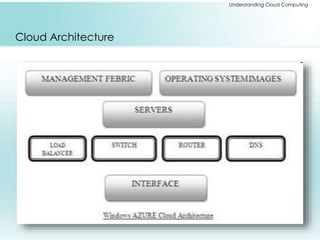
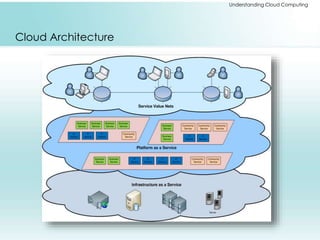
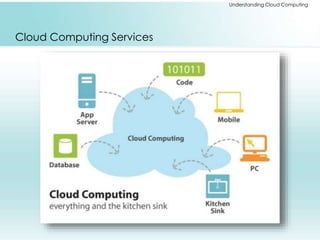
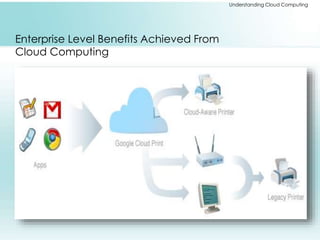
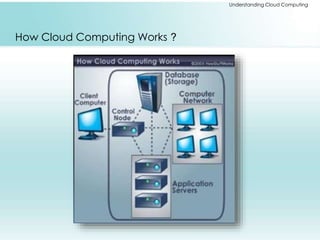
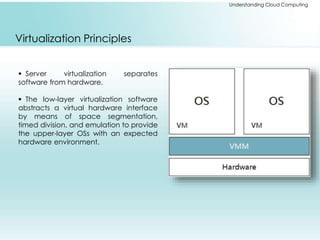
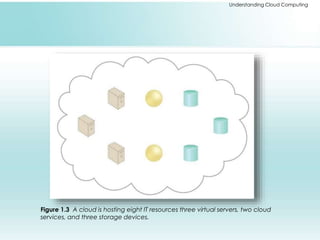
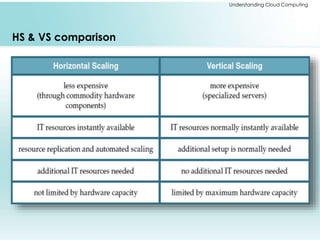
The document provides a comprehensive overview of cloud computing, including its history, architectures, service models, and deployment models. It discusses the benefits and challenges associated with cloud adoption and outlines various cloud service models such as SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. Additionally, it explores enterprise-level advantages, disadvantages, and key technologies enabling cloud computing.