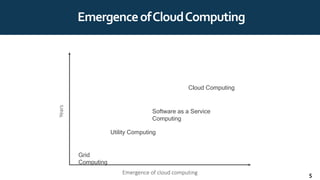
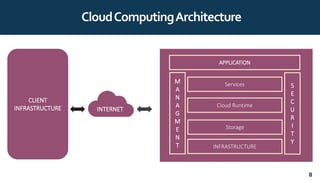
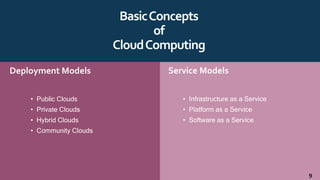
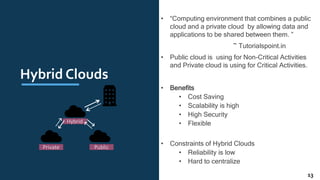
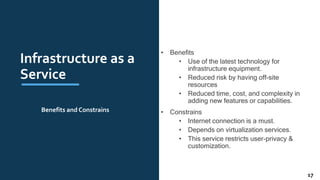
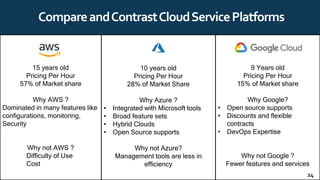
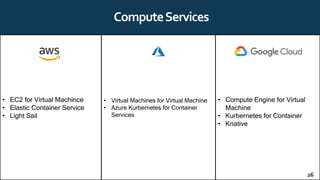
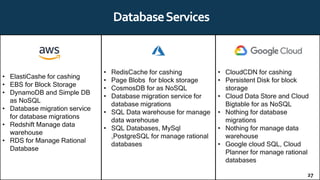
The document provides an overview of cloud computing, including definitions, history, benefits, architecture, deployment models, service models, and major cloud platforms. It defines cloud computing as services provided over the internet such as software, servers, storage, and networking. The history of cloud computing is traced from time-sharing mainframes to today's major public cloud platforms. Key cloud computing concepts covered include infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), software as a service (SaaS), and public, private, hybrid and community cloud deployment models. Major cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud are compared in terms of services offered, pricing models, and market share.