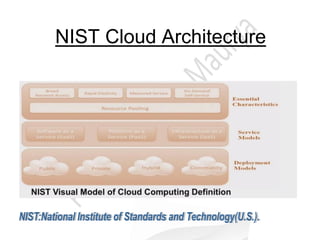
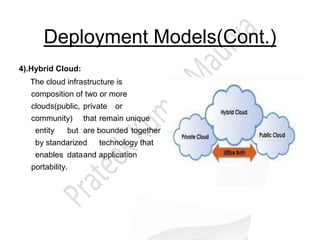
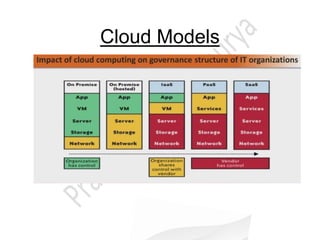
Cloud computing allows users to access software, storage, and computing power over the internet. It provides scalable resources and services to customers on-demand. There are several cloud deployment models including public, private, community, and hybrid clouds. The three main service models are infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS). Cloud computing provides businesses benefits like reduced costs and time to market. Technical benefits include automation, auto-scaling, and improved development cycles. Security and loss of control are concerns that need to be addressed for cloud adoption.