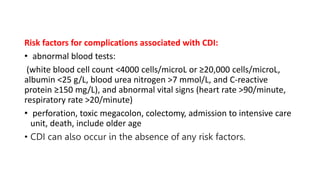
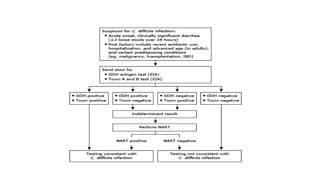
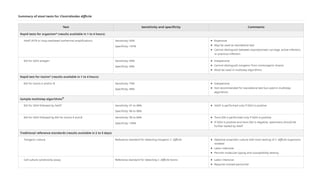
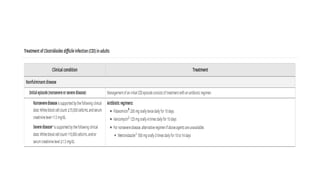
Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) is a leading cause of hospital-acquired infection, particularly impacting older adults, and is associated with antibiotic use that disrupts normal gut flora. The pathogen releases potent toxins that cause varying degrees of gastrointestinal symptoms, from asymptomatic carriage to severe colitis, and is highly transmissible via the fecal-oral route. Diagnosis and treatment strategies are crucial, especially considering the significant risk factors and potential complications associated with CDI.