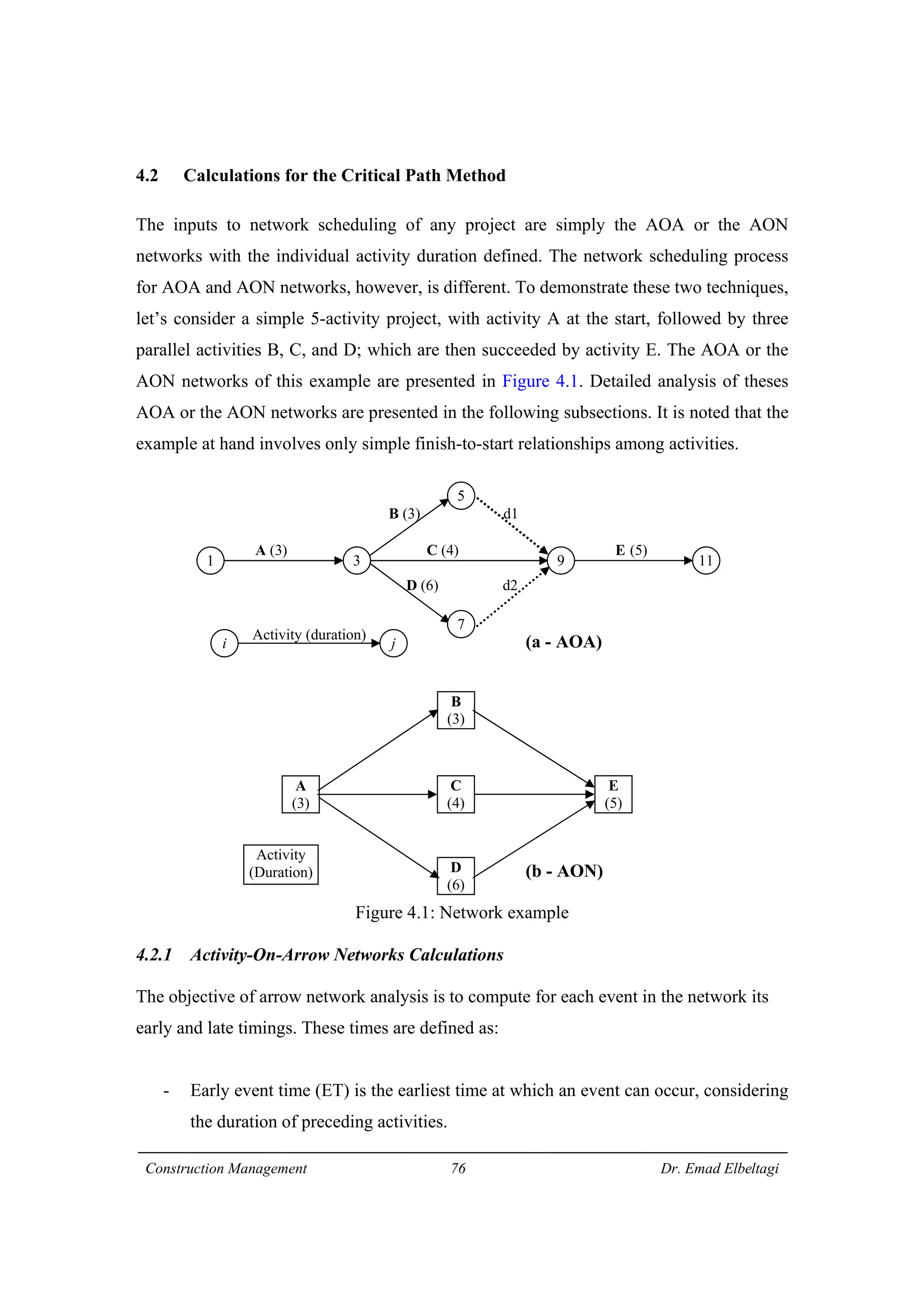
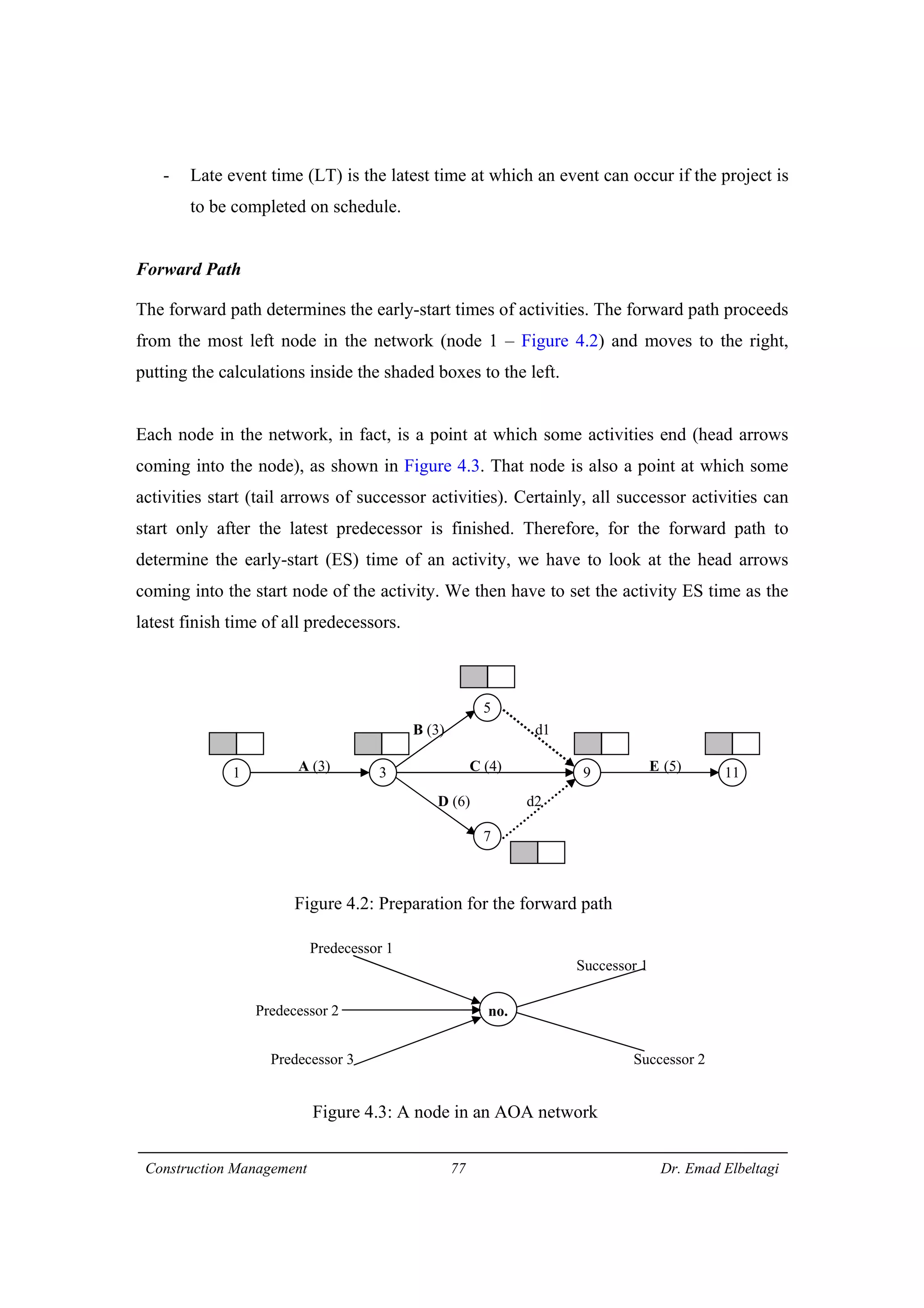
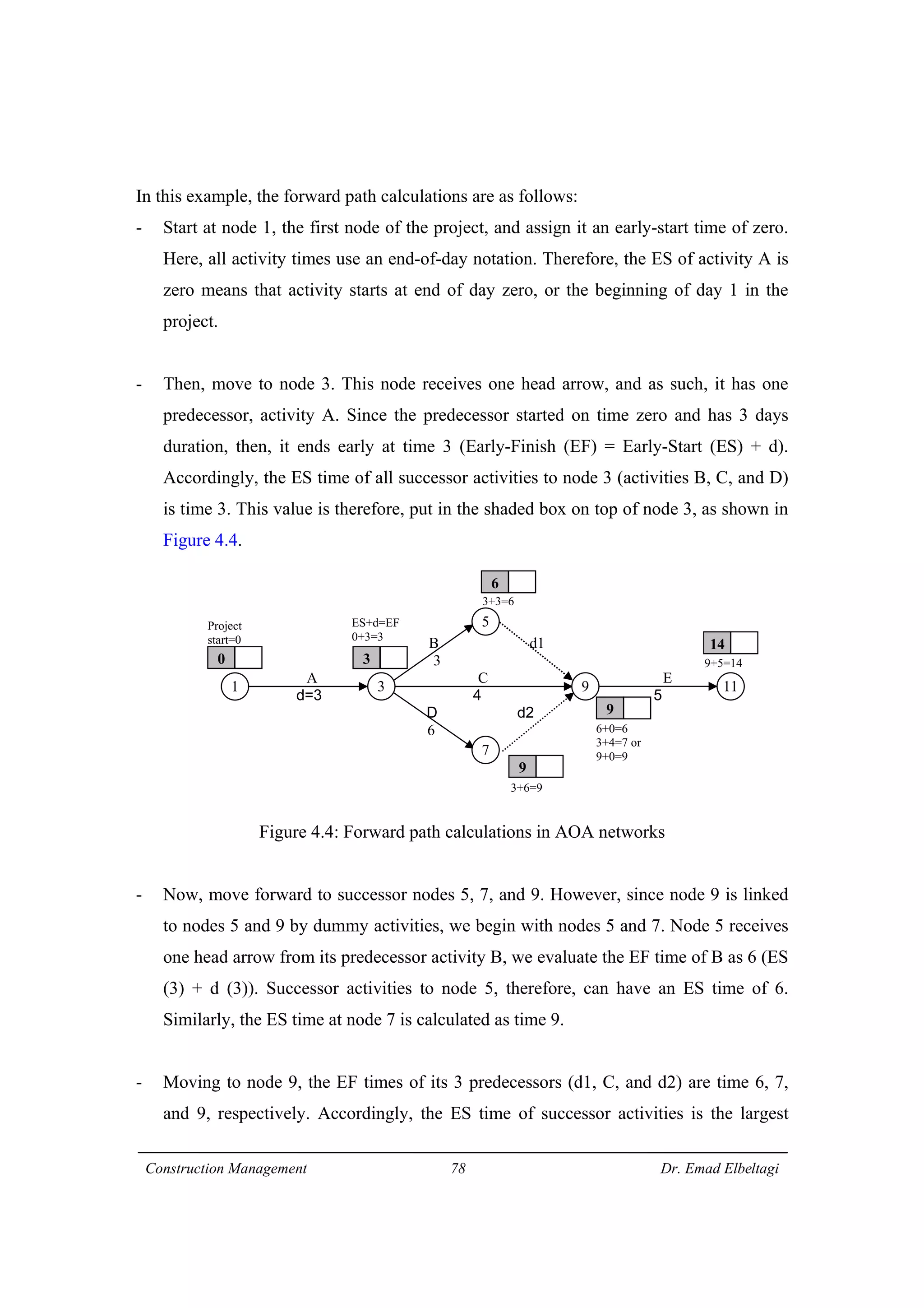
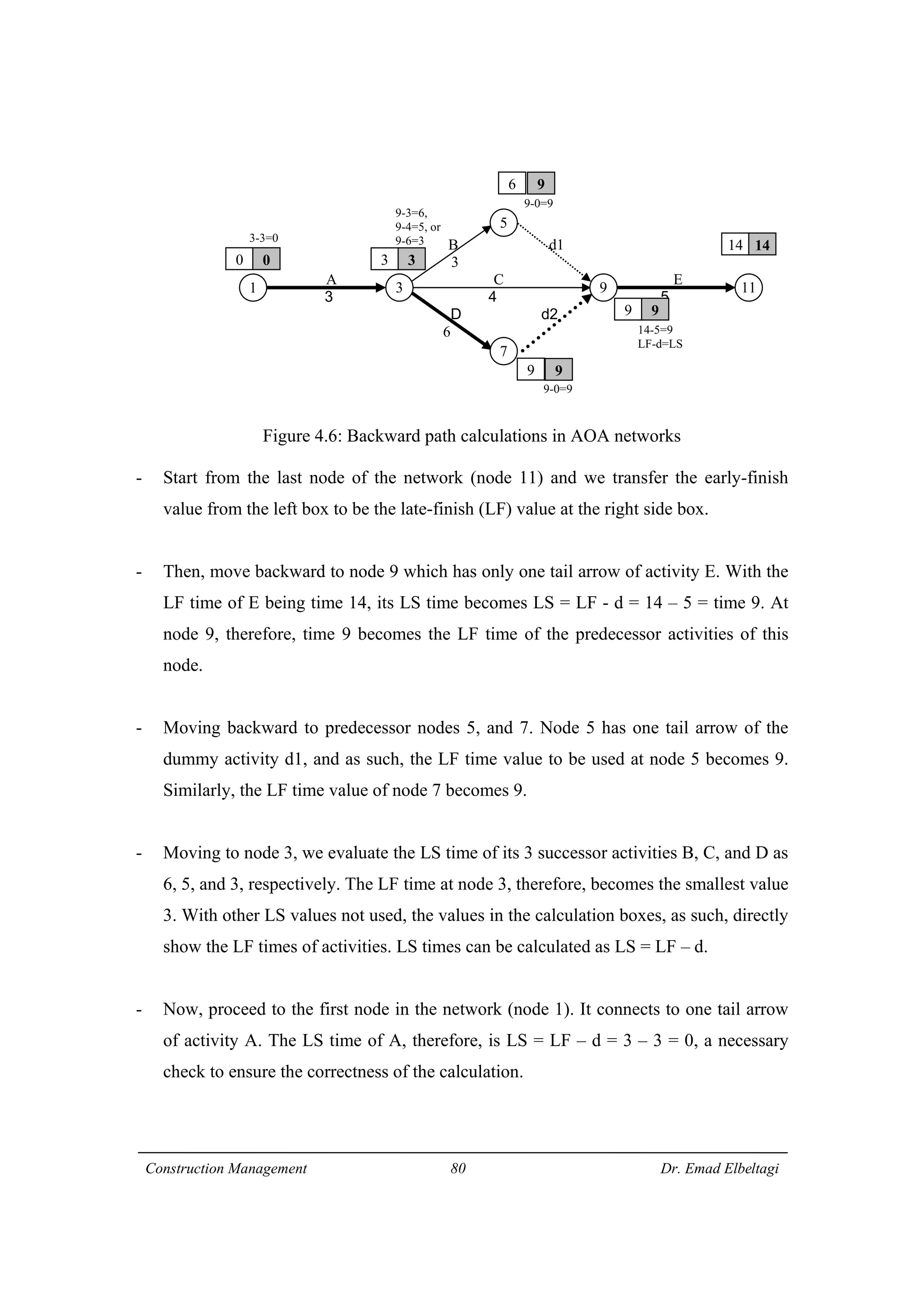
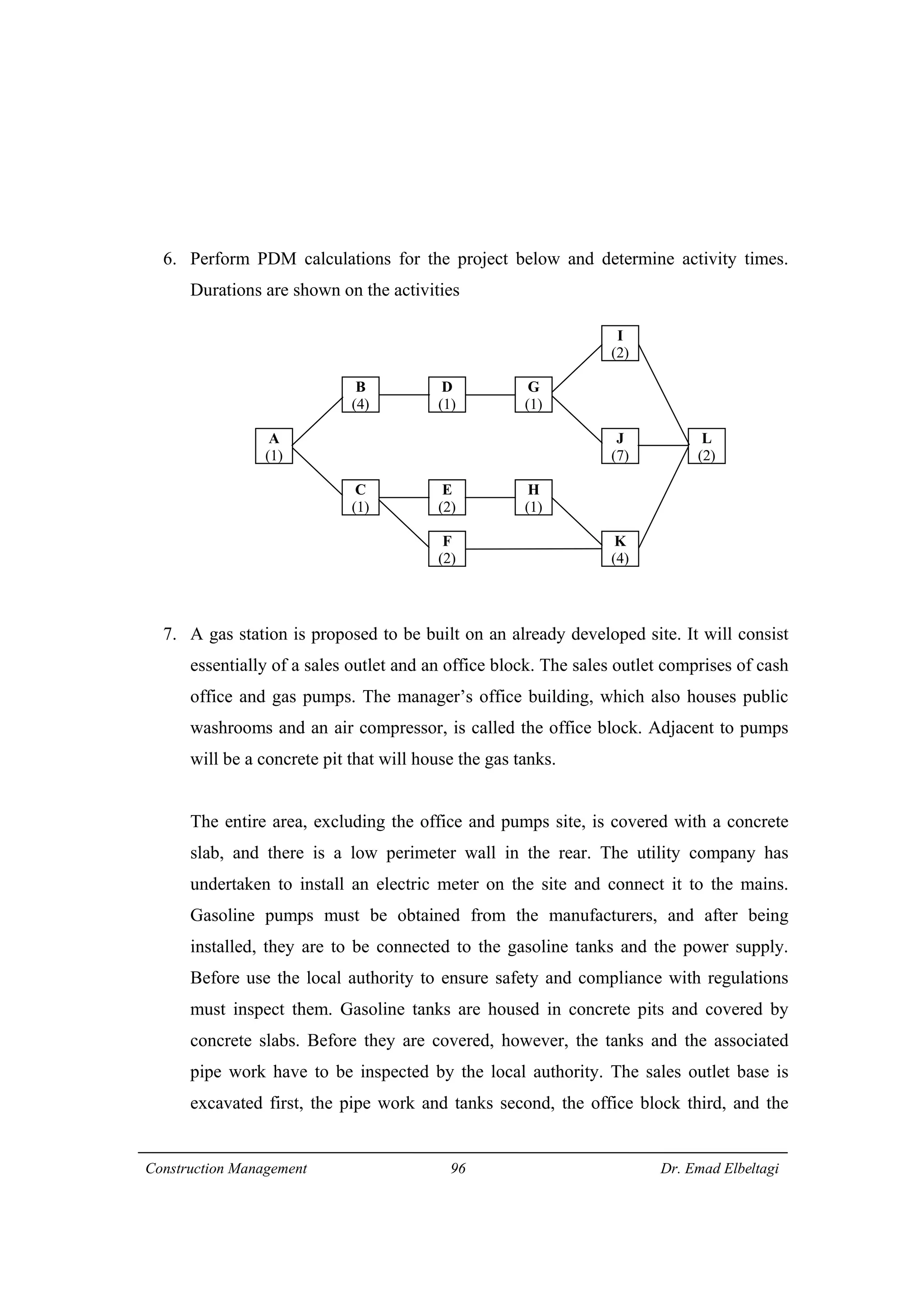
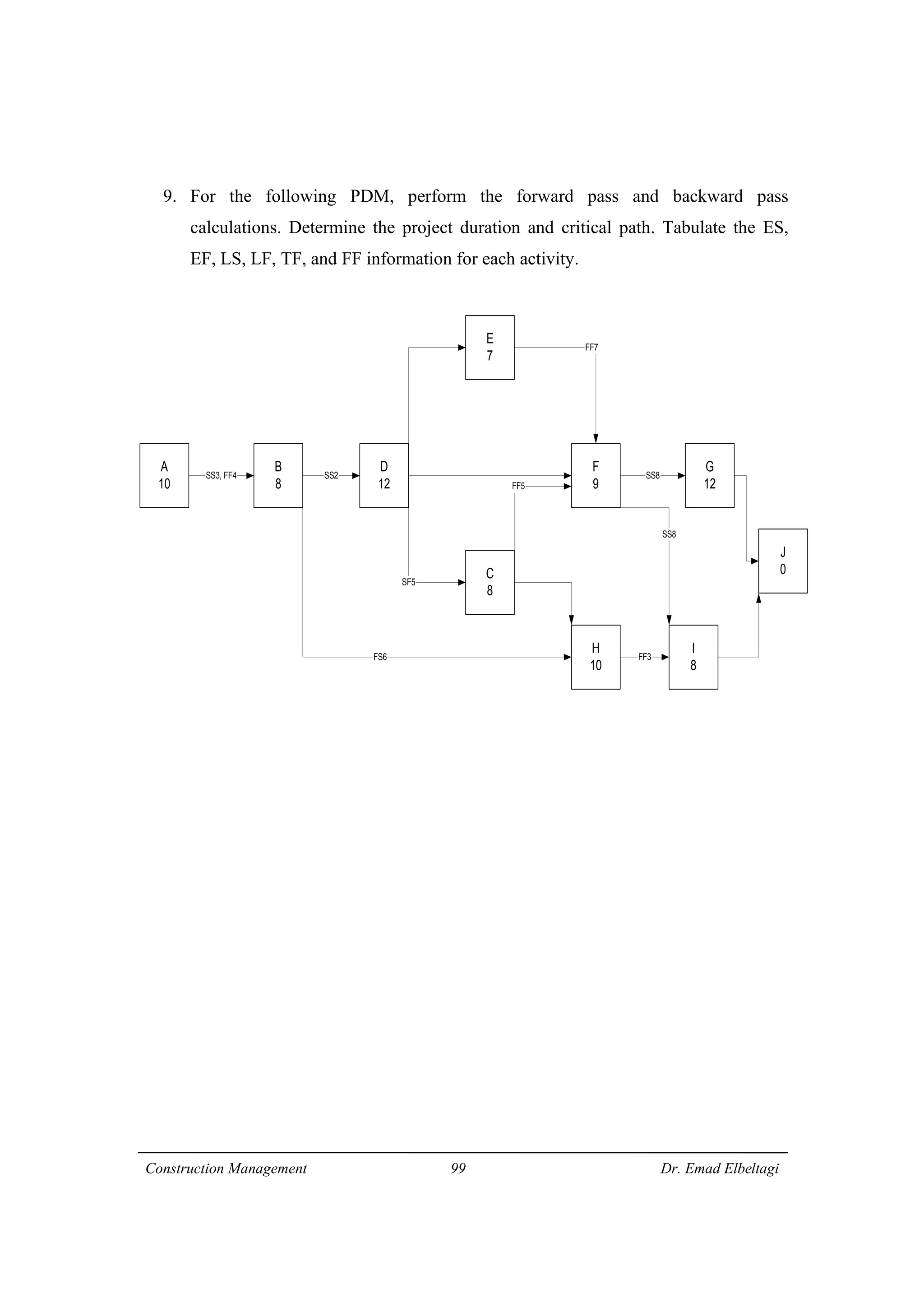
1) The document discusses project scheduling and the critical path method (CPM) for determining the minimum time needed to complete a project.
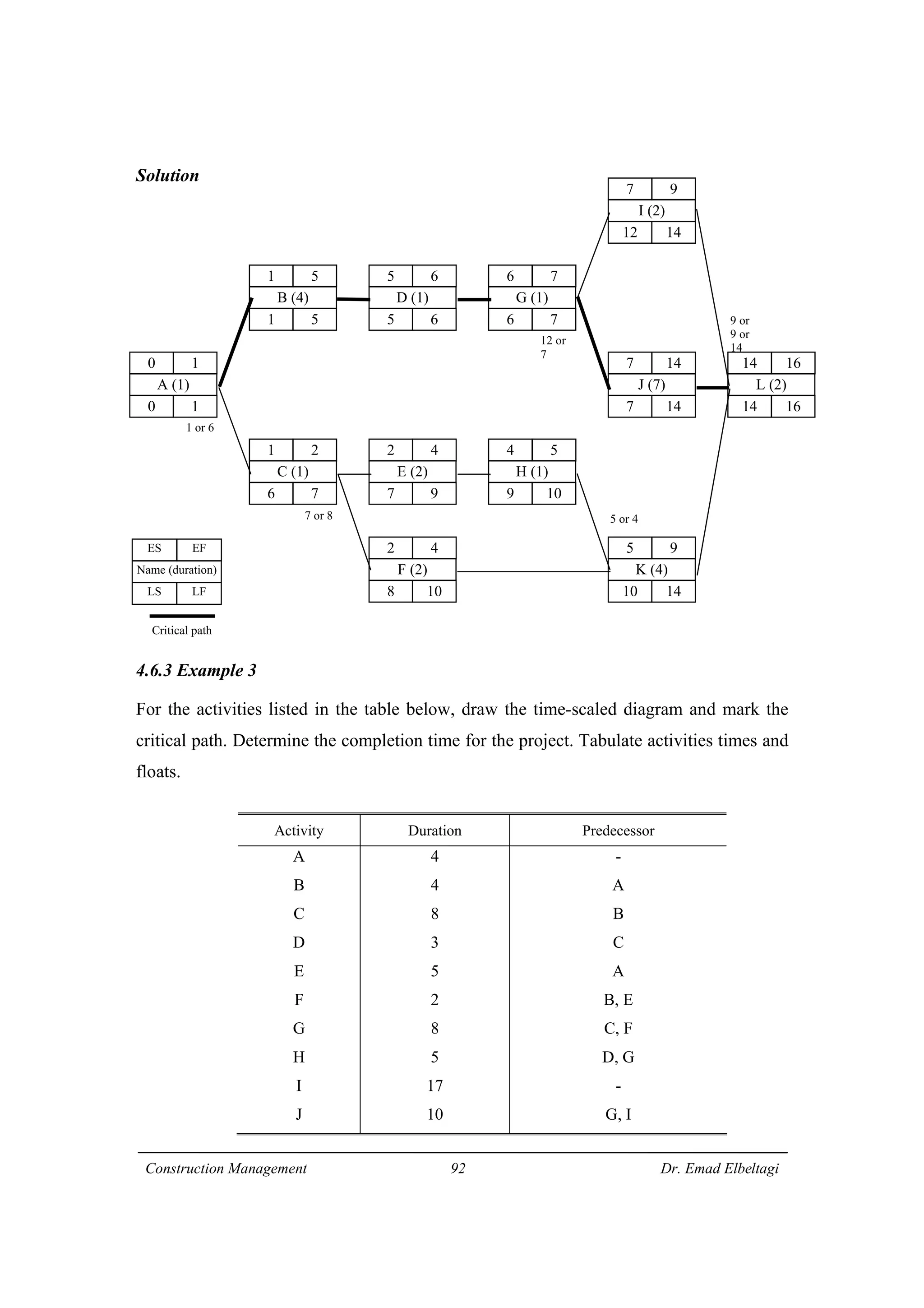
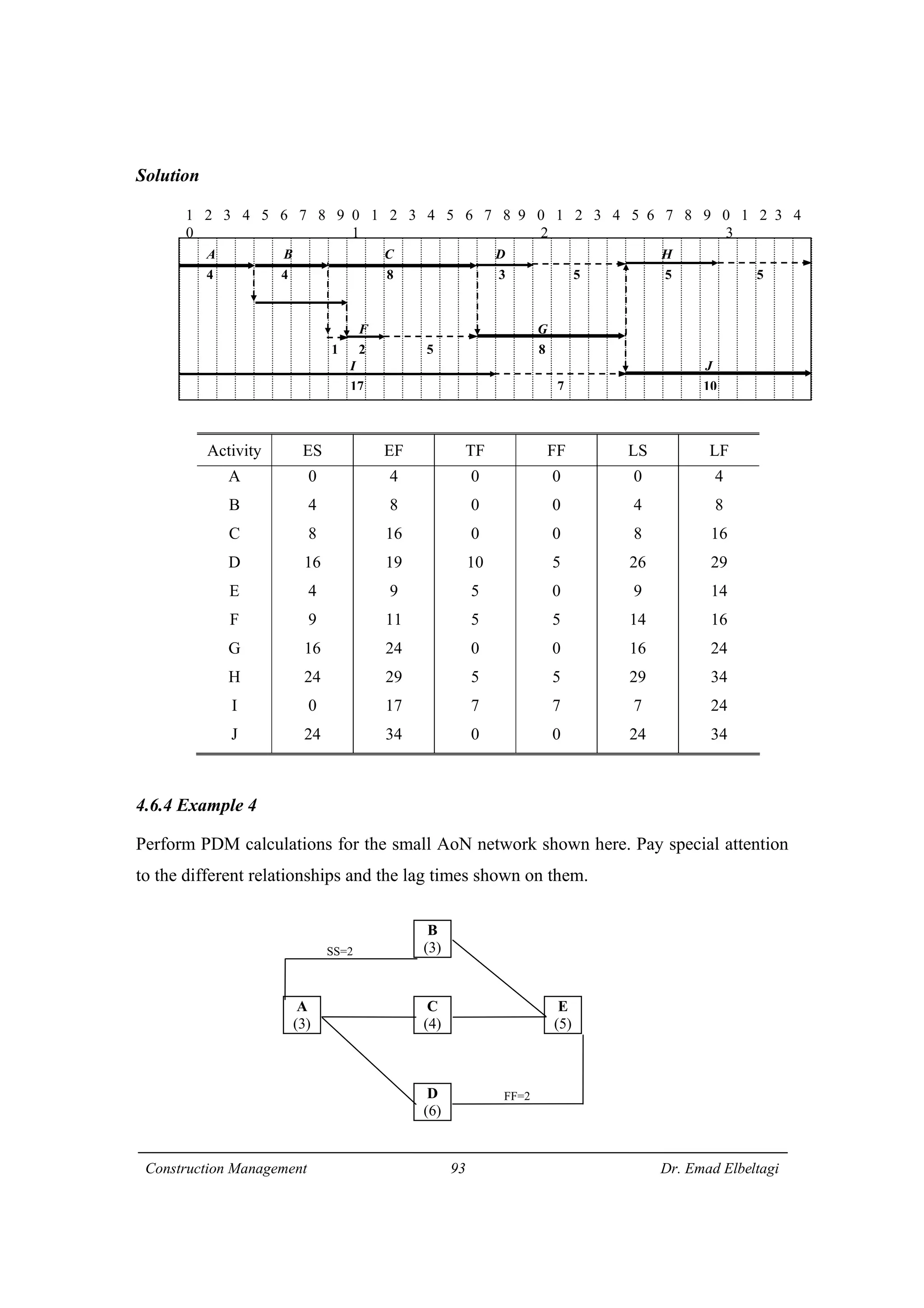
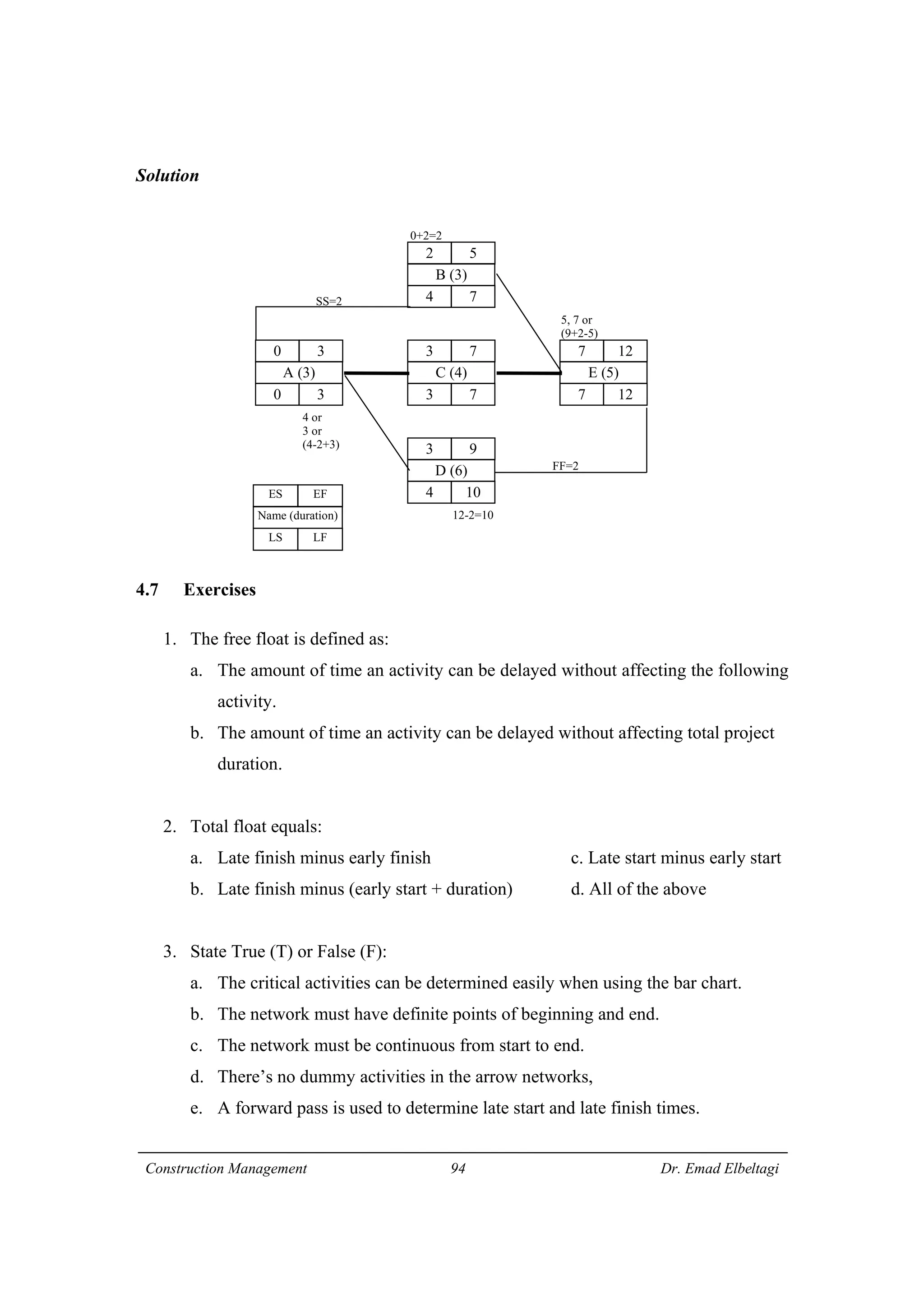
2) CPM involves calculating early and late start/finish times for activities through forward and backward passes through the network. It also identifies critical activities with zero float that must finish on schedule.
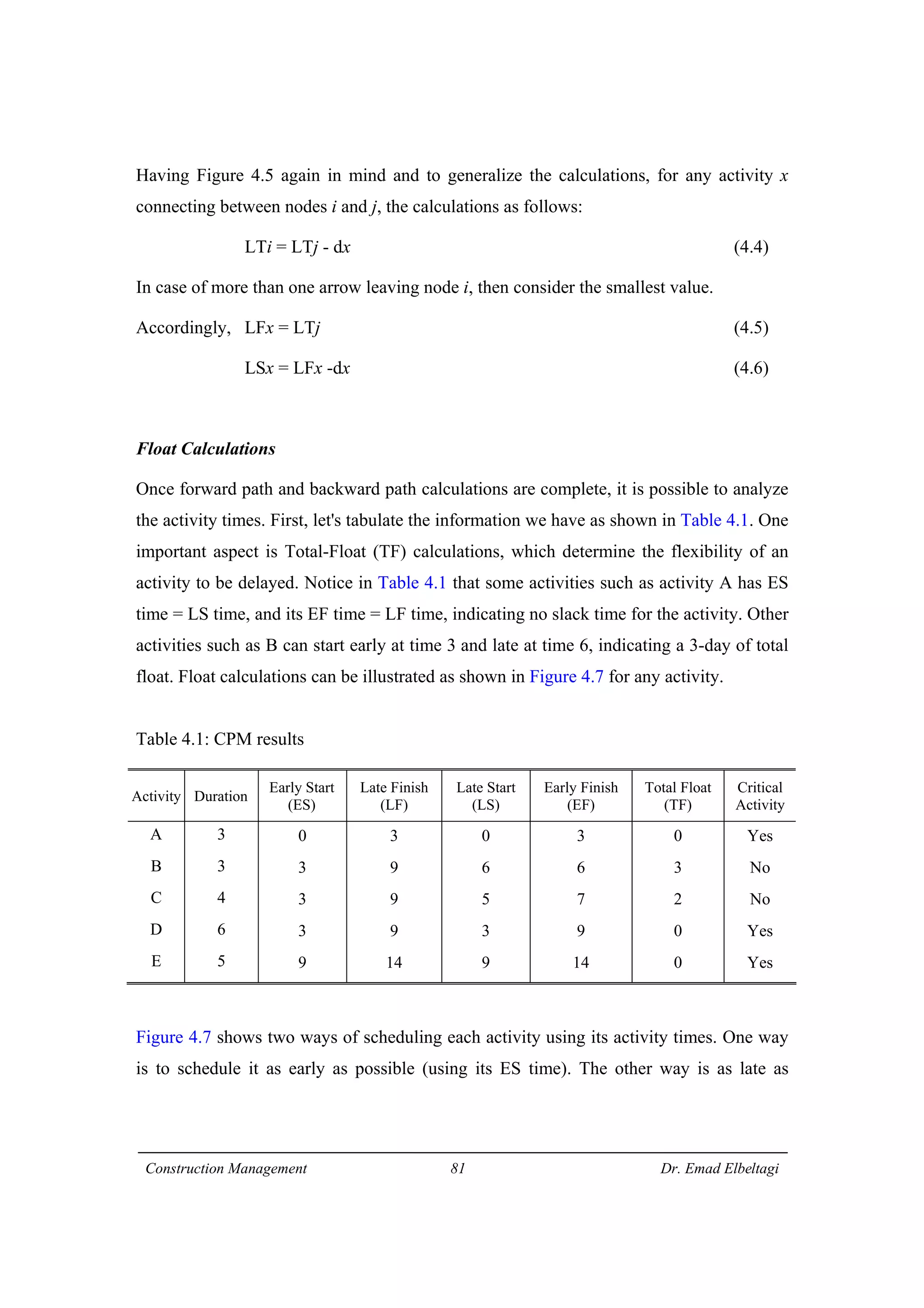
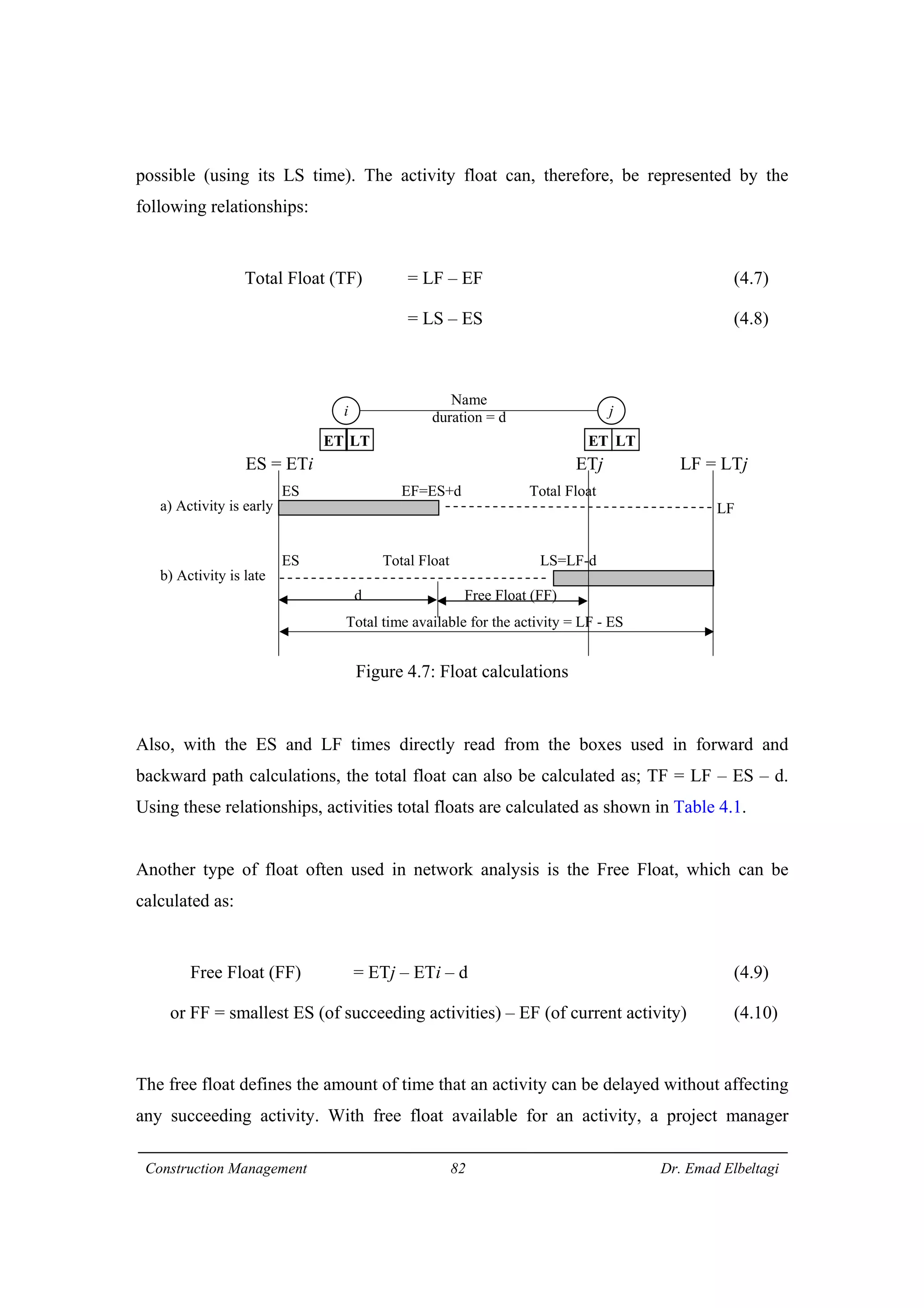
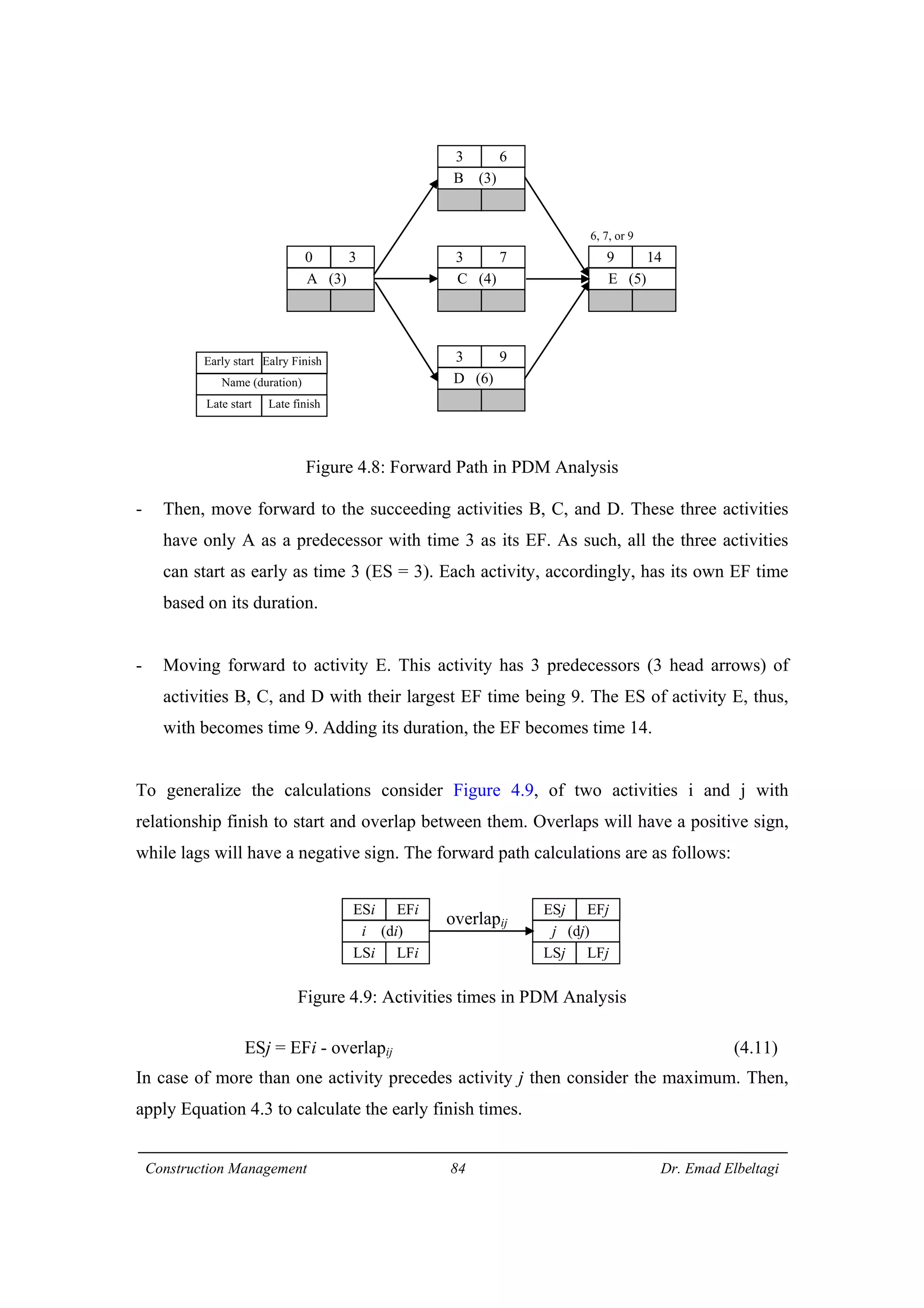
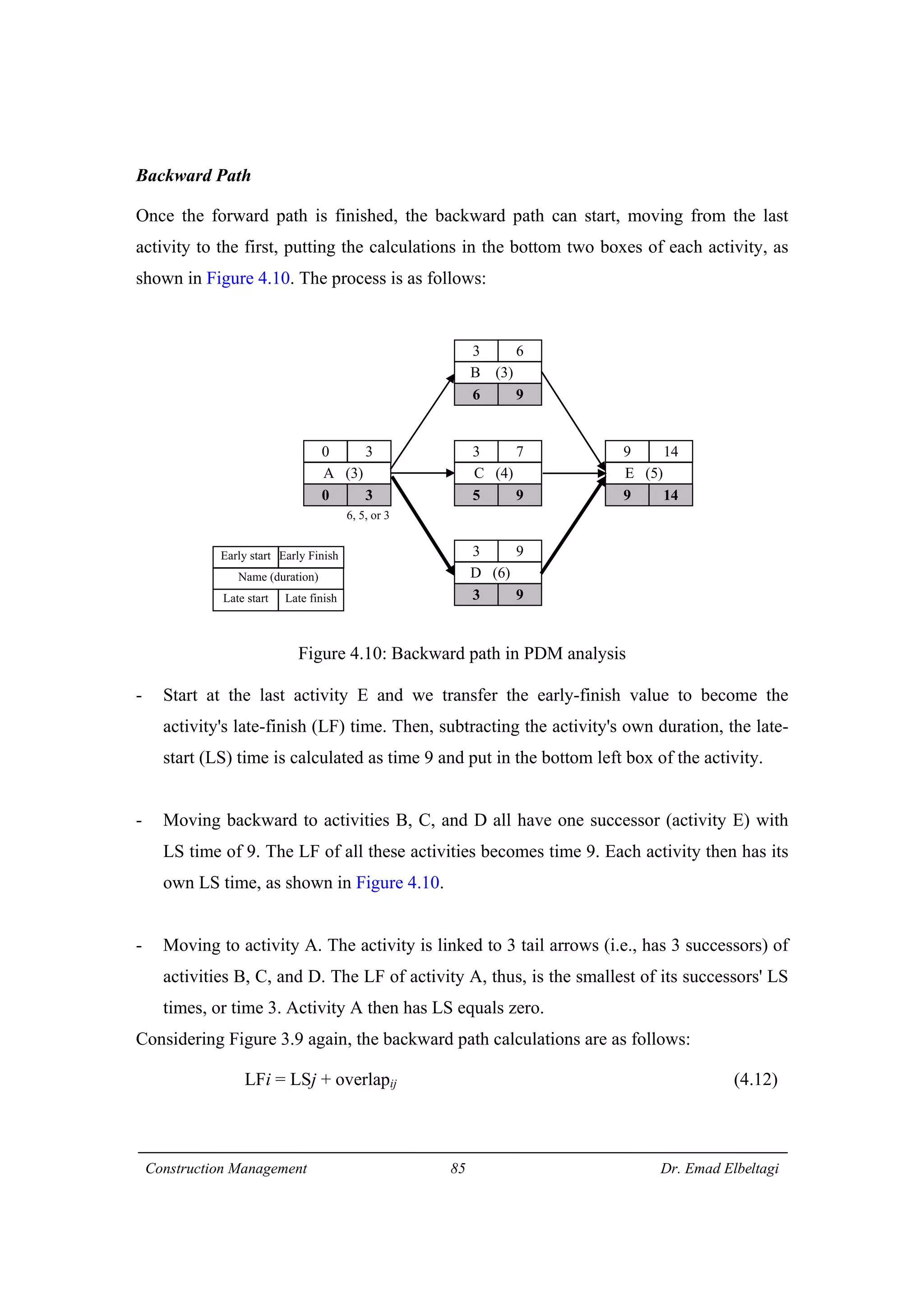
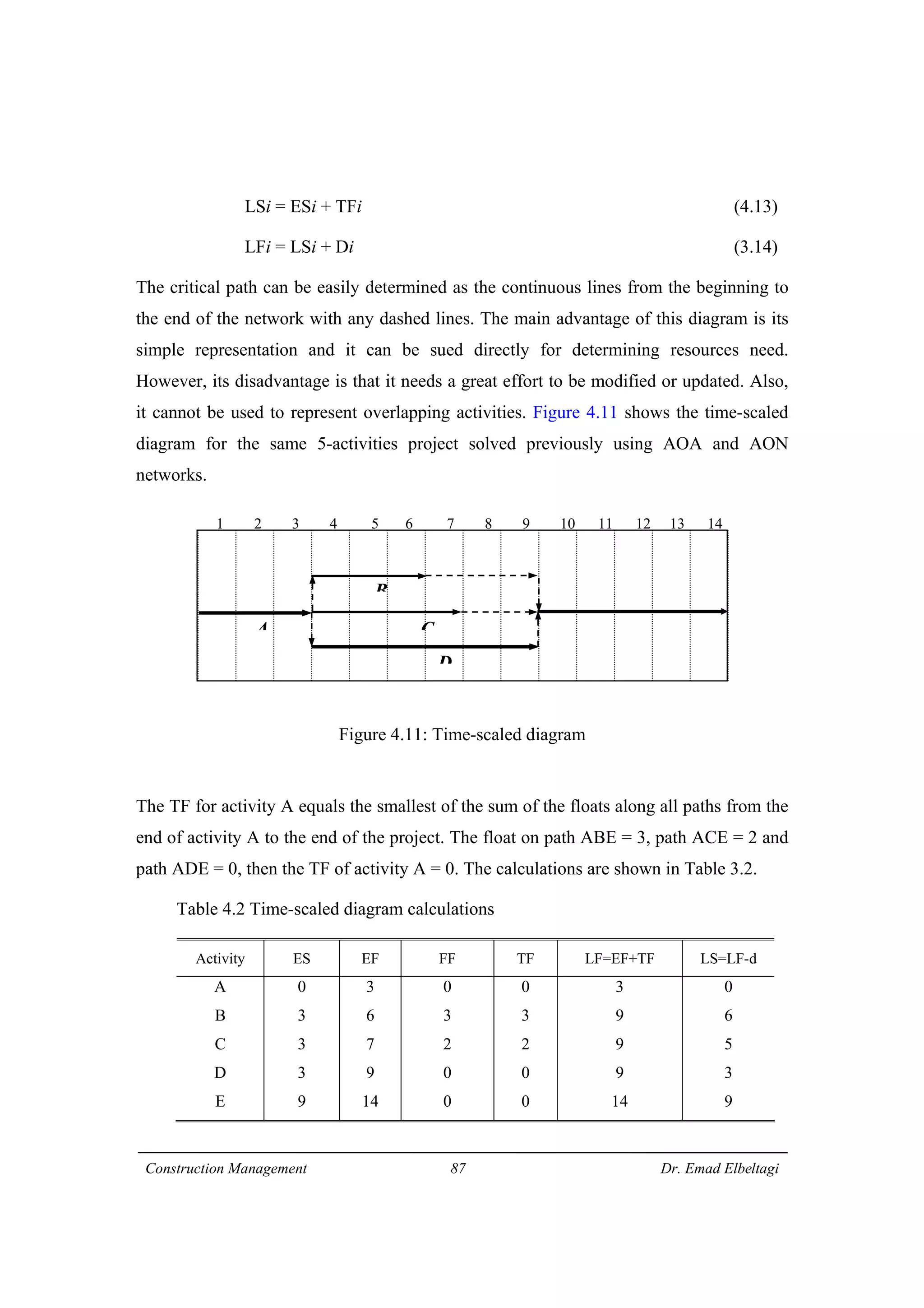
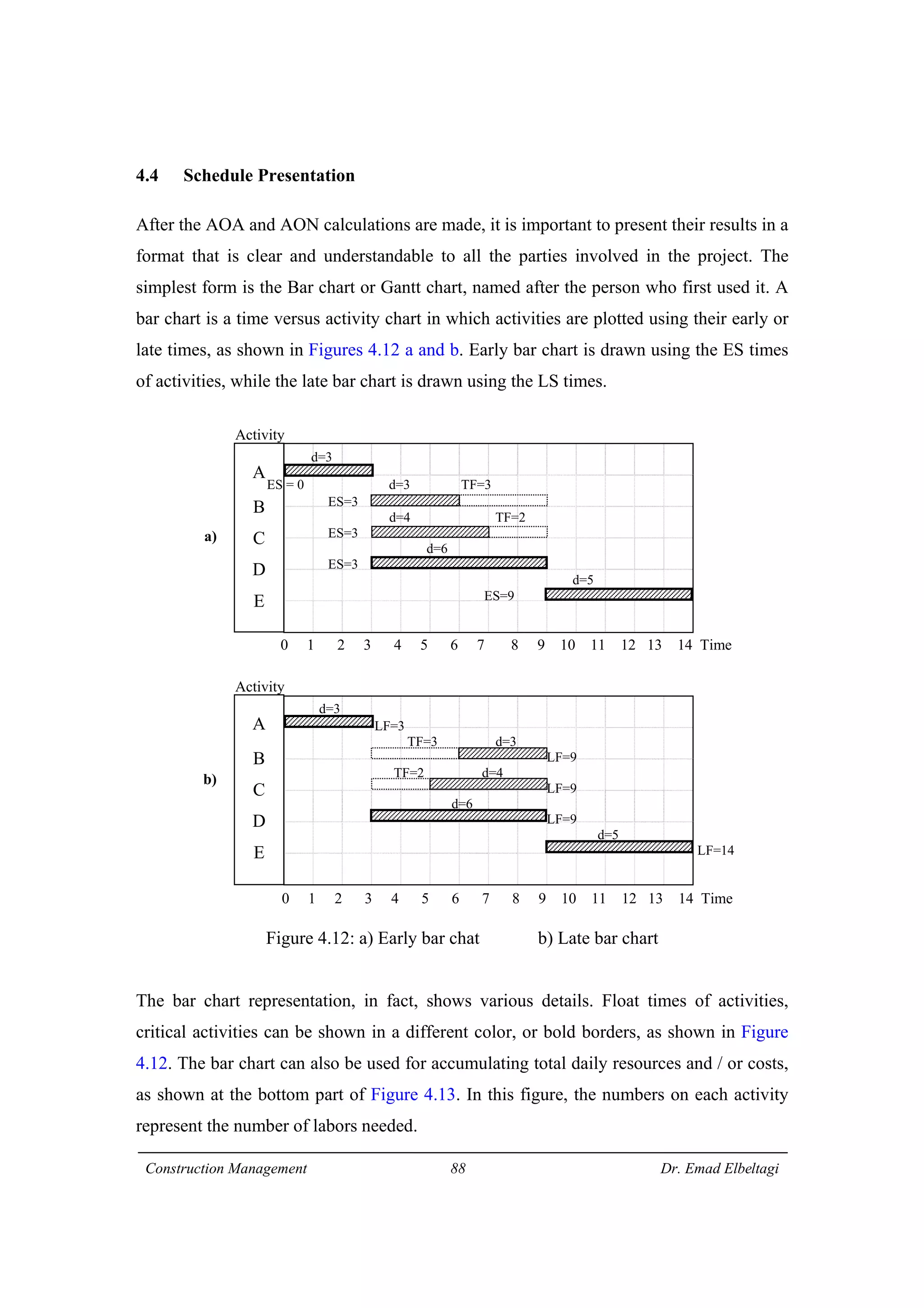
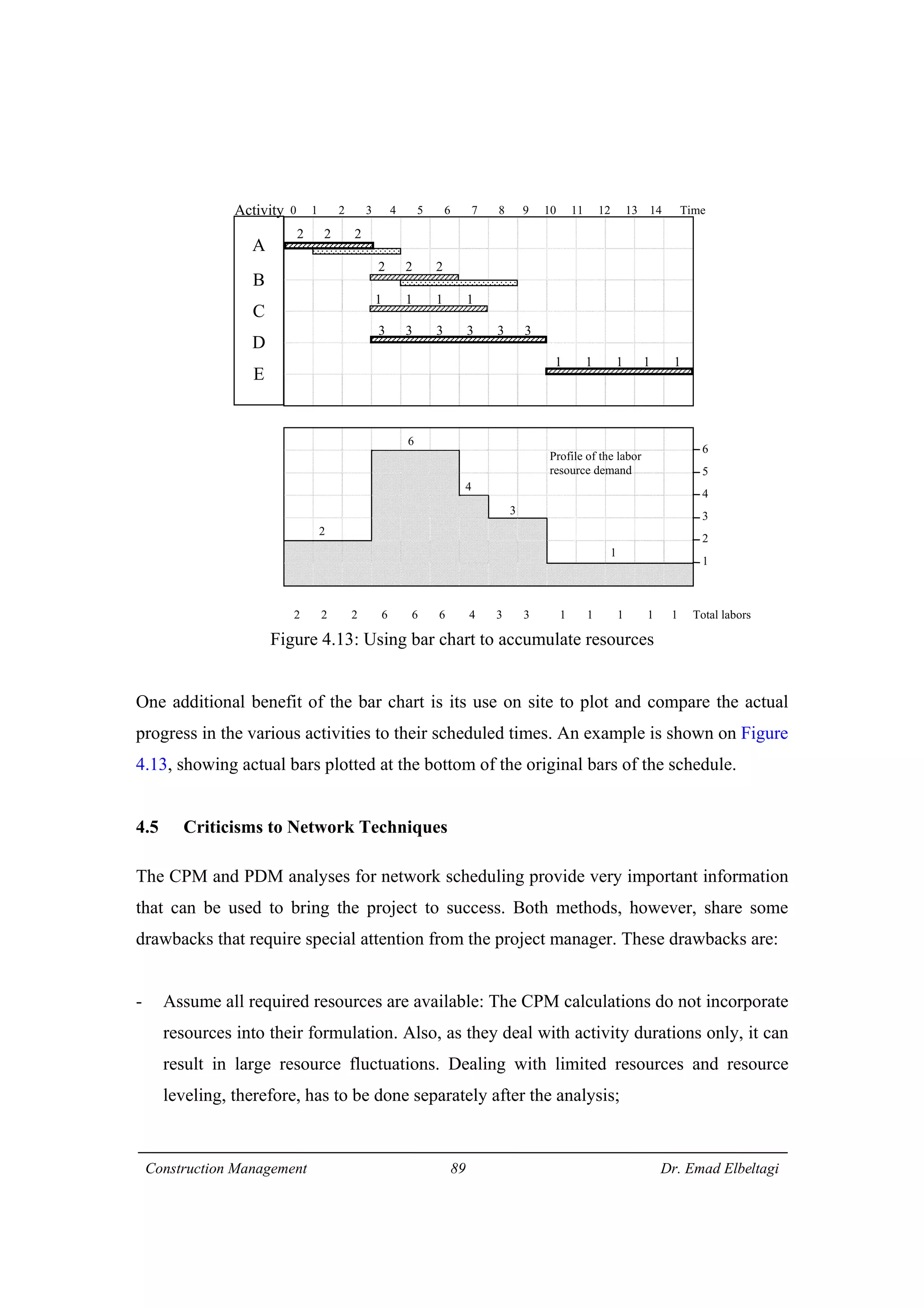
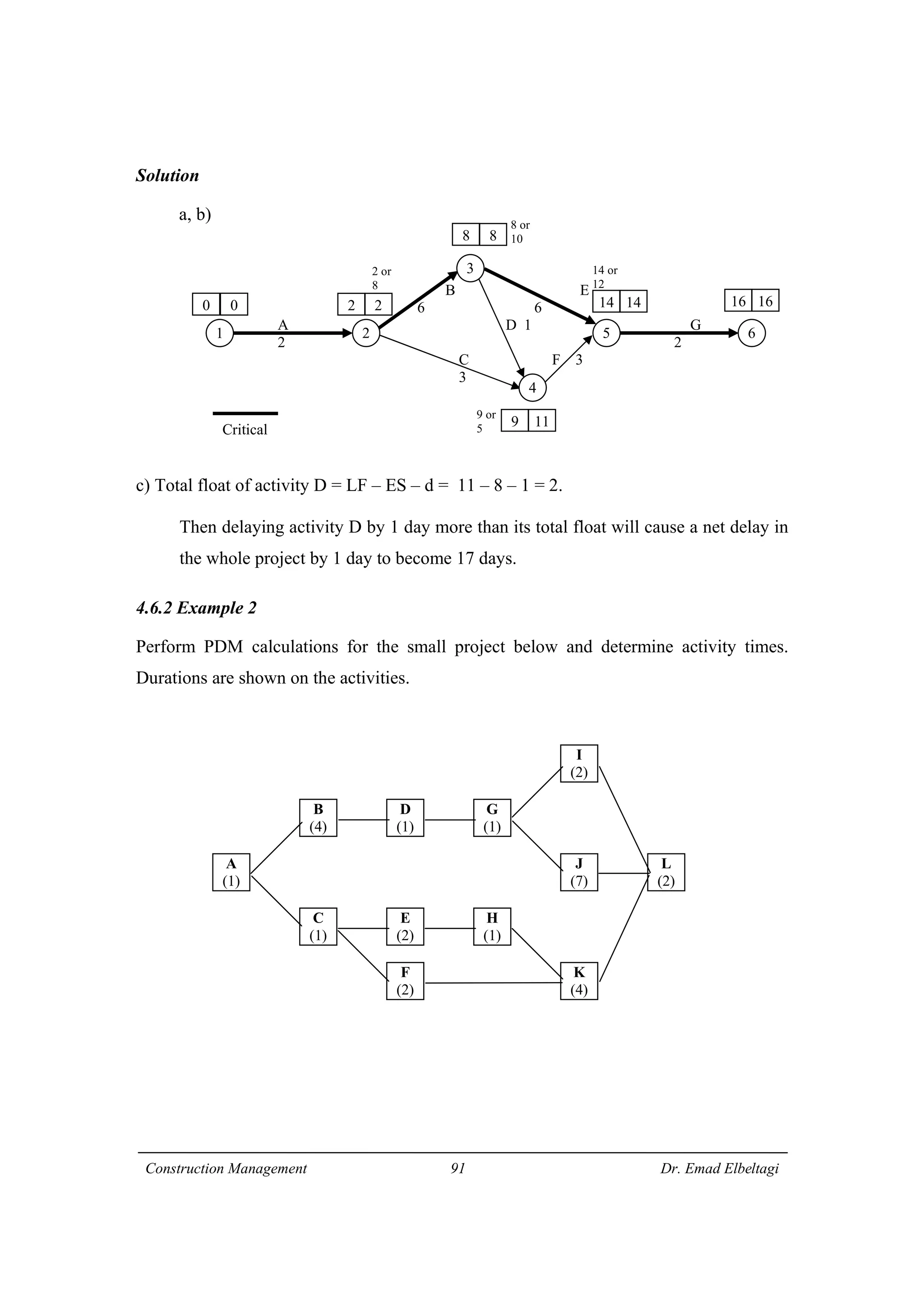
3) The example project network is analyzed using CPM. Forward processing determines early start times, while backward processing finds late finish times. Floats are then calculated to identify which activities have no scheduling flexibility.