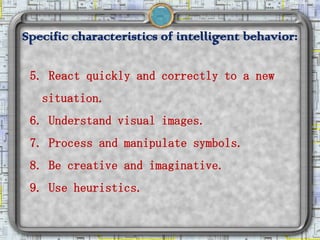
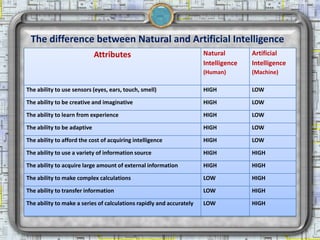
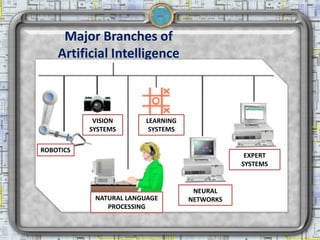
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the ability of machines to mimic human intelligence through learning, problem-solving, and experience. The Turing Test attempts to determine if a computer's responses are indistinguishable from a human's. There are several branches of AI including robotics, vision systems, natural language processing, learning systems, neural networks, and expert systems. Each branch focuses on developing technologies that can perform tasks requiring human-level abilities.