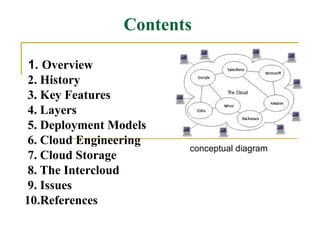
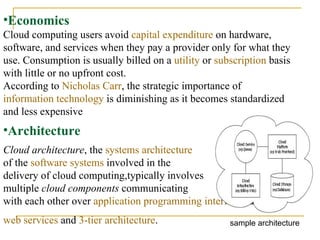
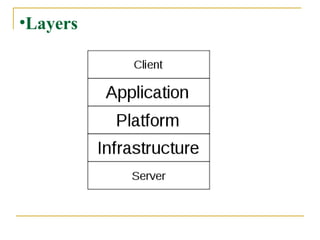
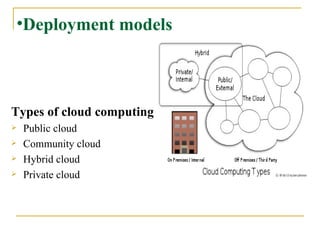
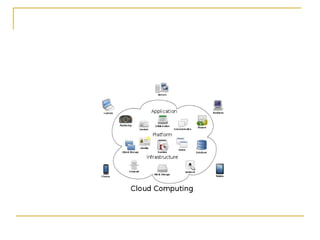
The document provides an overview of cloud computing, including its history, key features, deployment models, layers, engineering, storage, interconnection of clouds, and issues. It discusses how cloud computing evolved from earlier concepts and allows users to access computing resources over the internet on an as-needed basis. Some challenges include privacy, legal concerns, use of open standards and security issues.