1. The document discusses effective classroom management strategies presented by Mr. Keo Chhorthong and Mr. Kong Matta at ACLEDA Institute of Business.
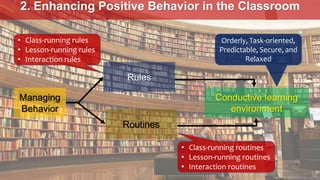
2. It outlines establishing a conductive learning environment through optimizing the physical and psycho-social aspects of the classroom. It also discusses enhancing positive student behavior through implementing clear rules and routines.
3. Building rapport with students is also covered as an important part of effective teaching. Strategies for rapport include knowing students, modeling good behaviors, and creating classroom synergy.
4. The presenters emphasize that effective teaching requires a repertoire of knowledge including content knowledge, knowledge of students and practices, and teaching skills. Professional development is important for acquiring and