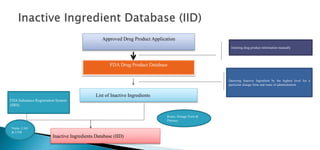
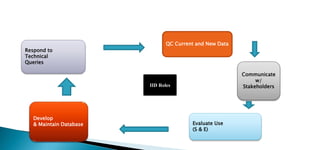
The document discusses the Inactive Ingredient Database (IID) maintained by the FDA which contains information on inactive ingredients in approved drug products. The IID provides data on inactive ingredients by route of administration, dosage form, and maximum potency amount. It is updated quarterly. Having information on previously approved inactive ingredients can help streamline review of new drug products. The FDA is working to improve the usability and functionality of the IID to better meet stakeholder needs.