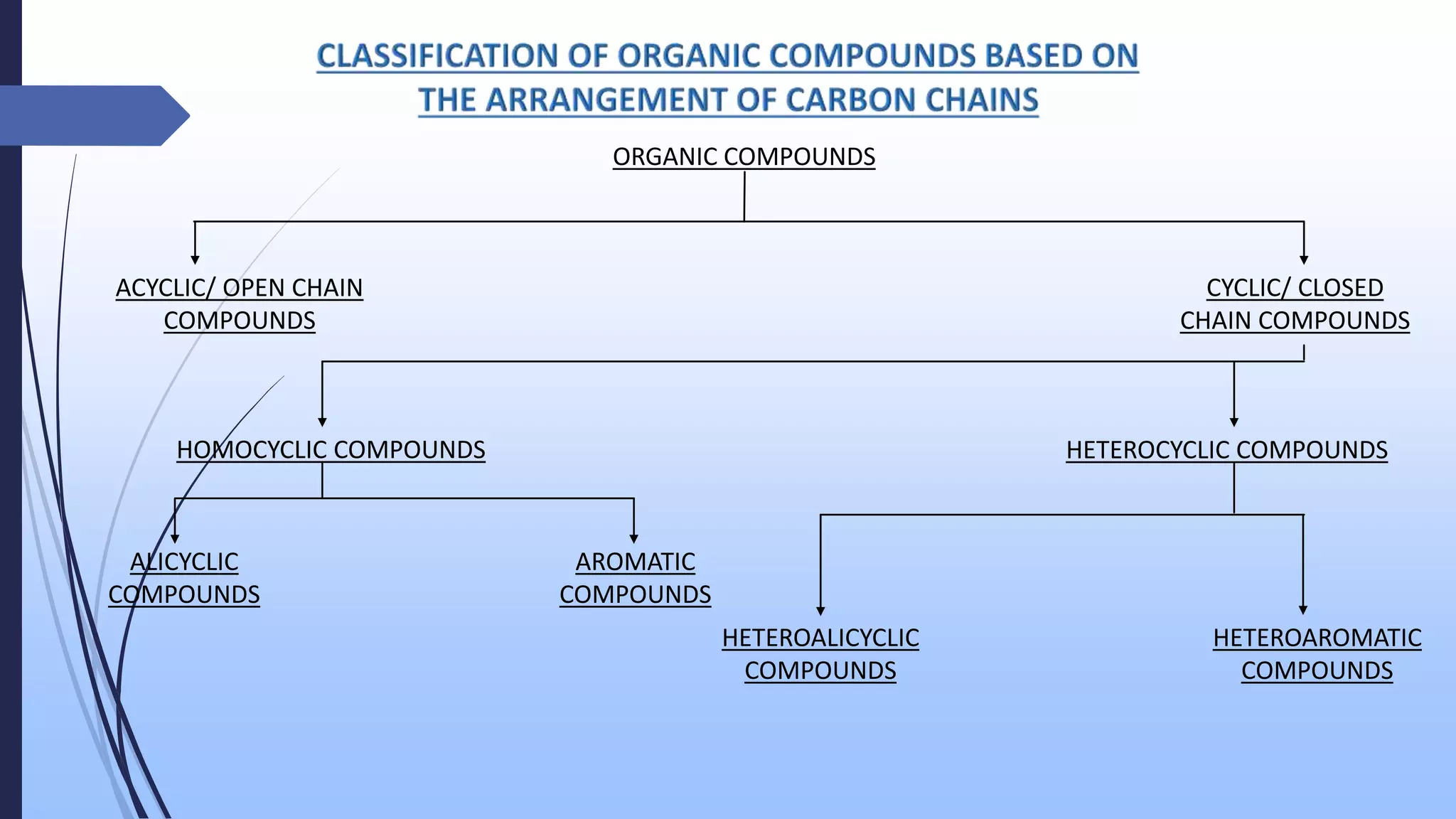
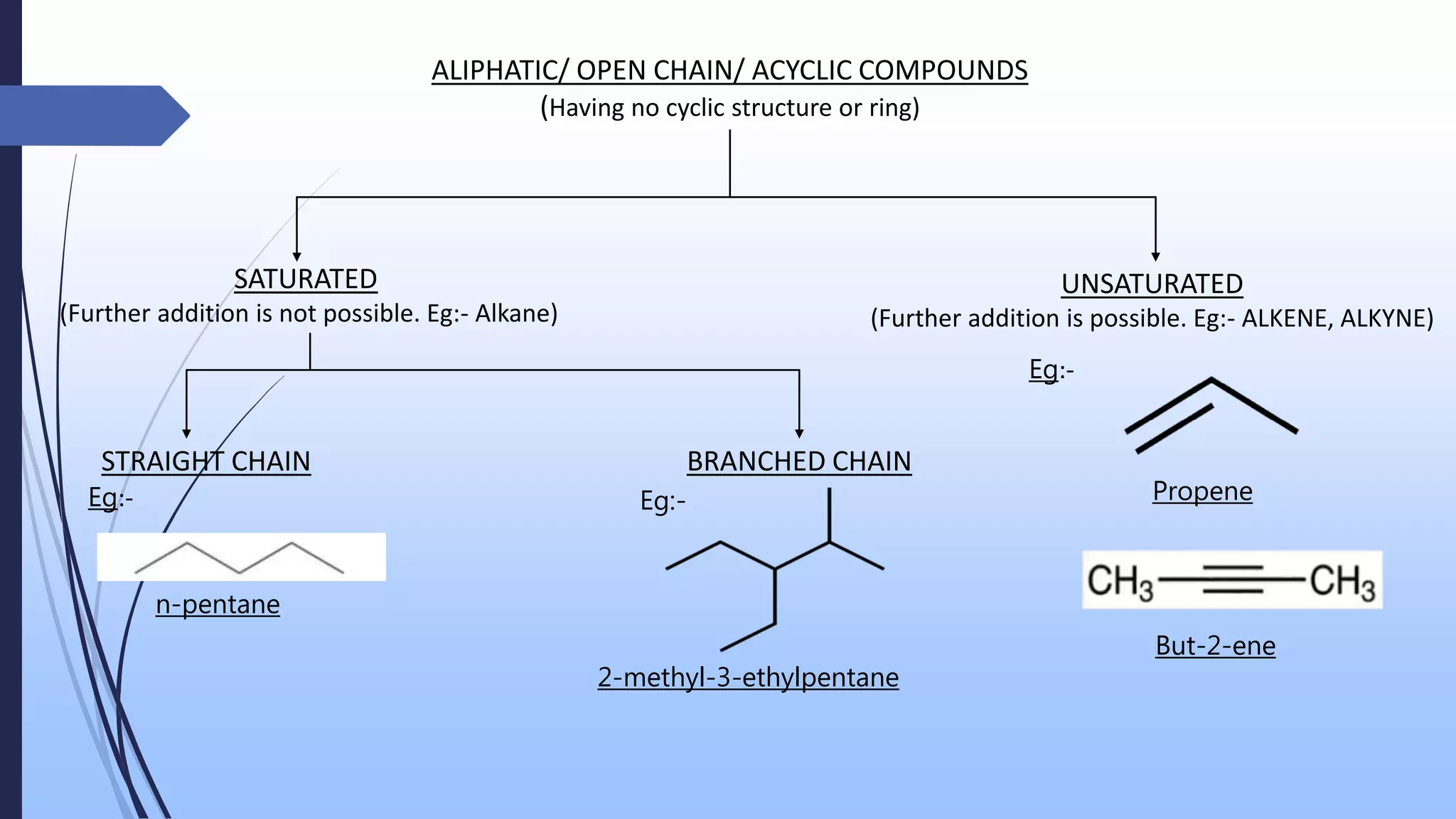
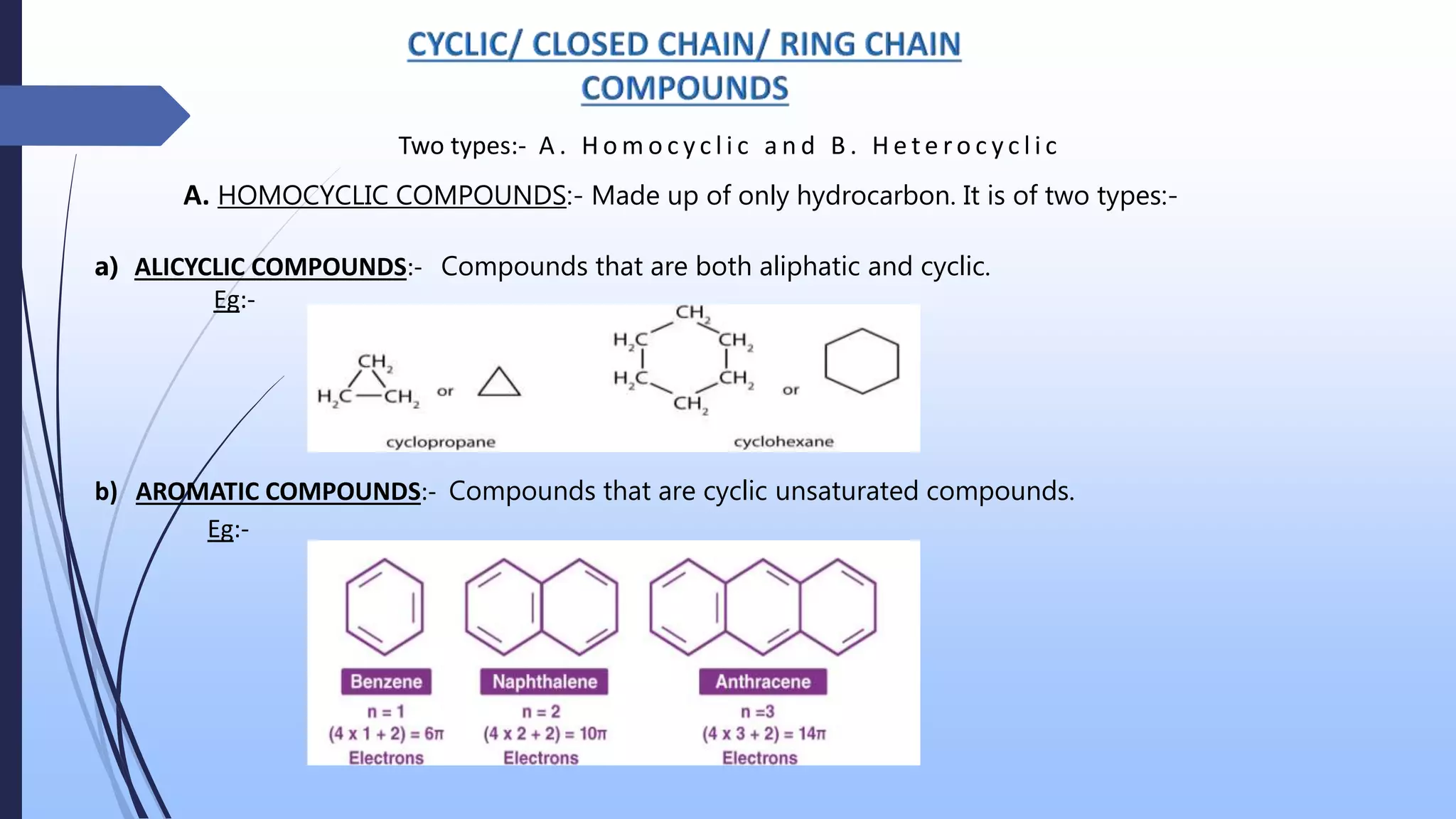
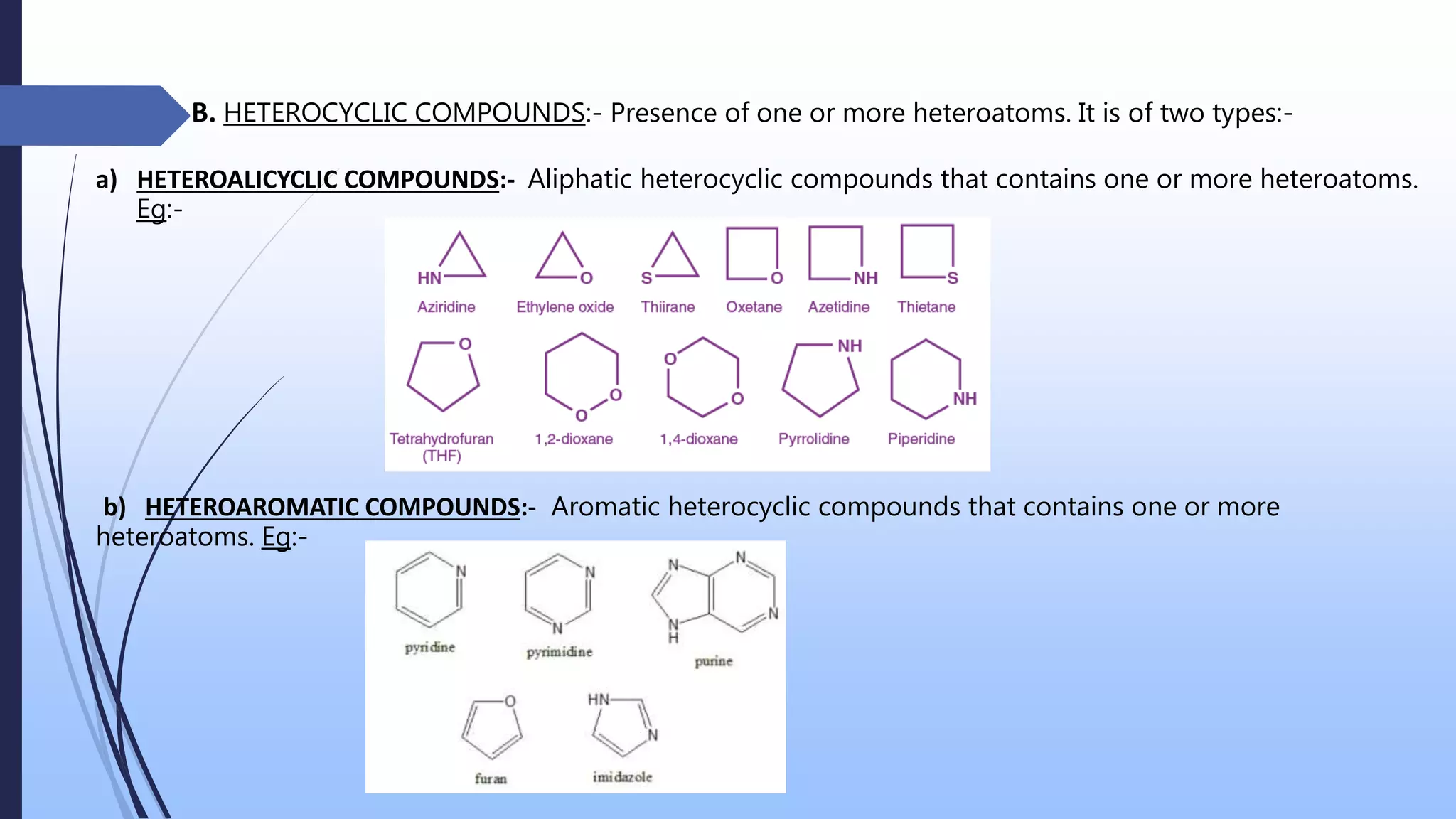
The document presents an overview of the classification of organic compounds, focusing on their arrangement and functional groups. It details various types of compounds, including acyclic, cyclic, homocyclic, and heterocyclic structures, and emphasizes the significance of bonding patterns and functional groups in determining the properties and reactions of these compounds. The document concludes with a bibliography of relevant organic chemistry textbooks.