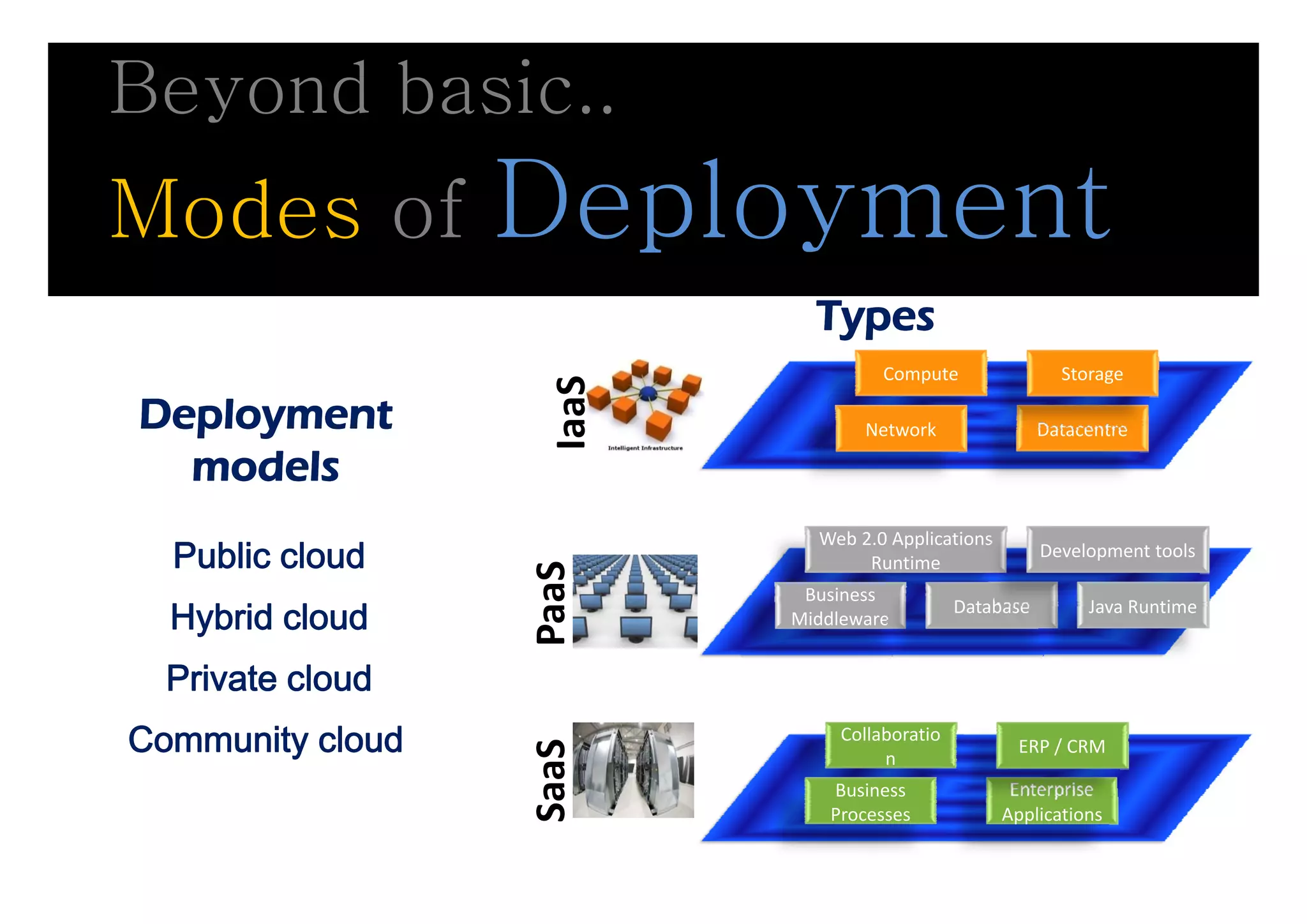
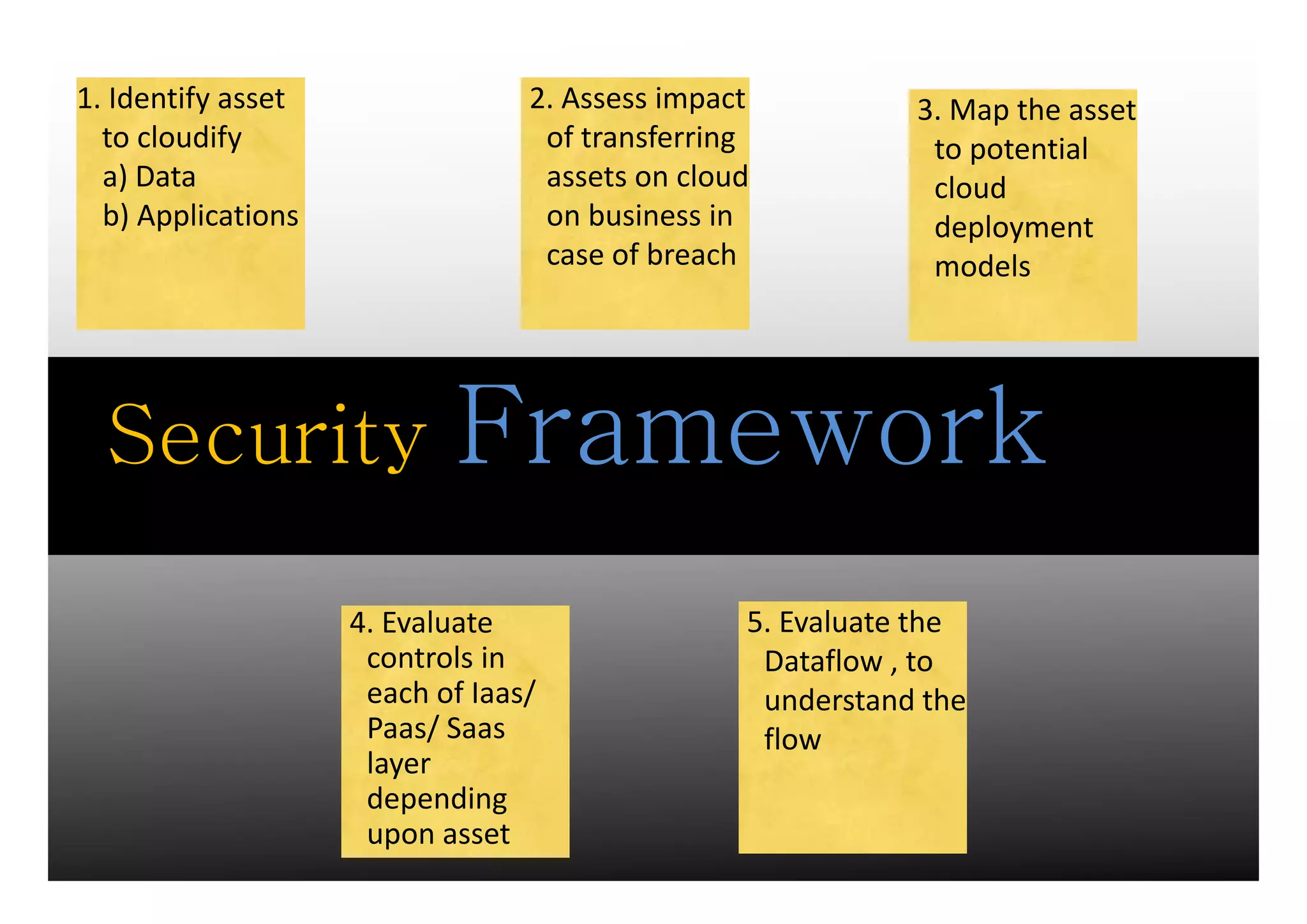
The document discusses cloud security, emphasizing the need for traditional information security practices to adapt to cloud environments. Key topics include the essential characteristics of cloud computing, types of services (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS), security threats, and a framework for managing security controls. It highlights the importance of considering assets, risk management, and business criticality when implementing security measures in the cloud.