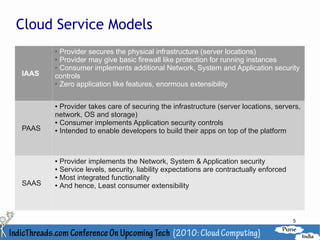
The document discusses various aspects of cloud security, highlighting the importance of understanding threats and implementing effective mitigations across different service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS). It outlines key security areas such as physical, network, system, and application security, emphasizing the need for strong authentication, data protection, and compliance measures against risks like data loss, hijacking, and insider threats. Additionally, it advises on best practices for securing cloud environments, including regularly monitoring configurations and utilizing specific tools for enhanced security management.