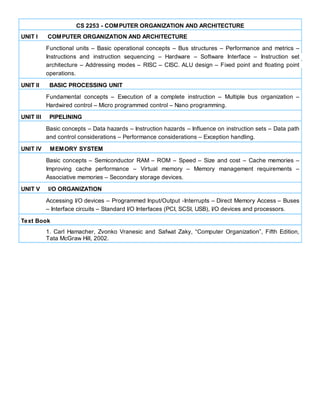
The document outlines the units of study for a course on computer organization and architecture. Unit I introduces functional units, bus structures, instruction sets, addressing modes, and ALU design. Unit II discusses the basic processing unit and control methods. Unit III covers pipelining, hazards, and performance. Unit IV examines memory systems including caches, virtual memory, and secondary storage. Unit V describes I/O organization, interrupts, and standard interfaces. The primary textbook for the course is listed.