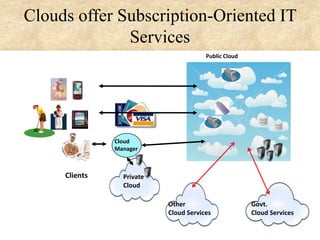
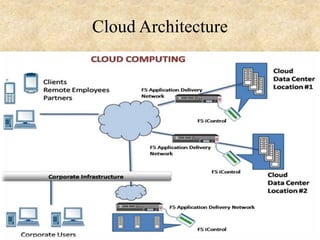
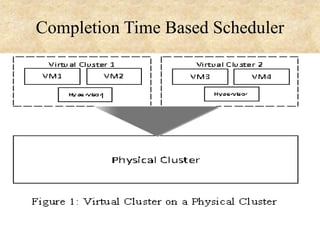
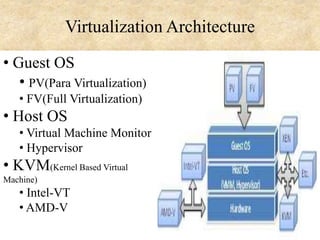
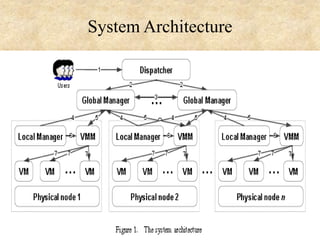
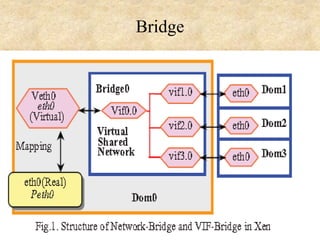
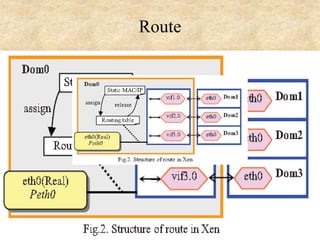
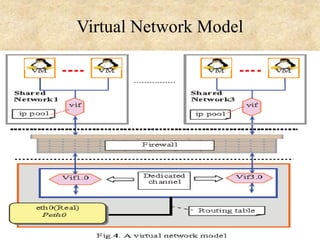
This document presents an overview of cloud computing concepts including cloud architecture, deployment models, service models, characteristics, job scheduling, virtualization, energy conservation, and network security. It discusses key cloud computing topics such as Infrastructure as a Service, Platform as a Service, Software as a Service, public clouds, private clouds, hybrid clouds, community clouds, resource pooling, broad network access, on-demand self-service, and measured service. Virtualization concepts like hypervisors, virtual machine monitors, and virtual network models are also covered.