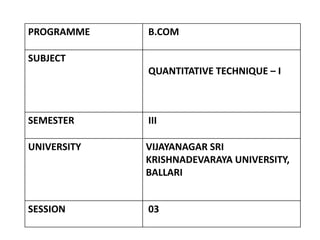
This document provides an overview of quantitative techniques - 1 as part of a B.Com program. It discusses the meaning and definitions of statistics, the objectives of statistics which include determining values to represent data, estimating present trends and predicting the future. It also discusses descriptive and inferential statistics. The functions of statistics are presented, including presenting facts precisely, facilitating comparison, formulation and testing of hypotheses, forecasting, policy making, and measuring uncertainty. Learning objectives and outcomes are provided which are to understand the overview of statistics and data collection techniques. Examples of objectives and functions of statistics are discussed in detail. The session concludes with sample multiple choice questions to test understanding.