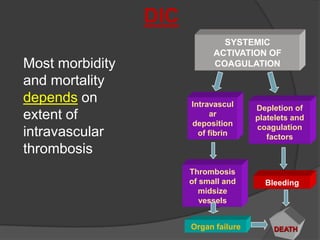
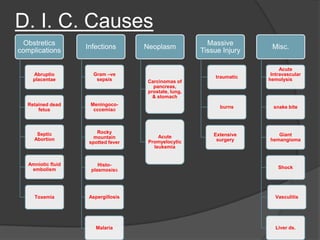
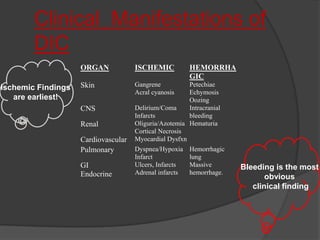
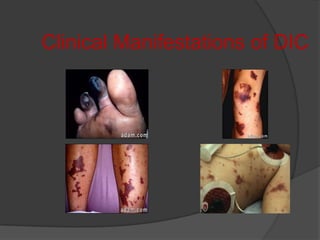
DIC is an acute, subacute, or chronic thrombohemorrhagic disorder characterized by systemic intravascular coagulation. It occurs as a secondary complication of various diseases and is initiated by coagulation within blood vessels, leading to thrombosis, bleeding, and potentially organ failure. The only proven treatment is stopping the triggering process and supporting therapy, as there are no specific treatments for DIC itself.