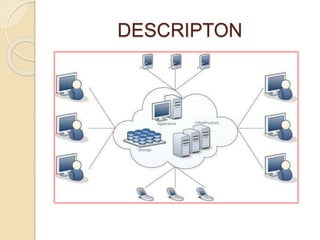
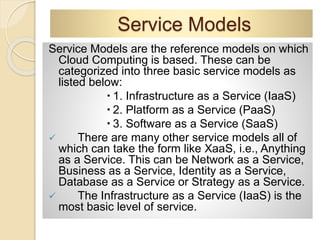
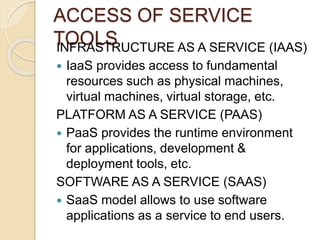
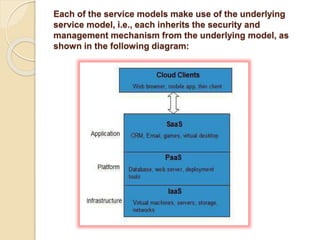
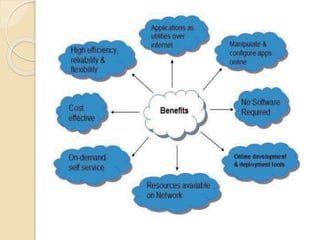
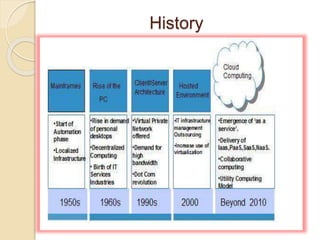
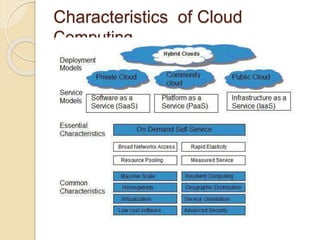
This document provides an introduction to cloud computing, including definitions, models, and characteristics. It defines cloud computing as accessing applications over the Internet as utilities. There are three deployment models (public, private, hybrid clouds) and three service models (Infrastructure as a Service, Platform as a Service, Software as a Service). Key characteristics of cloud computing include on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, and rapid elasticity.