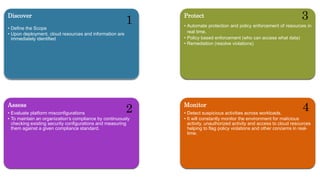
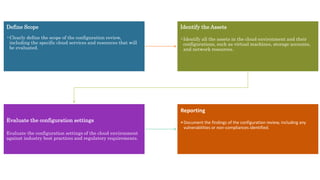
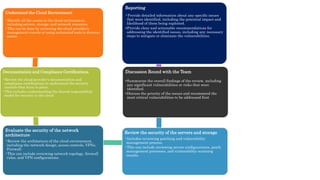
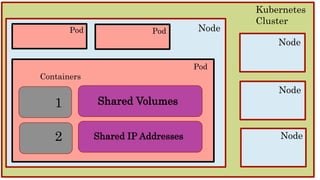
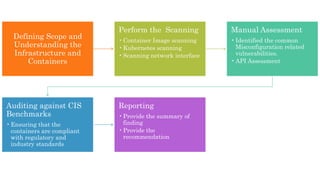
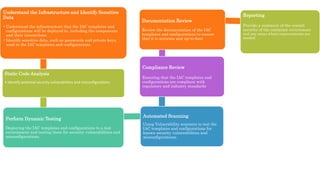
The document discusses various methods for assessing cloud security, emphasizing the need for a unique approach tailored to cloud environments. It details strategies such as cloud security posture management, configuration reviews, and architecture assessments to identify vulnerabilities and improve security measures. Key tools and practices are highlighted, including the importance of continuous monitoring and compliance checks to mitigate risks associated with cloud deployments.