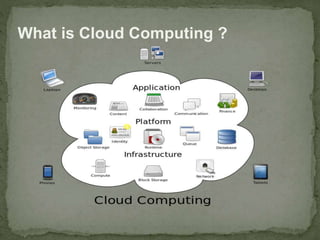
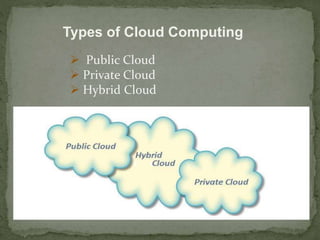
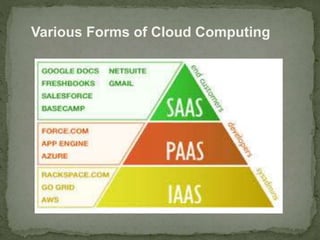
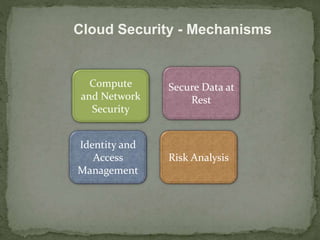
This document discusses cloud security. It begins by defining cloud computing and its various forms. It then discusses the benefits of cloud computing and why cloud security is needed. The document outlines common cloud security concerns like multitenancy, velocity of attacks, information assurance and data privacy. It also describes threats to cloud security such as VM theft, hyperjacking, data leakage and denial-of-service attacks. Finally, it discusses various cloud security mechanisms for securing systems, data, identities and performing risk analysis.