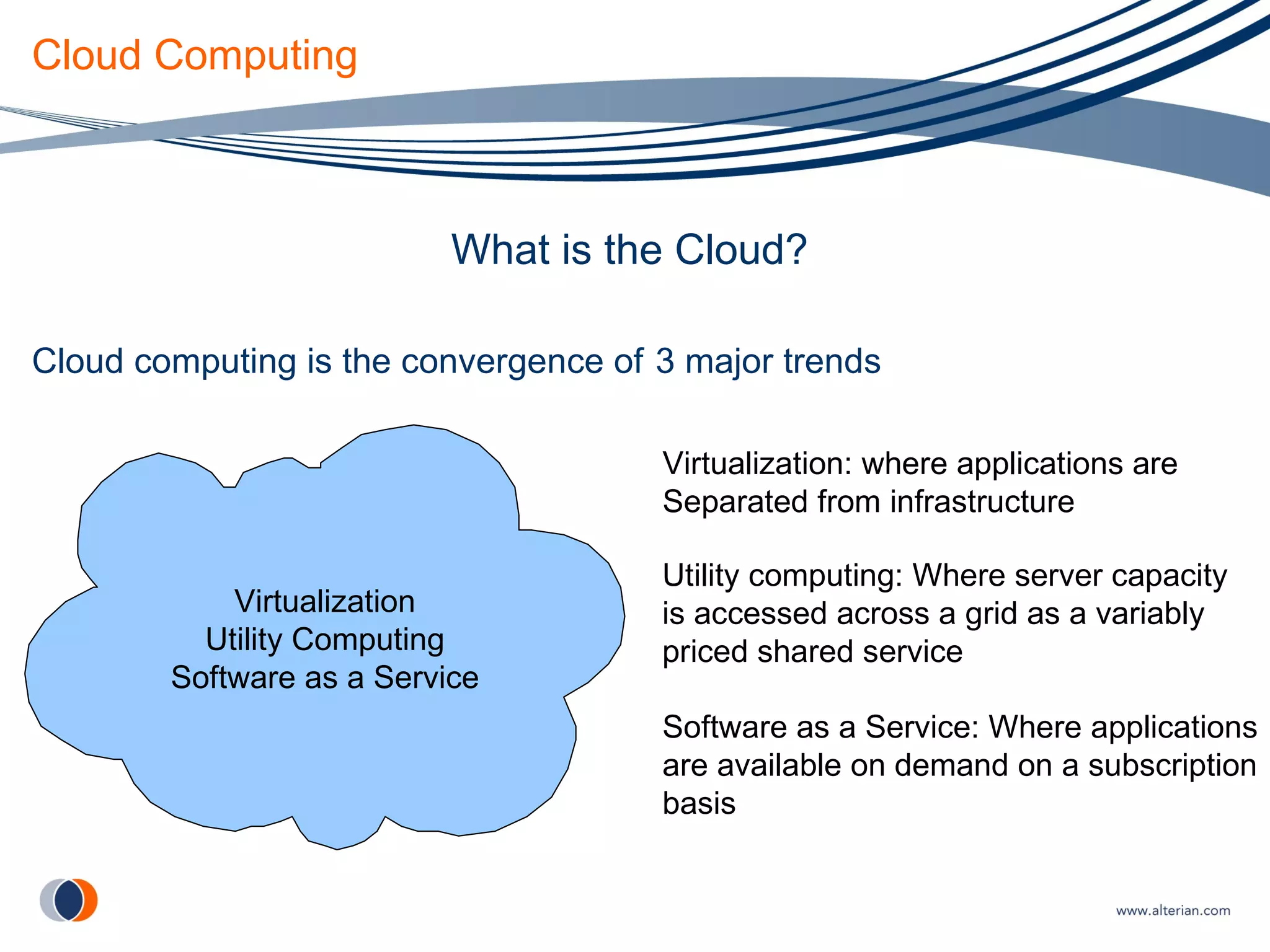
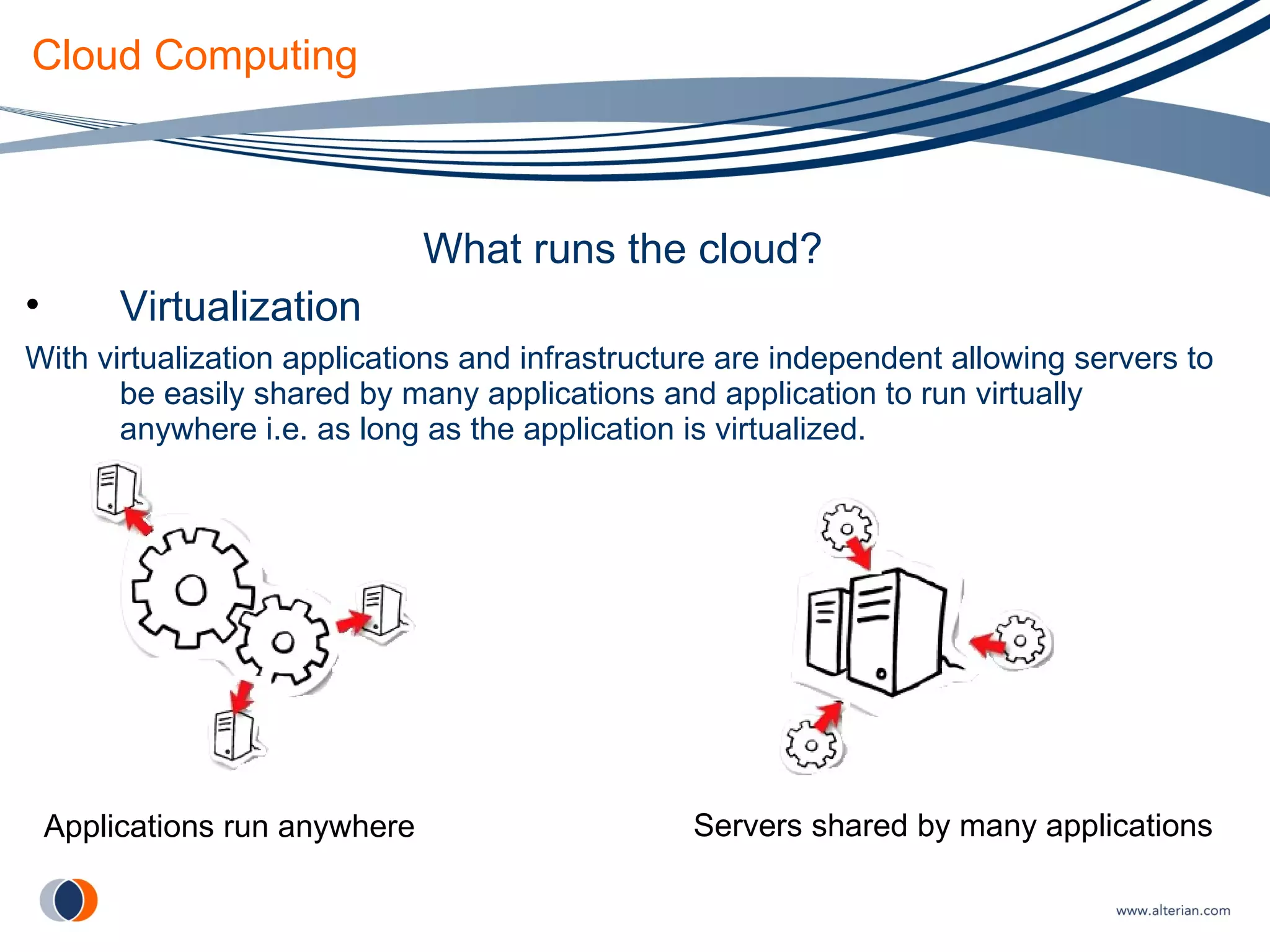
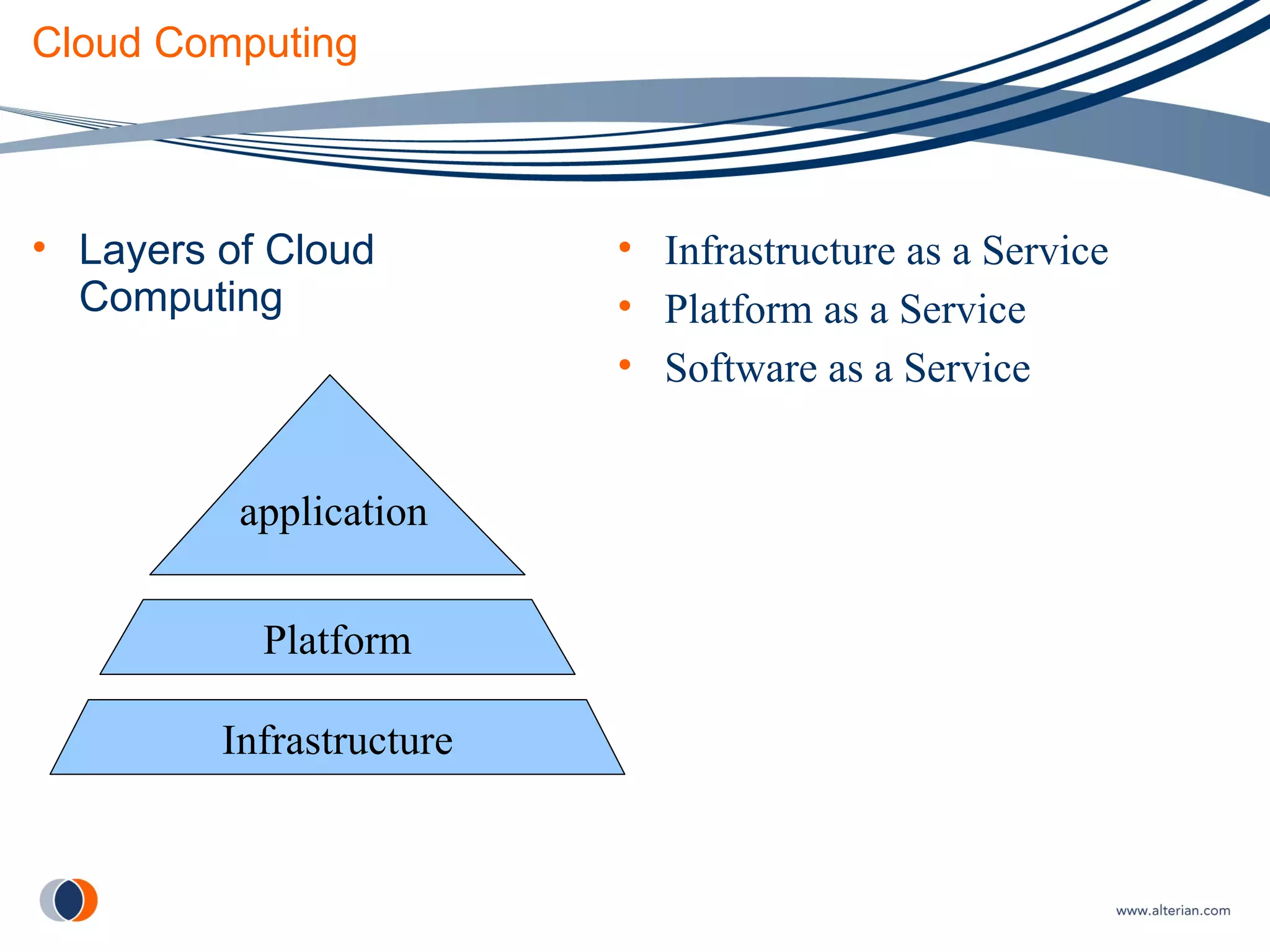
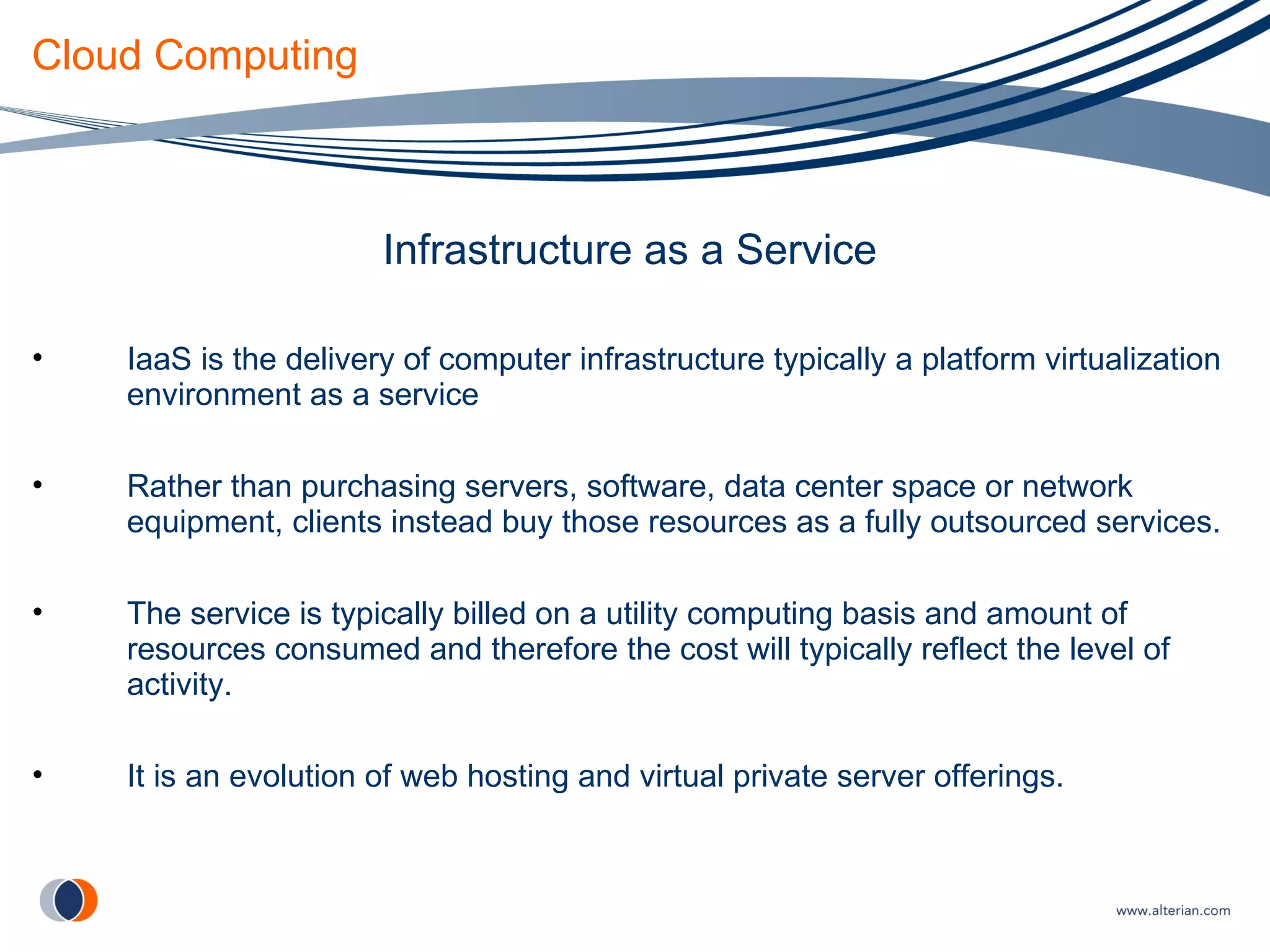
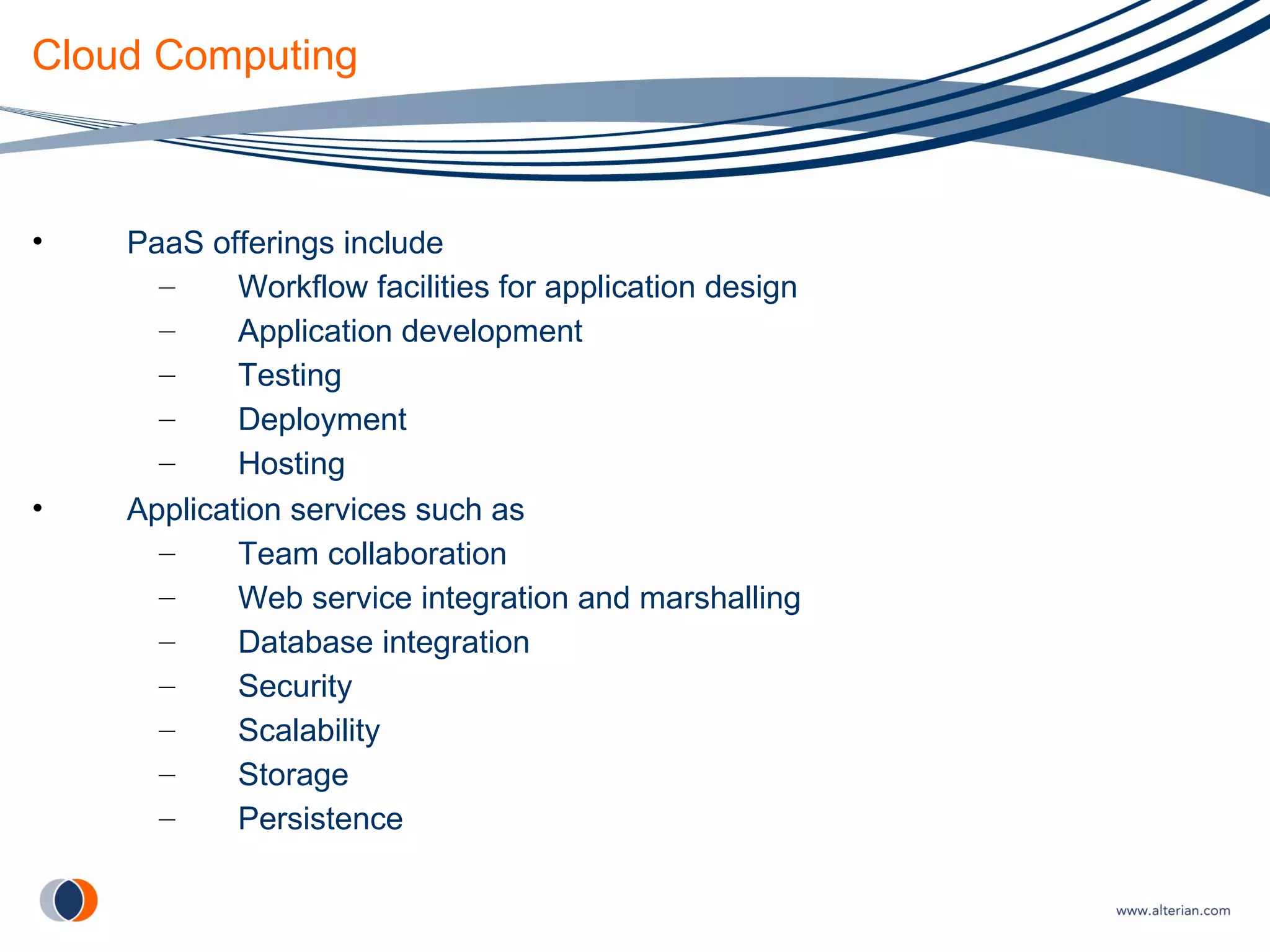
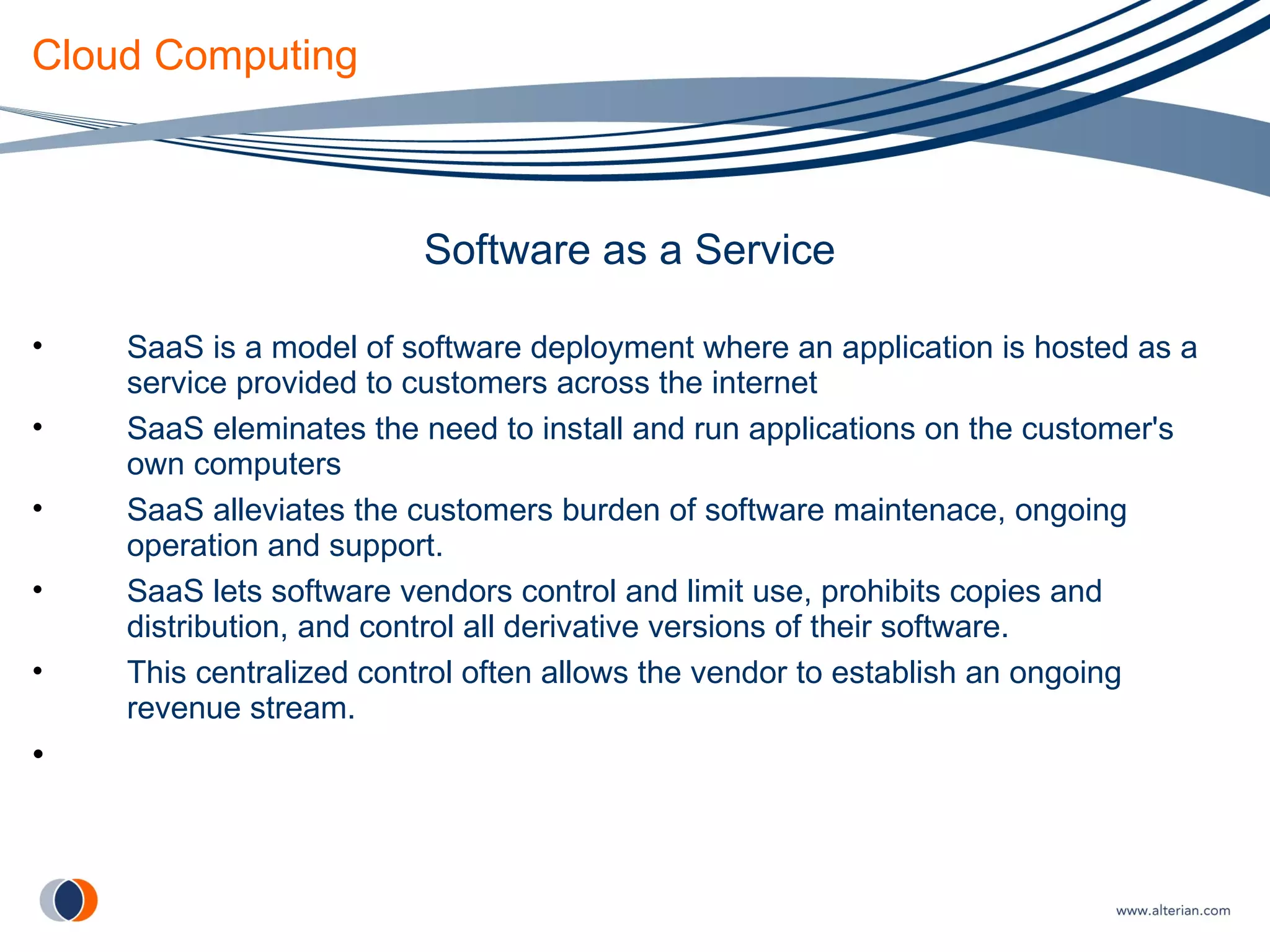
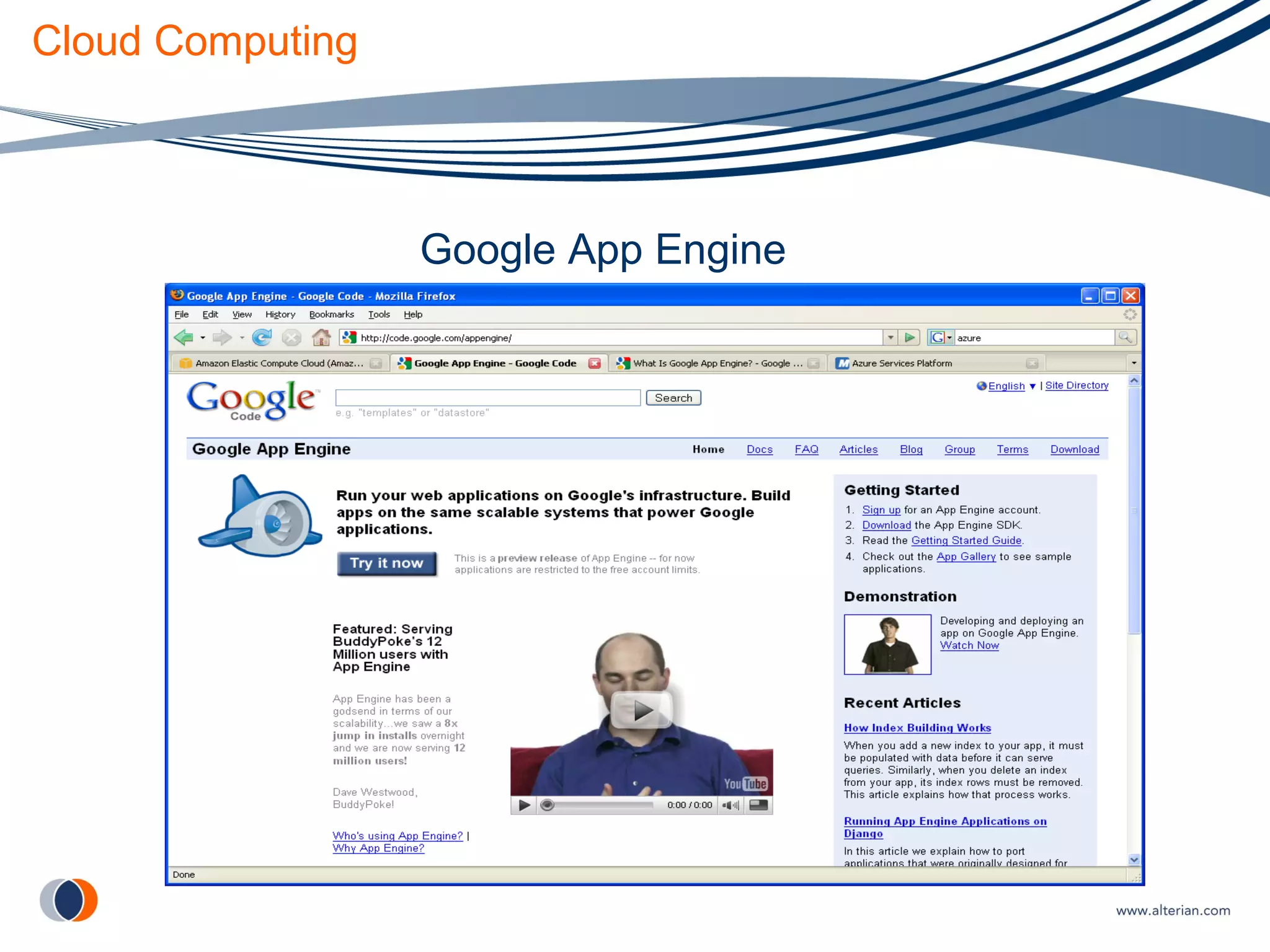
The document discusses cloud computing, defining it as internet-based computing where scalable resources are provided as a service over the network. It outlines the key aspects of cloud computing including virtualization, software as a service, platform as a service, and infrastructure as a service. Major cloud providers like Amazon EC2, Google App Engine, and Microsoft Azure are described. Benefits of adopting cloud computing include flexibility, lower costs, and scalability. Potential drawbacks relate to data transfer speeds, vendor lock-in, and lack of interoperability.