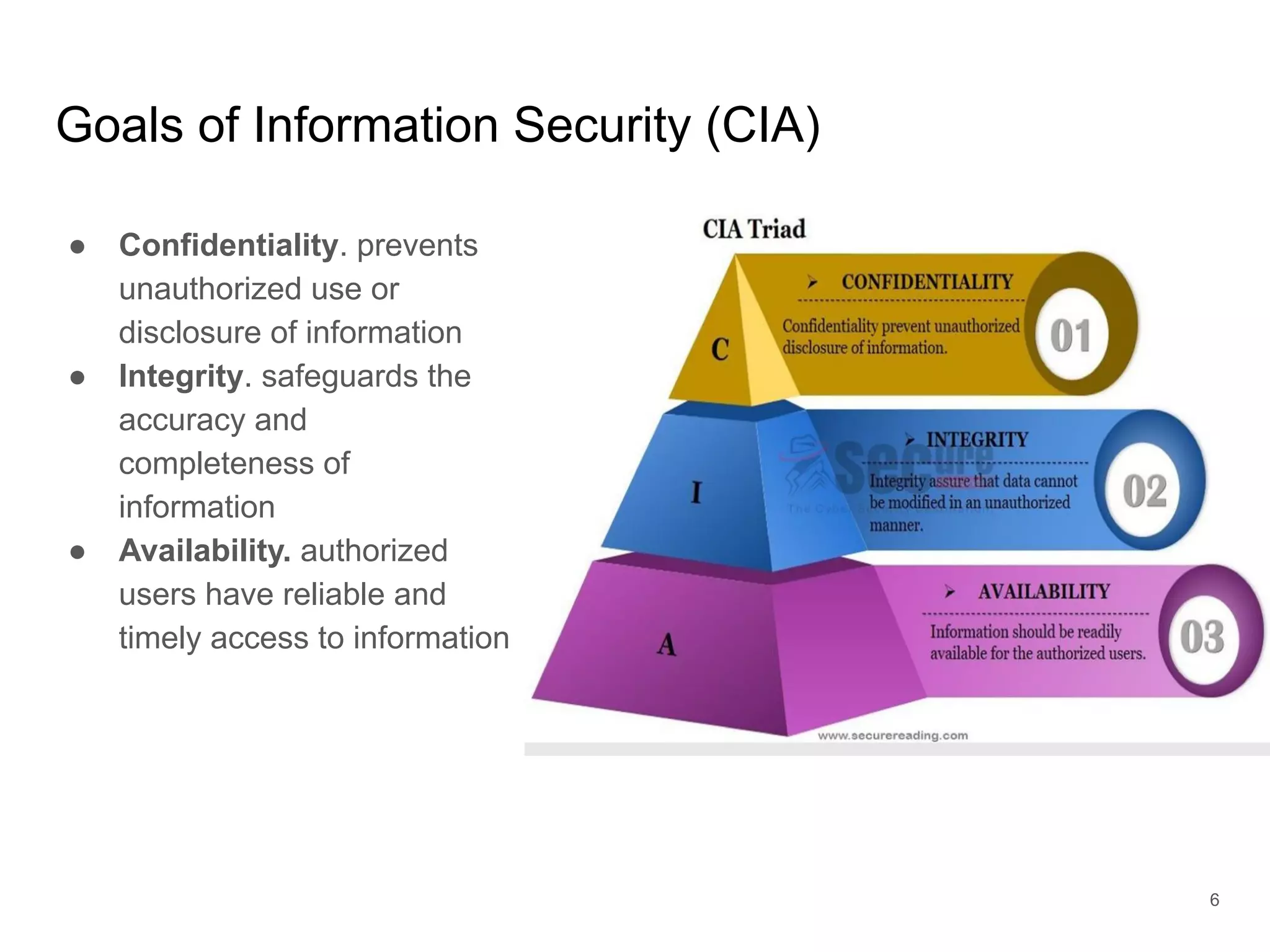
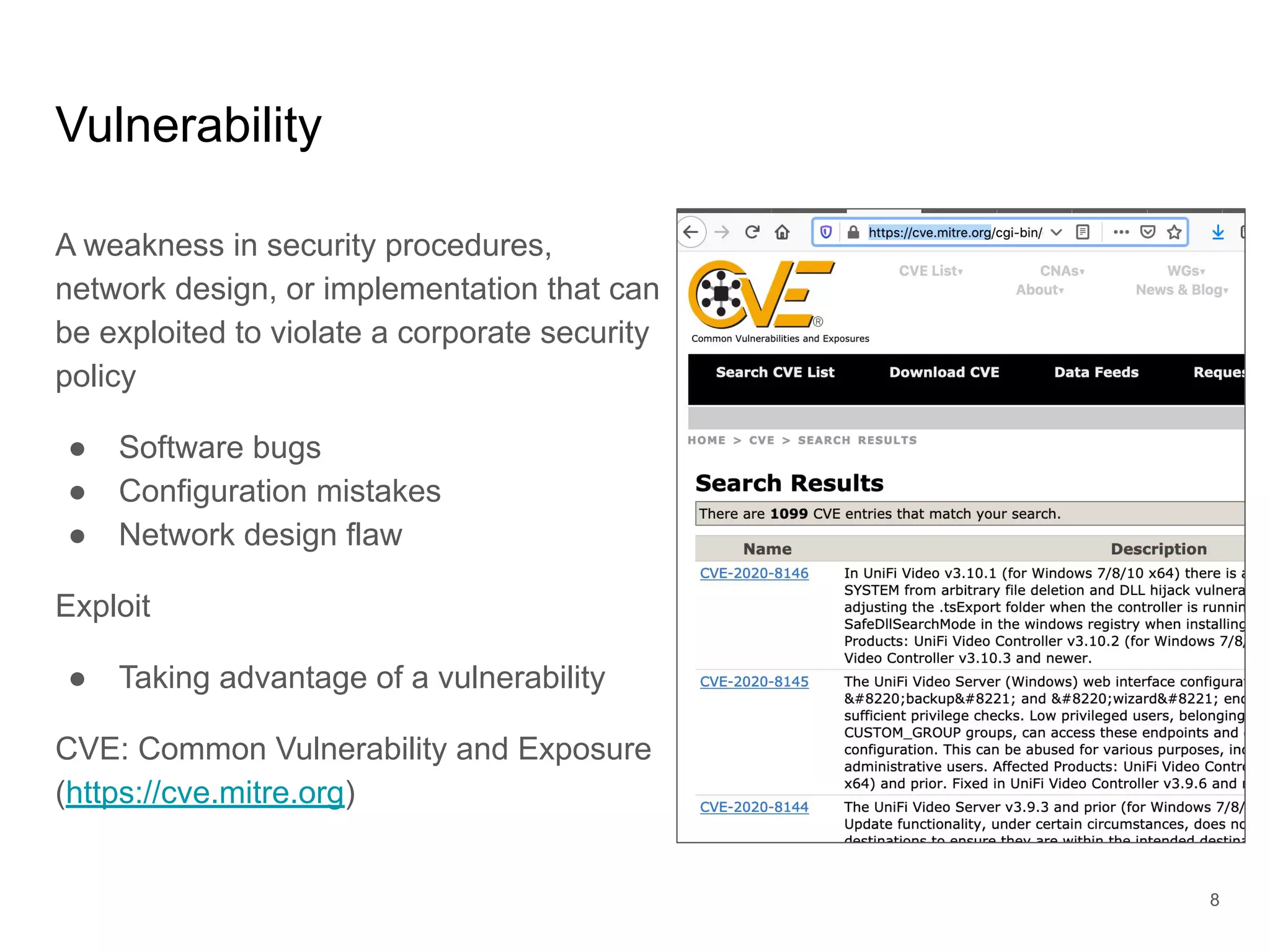
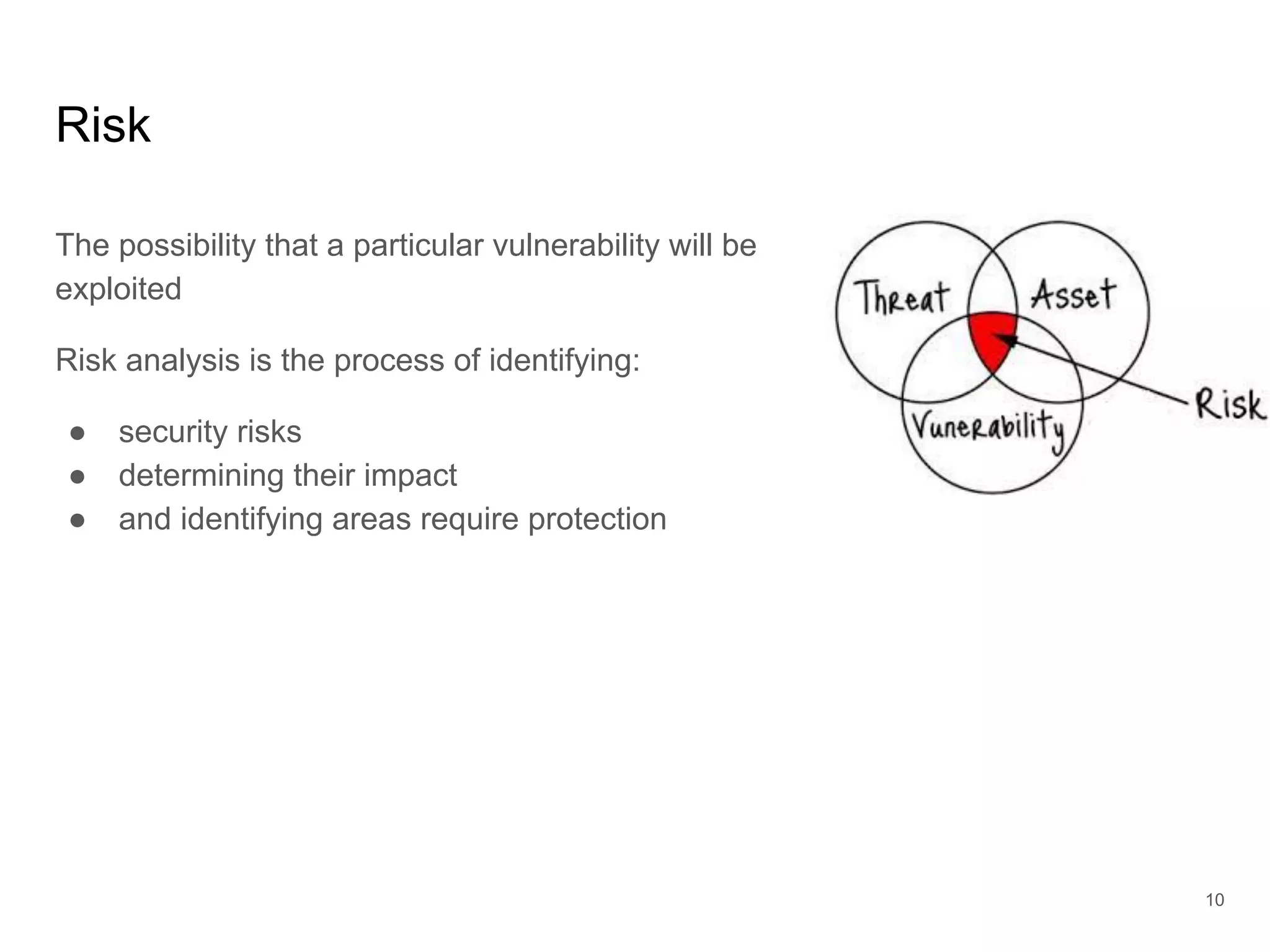
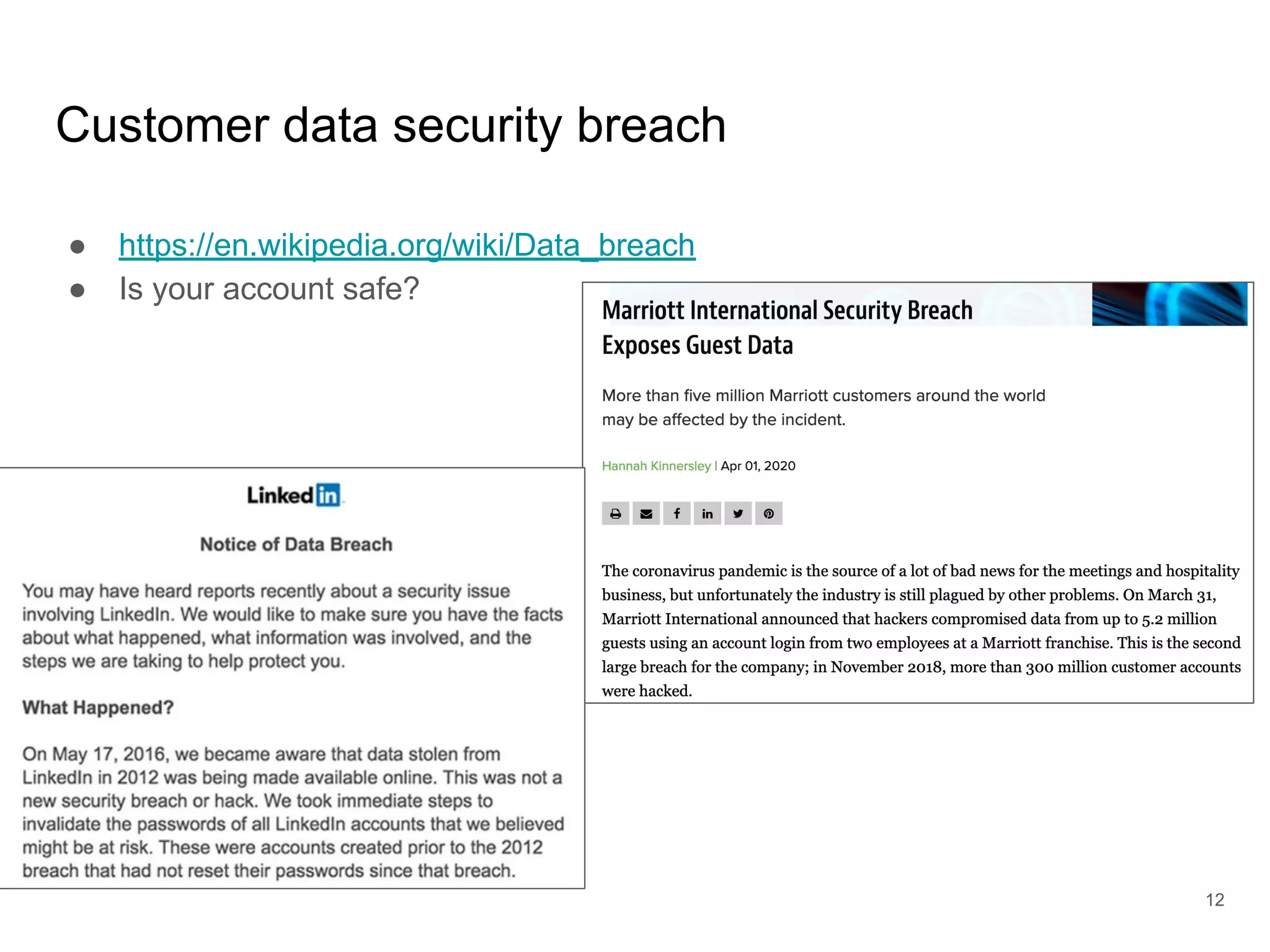
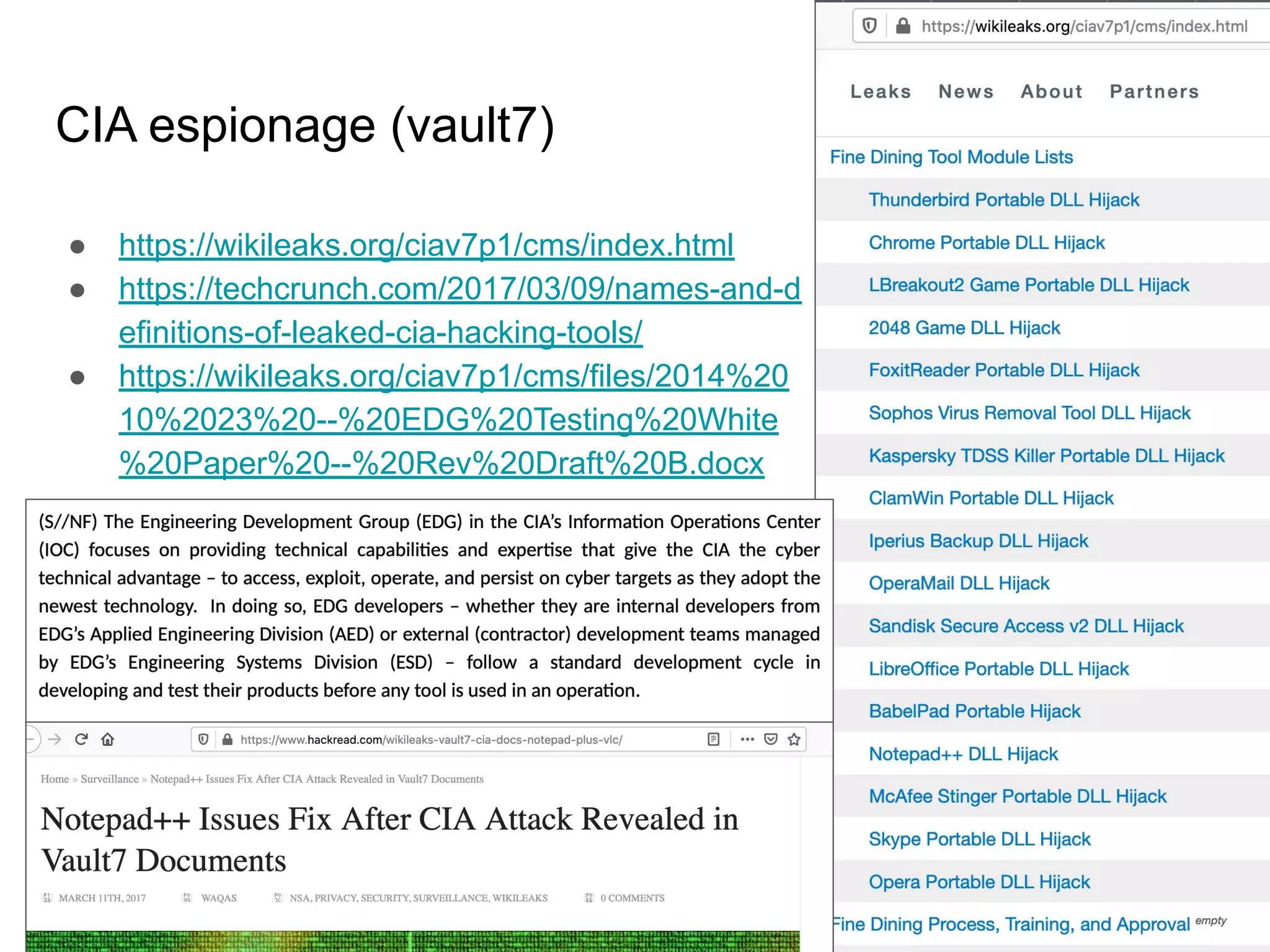
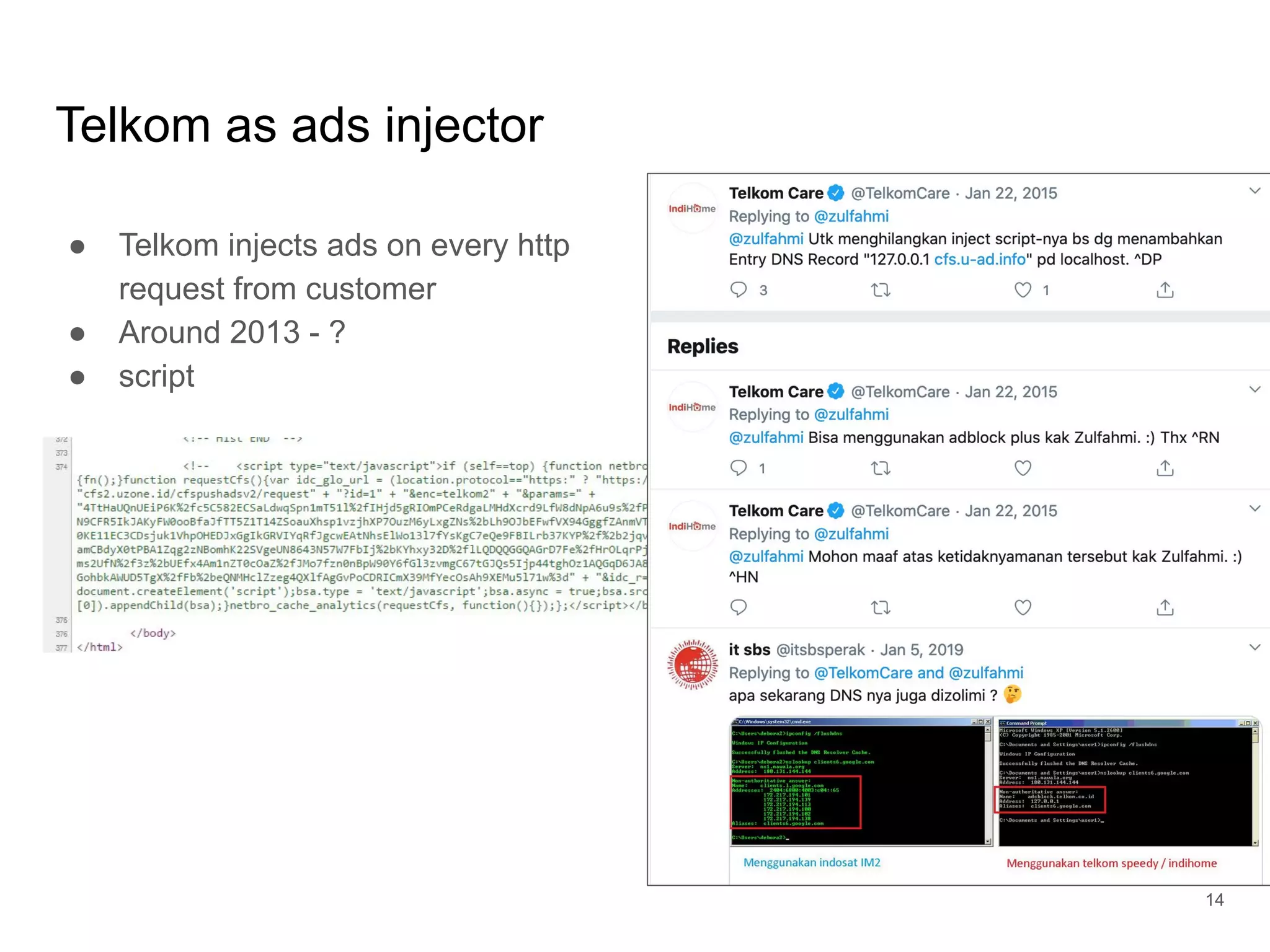
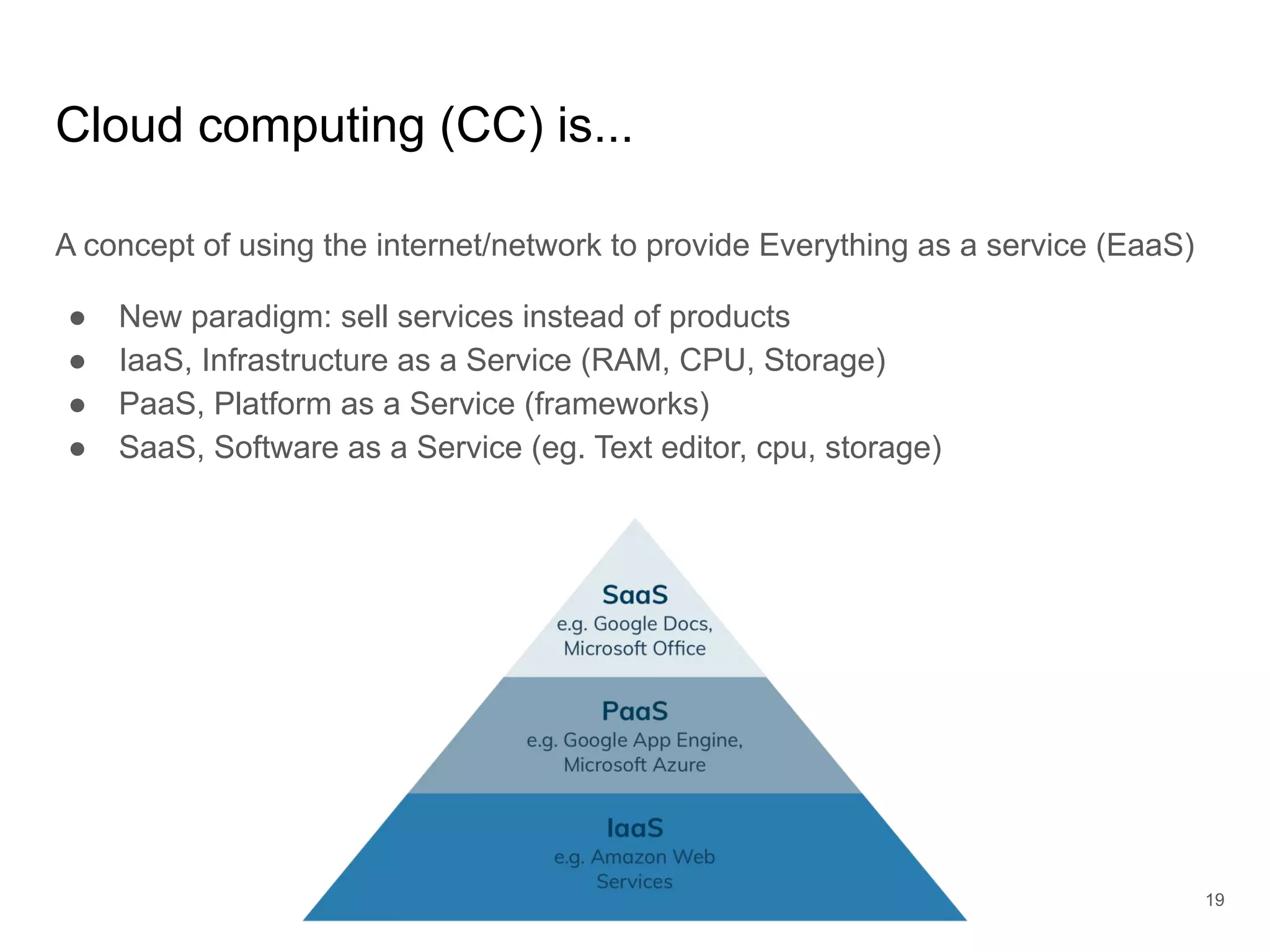
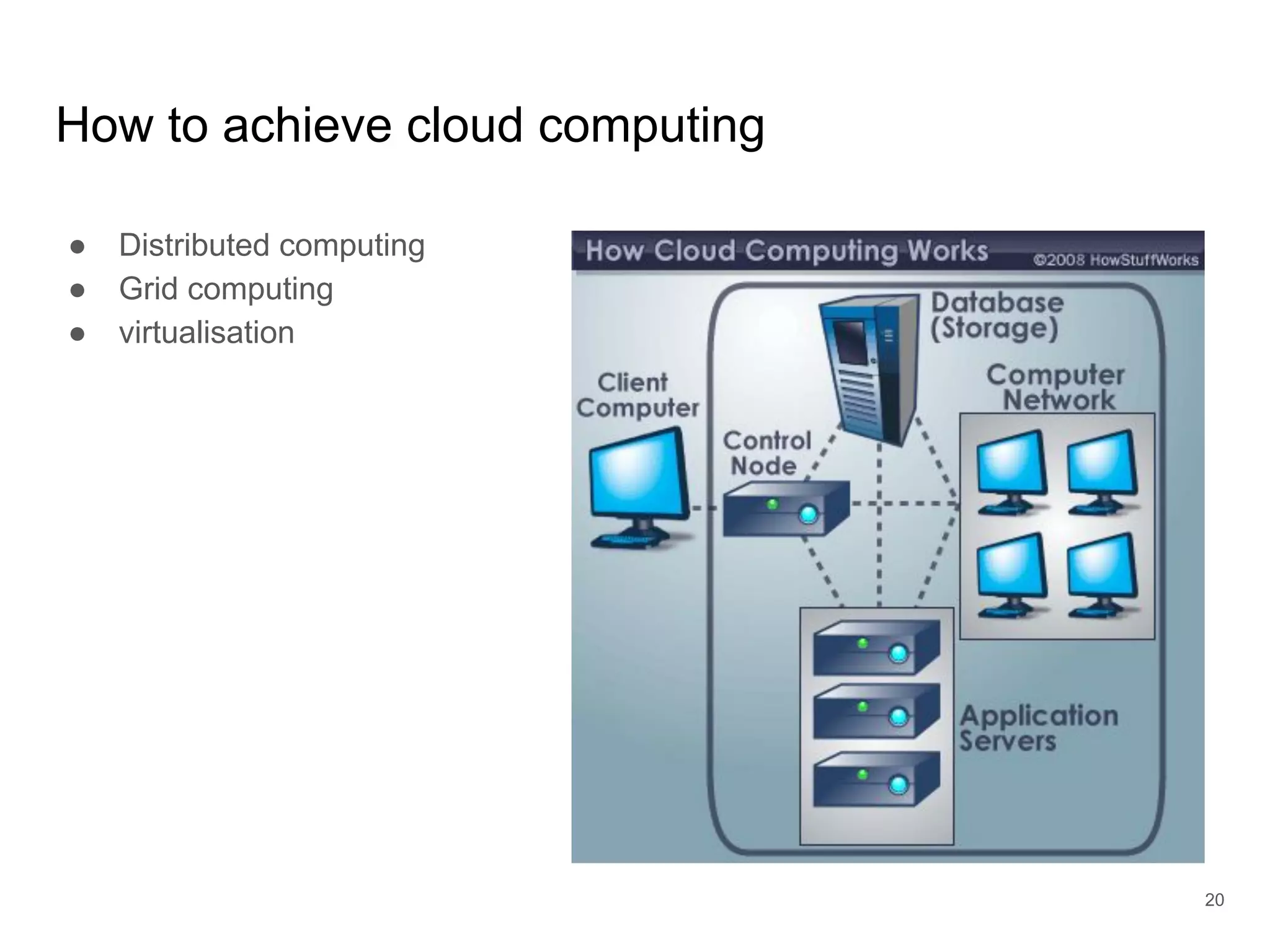
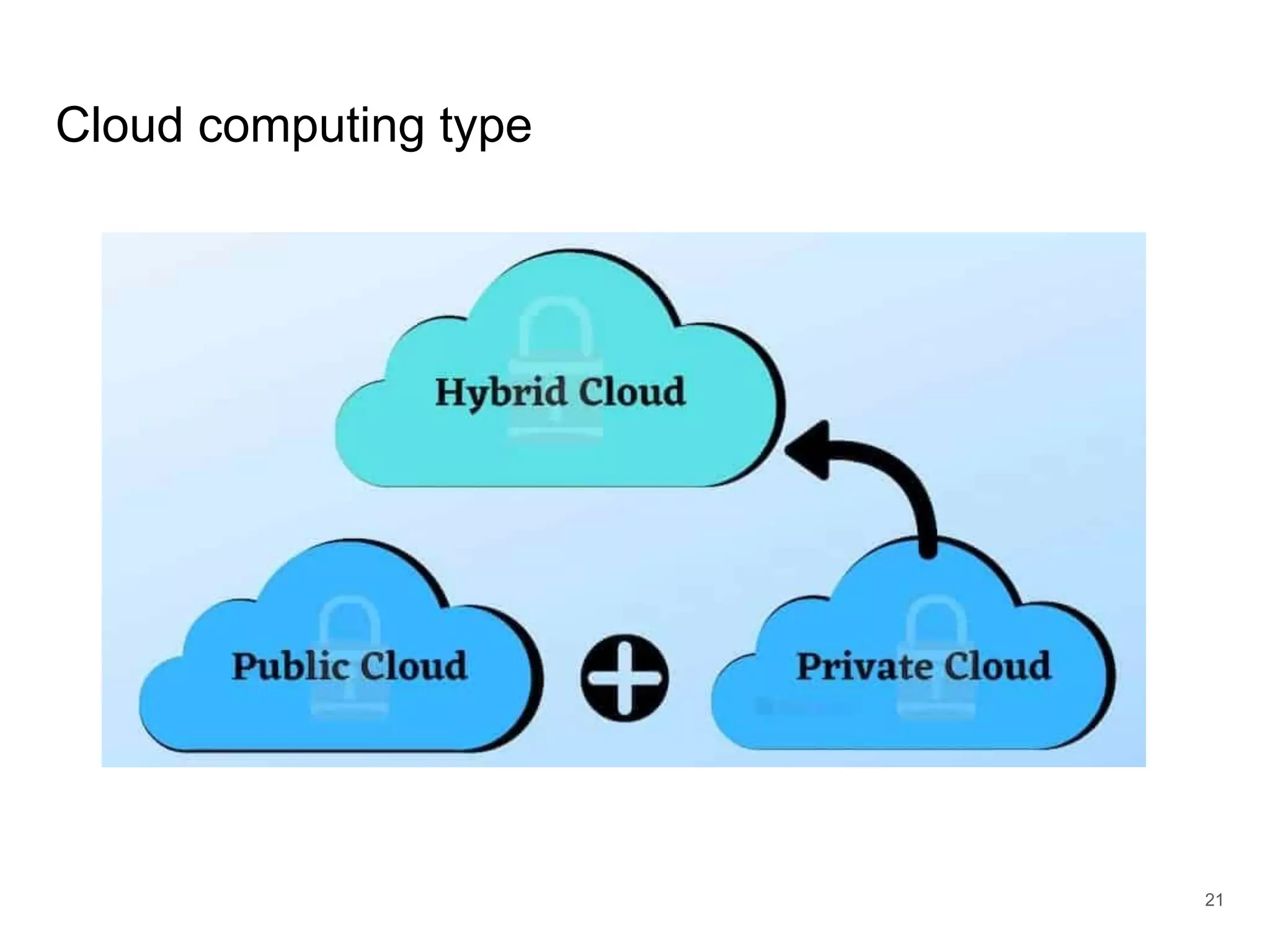
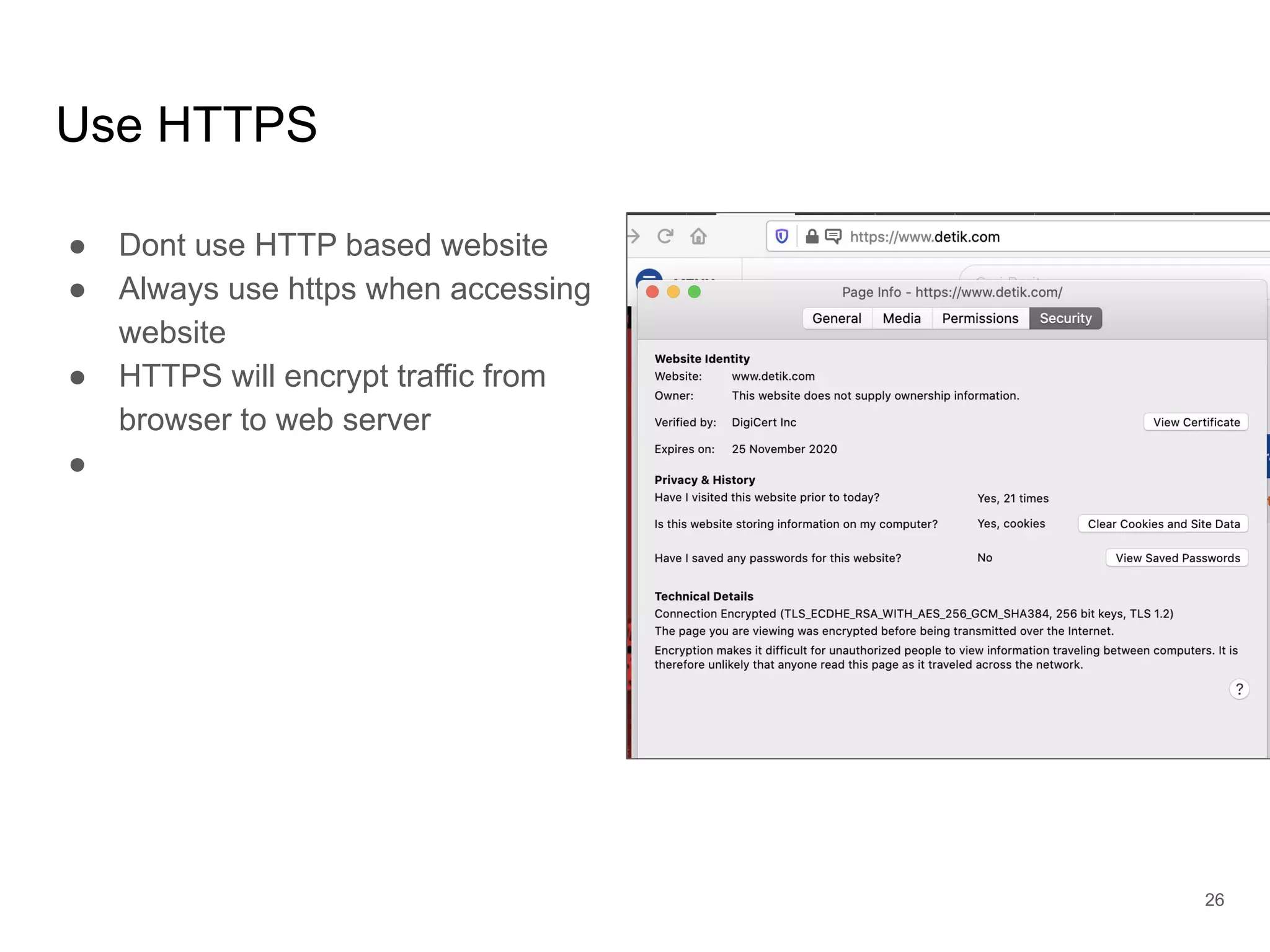
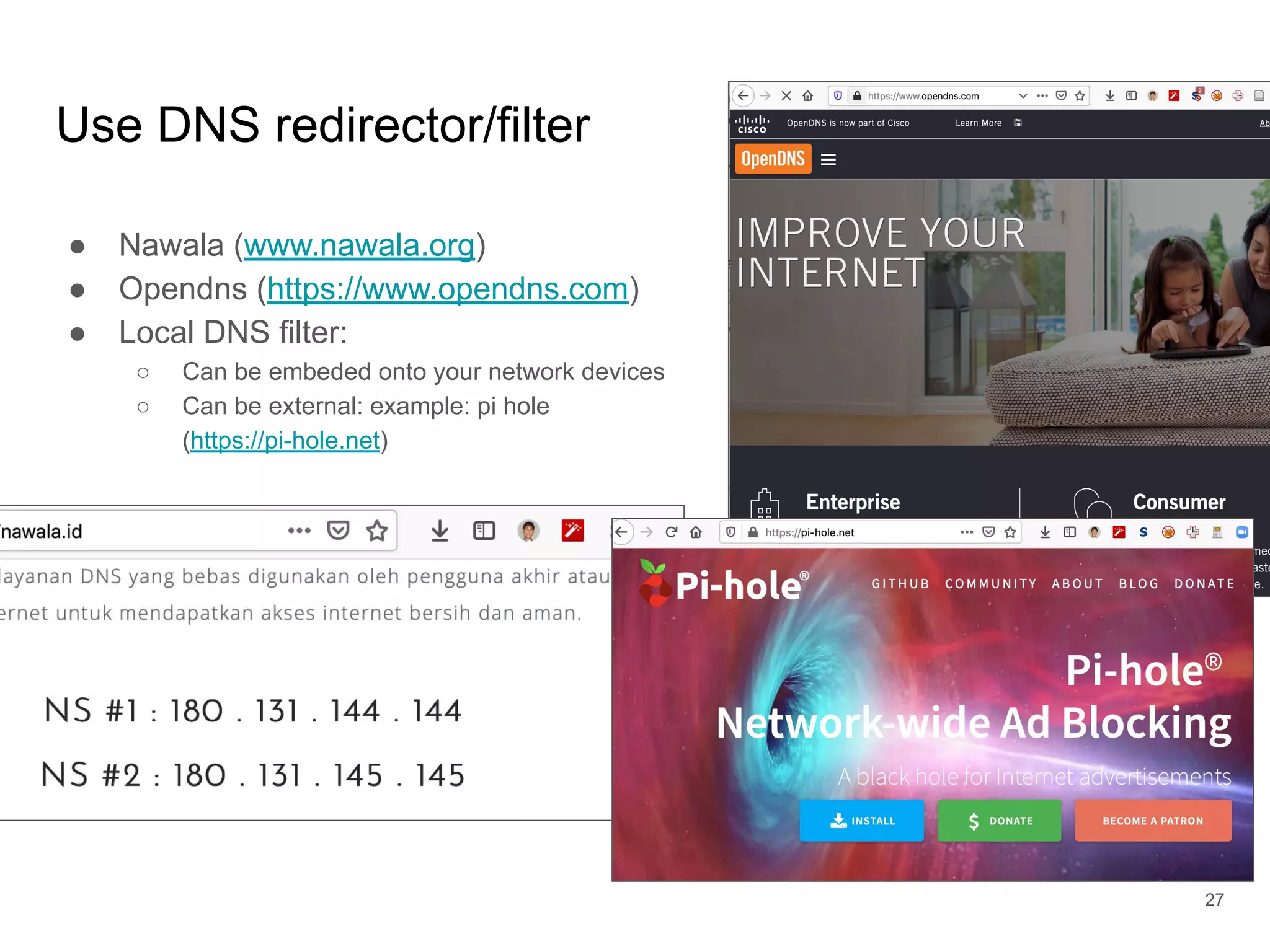
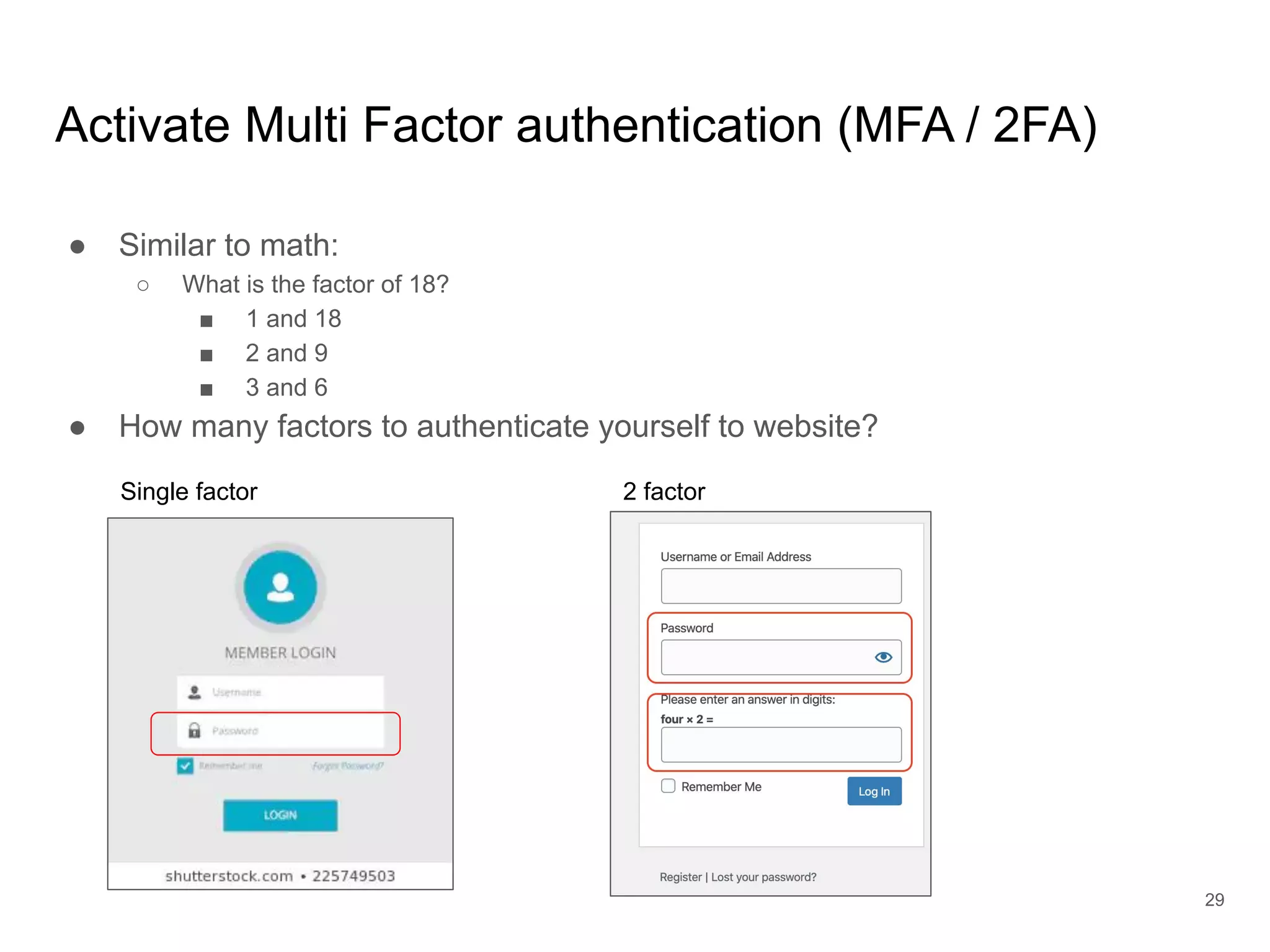
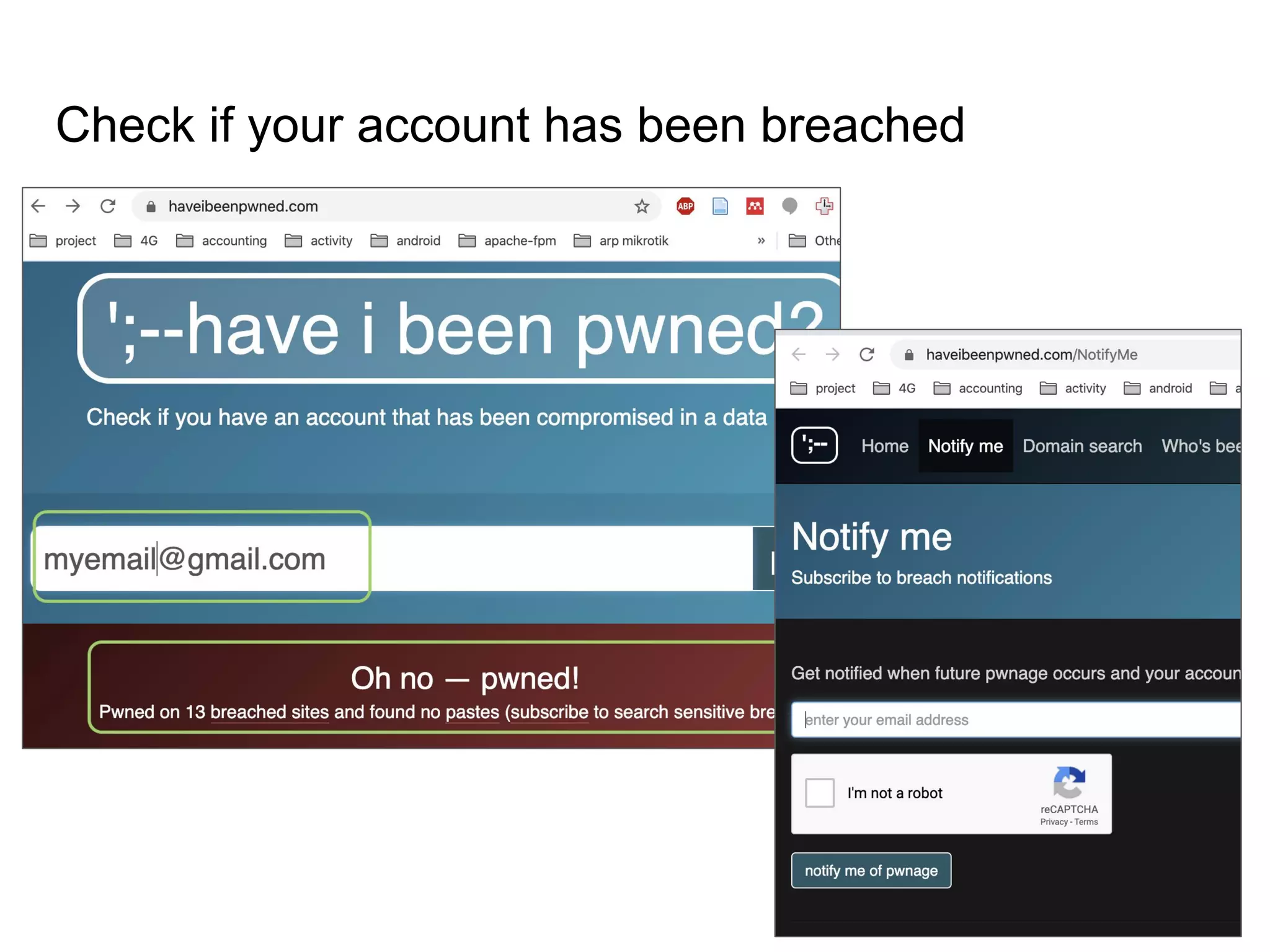
The document provides an introduction to cloud security, covering key aspects of cybersecurity such as types of security, goals of information security, and access control. It discusses vulnerabilities, threats, and risk analysis while emphasizing the importance of securing customer data and using cloud computing. The document concludes with best practices for cloud security, including using HTTPS, DNS filter, and multi-factor authentication.