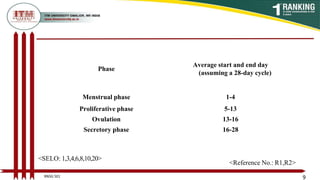
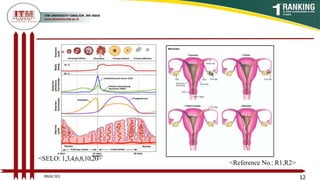
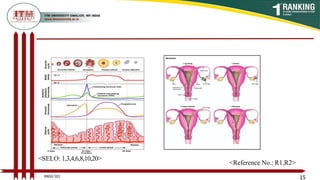
This document provides an overview of the menstrual cycle in 3 phases - the menstrual, proliferative, and secretory phases. It defines key terms like menarche and menopause. The menstrual phase involves menstruation and lasts 1-4 days. The proliferative phase involves follicle development under FSH stimulation. Ovulation occurs in the proliferative phase. In the secretory phase, the corpus luteum forms and produces progesterone to prepare the uterus for potential implantation.