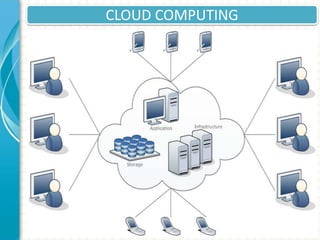
The document discusses the cloud ecosystem, including concepts of cloud computing, technologies like virtualization and service-oriented architecture, security considerations, challenges around data protection and management capabilities, and benefits such as reduced costs and increased flexibility. Cloud computing provides on-demand access to shared computing resources over a network in various service models like SaaS, PaaS and IaaS. While cloud offers benefits, challenges remain around data security, availability and regulatory compliance.