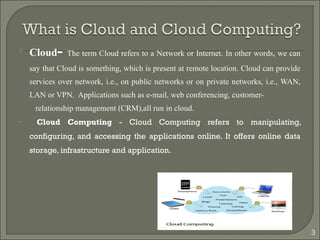
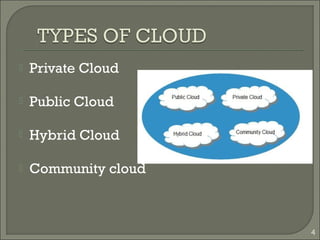
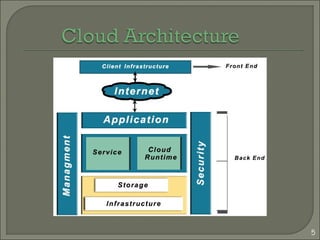
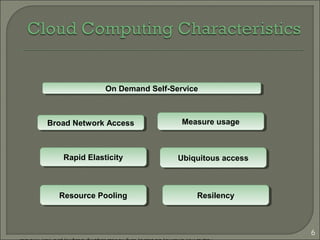
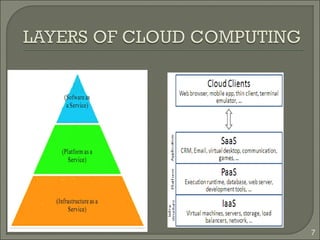
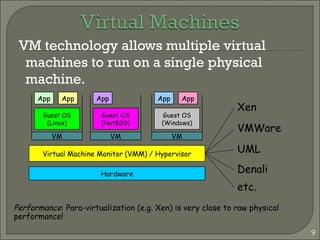
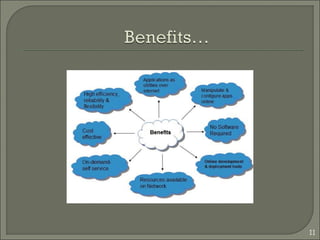
This document summarizes a technical seminar on cloud computing and its applications. The seminar defines cloud computing as manipulating and accessing applications online through data storage, infrastructure, and software provided via the internet. It discusses different types of cloud models (private, public, hybrid, community) and key characteristics of cloud computing including resilience, ubiquitous access, resource pooling, broad network access, rapid elasticity and on-demand self-service. The seminar outlines benefits of cloud computing such as reduced costs, flexibility and scalability. Potential issues discussed include security concerns and dependency on constant internet access.