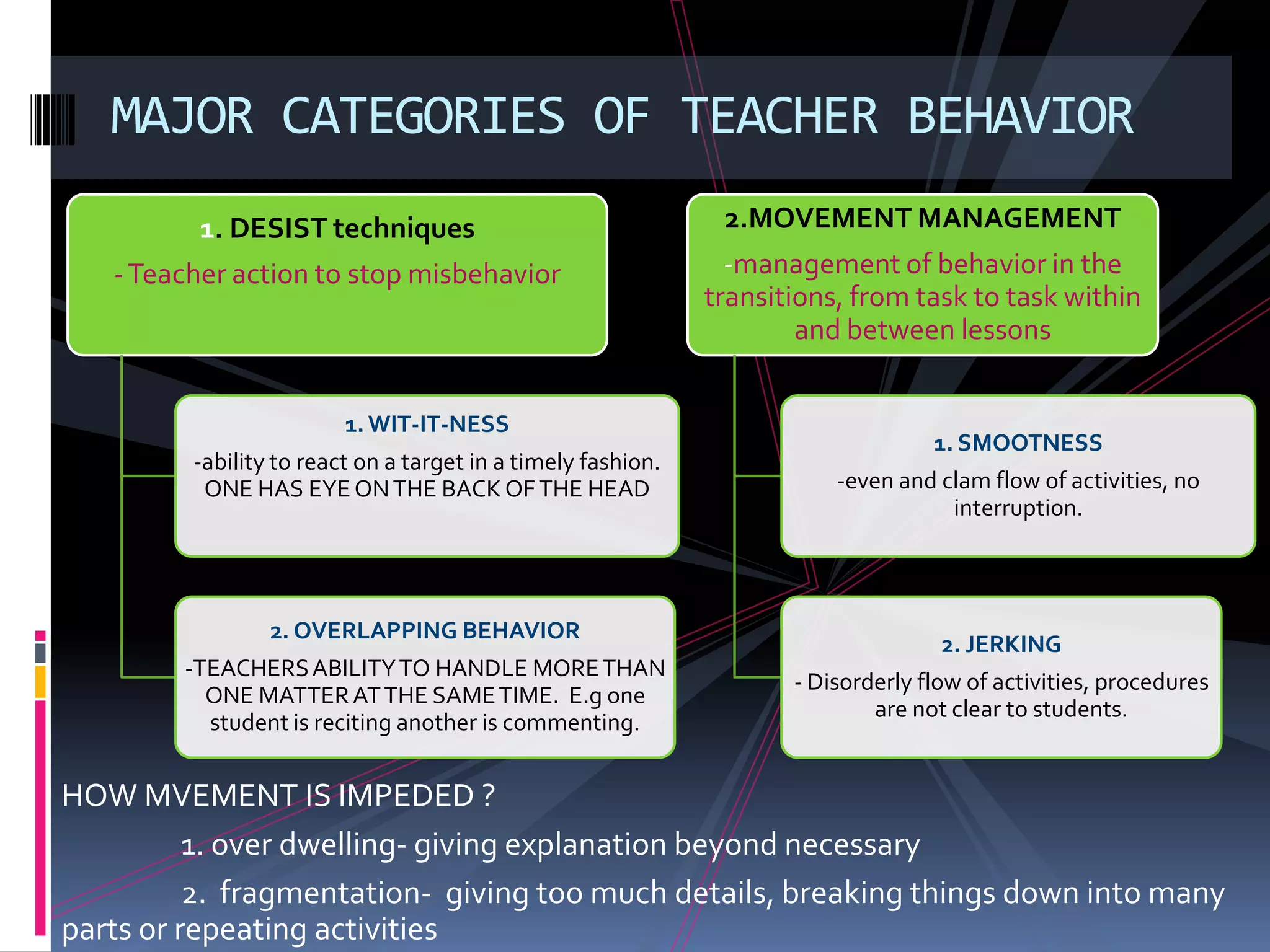
Classroom management involves addressing issues related to student discipline, teaching techniques, supplies, classroom environment, and student relationships. There are several approaches to classroom management, including assertive, business academic, behavior modification, group managerial, group guidance, acceptance, and success approaches. The assertive approach involves clearly communicating rules and consequences. The behavior modification approach uses reinforcement to modify behavior. The group managerial approach aims to quickly address inappropriate group behavior. Effective classroom management also requires preventing problems through planned activities, rules, routines, and monitoring of students.