Embed presentation
Download to read offline

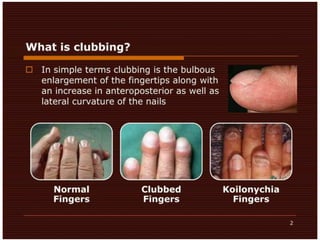
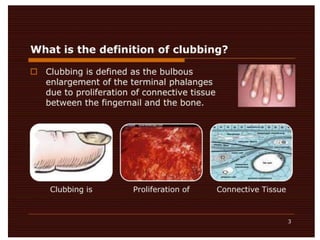
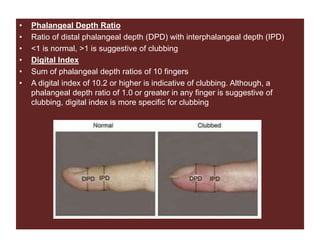









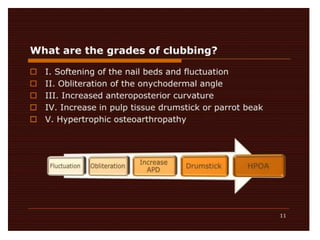





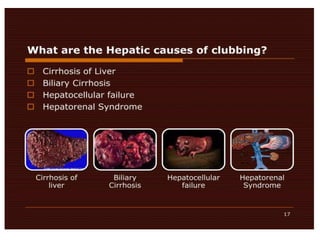







Clubbing refers to enlargement and rounding of the fingertips. Two methods are used to diagnose clubbing: the phalangeal depth ratio and digital index. A phalangeal depth ratio greater than 1 or a digital index over 10.2 indicates clubbing. The main respiratory causes of clubbing include lung cancers, mesothelioma, lung infections like bronchiectasis and cystic fibrosis, and interstitial lung diseases. Other causes include syphilis, syringomyelia, acromegaly, and thyrotoxicosis. Reverse clubbing, where the upper limbs show clubbing and lower limbs do not, can indicate transposition of the great arteries.




























