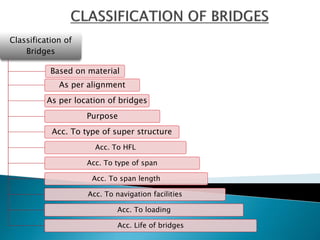
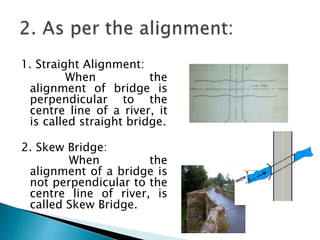
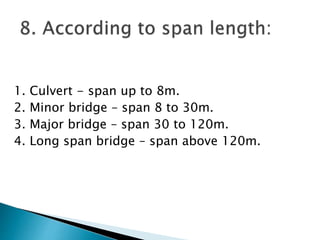
This document provides a classification of bridges based on various criteria such as material, alignment, location, purpose, superstructure type, flood hazard level, span, navigation facilities, loading, and lifespan. Some of the main bridge types discussed include slab bridges, girder bridges, truss bridges, suspension bridges, arch bridges, swing bridges, bascule bridges, and lift bridges. Bridges are also classified based on their span length from minor bridges to long span bridges. Temporary bridges discussed include pontoon, boat, and flying bridges while permanent bridges include RCC, masonry, and steel bridges.