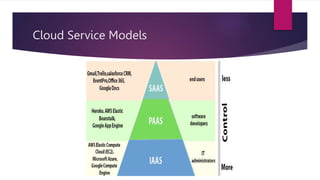
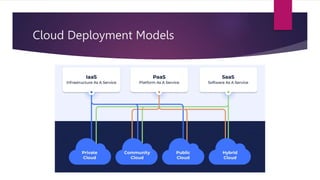
The document presents an extensive overview of cloud computing, covering its history, service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS), deployment models (public, private, hybrid, community), and associated benefits and challenges. It discusses future trends such as edge computing and AI, as well as the critical business needs for cloud deployment, including cost efficiency and scalability. Additionally, it highlights potential obstacles to cloud adoption and proposes solutions for mitigating risks, concluding with necessary actions for writing and sharing knowledge on related technologies.