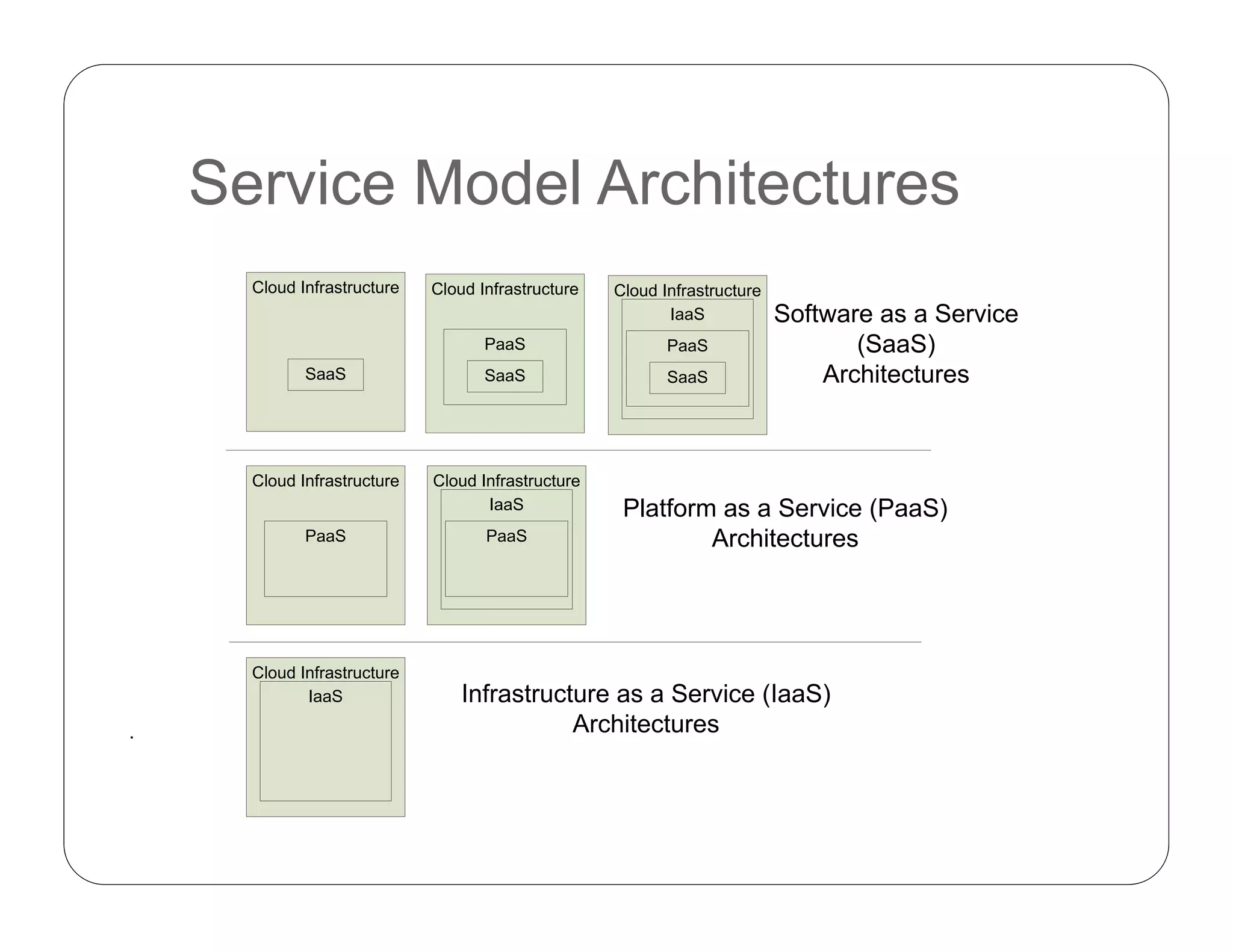
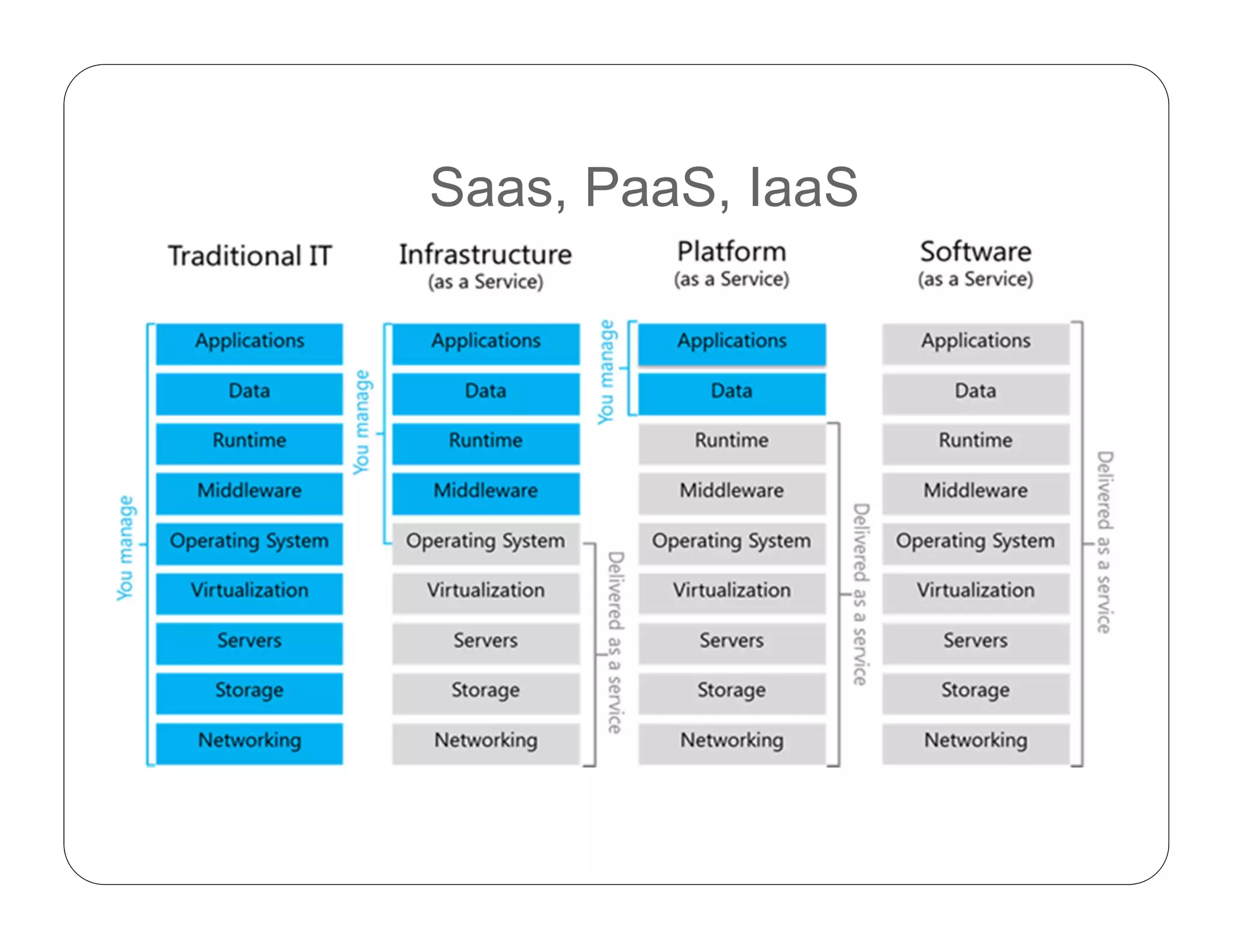
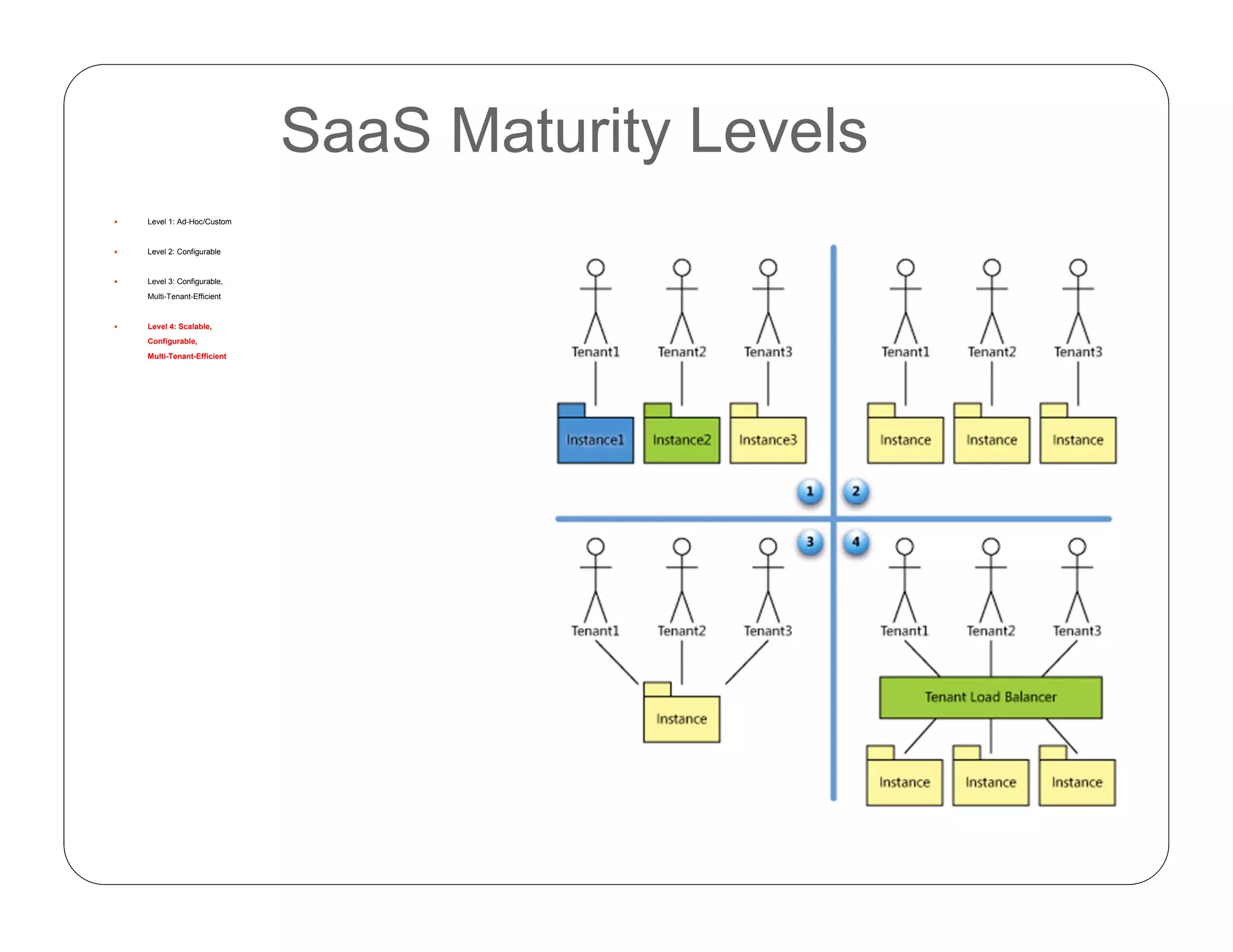
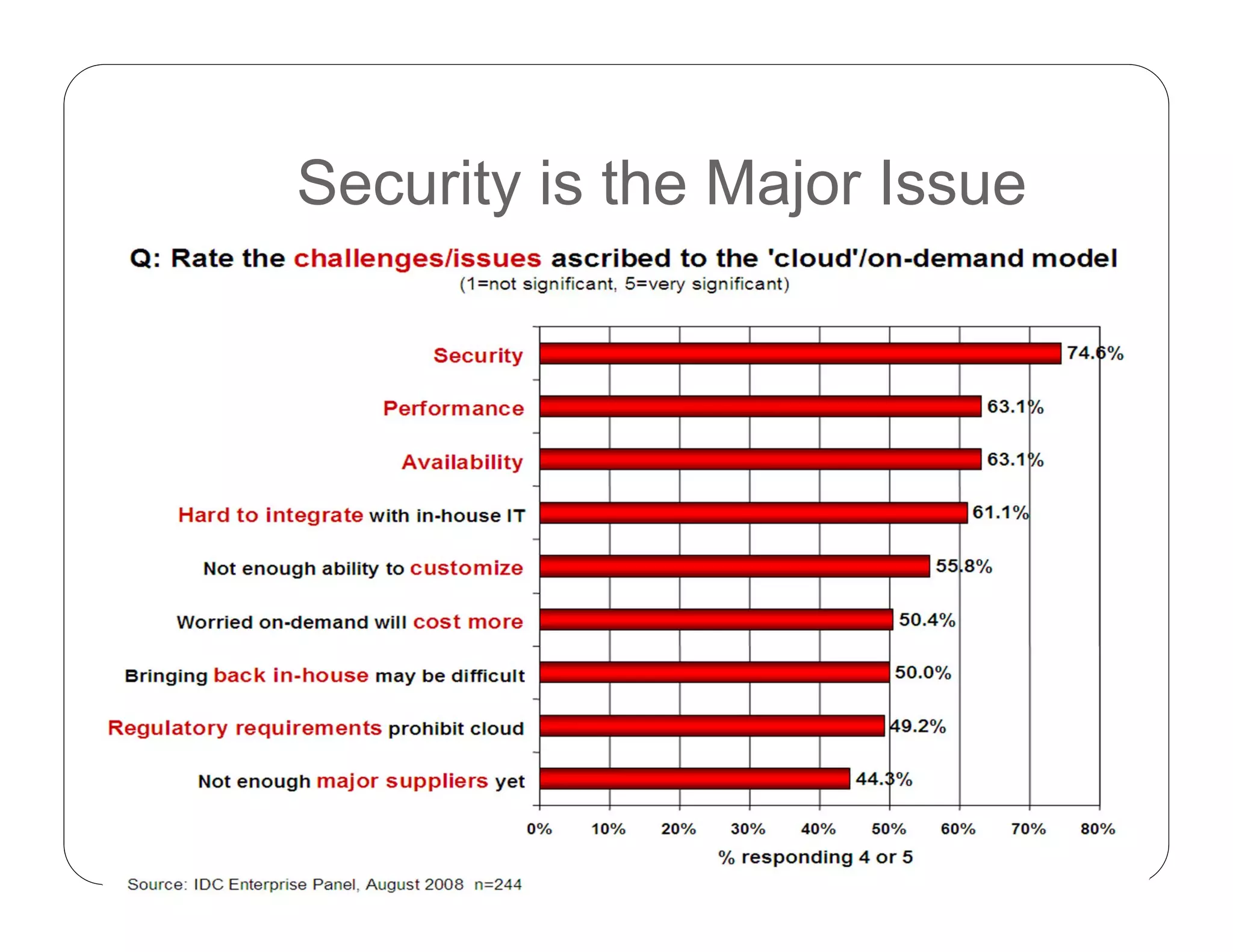
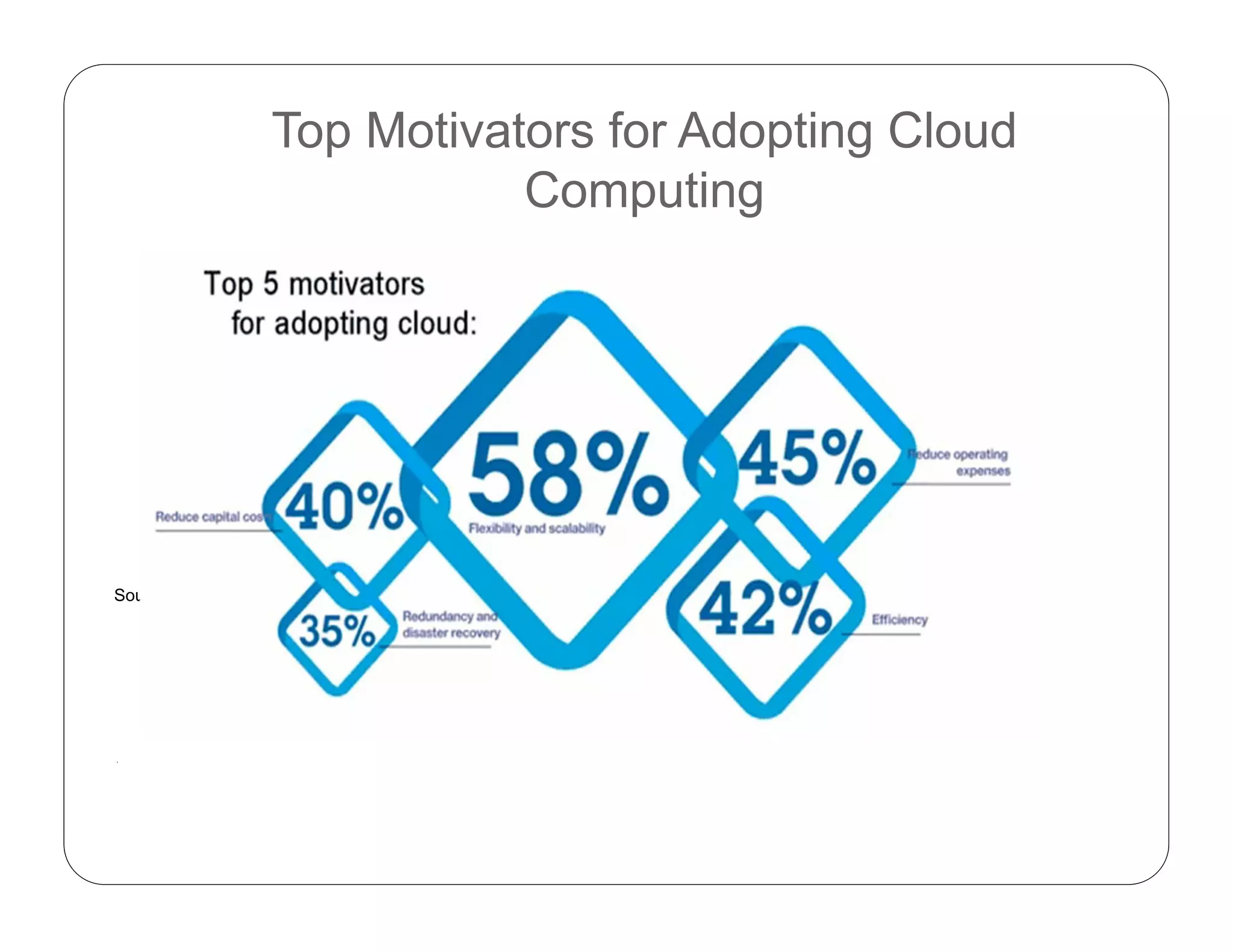
Cloud computing allows on-demand access to shared computing resources like servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics and more. It has 5 essential characteristics: on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity, and measured service. The three main service models are Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). Cloud deployment models include private, public, hybrid and community clouds.