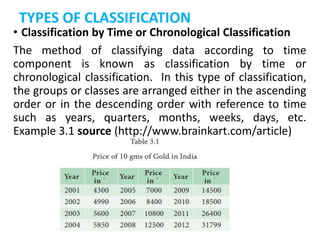
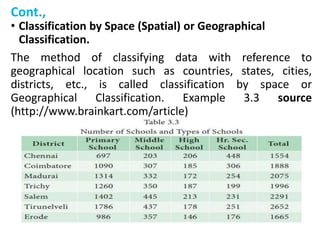
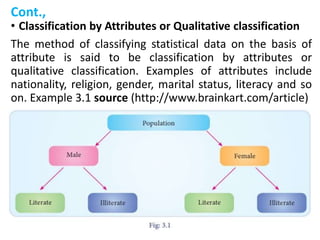
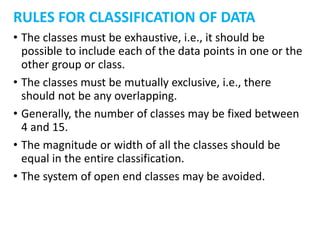
This document discusses classification, which is the process of arranging primary data into groups according to common characteristics. It defines classification and lists its objectives as facilitating comparison, striking homogeneity, and enabling further statistical analysis. The document describes types of classification like chronological, geographical, qualitative, and quantitative. It provides rules for classification, such as classes being exhaustive, mutually exclusive, and of equal magnitude. The document presents an example and MCQs to test understanding of classification concepts.