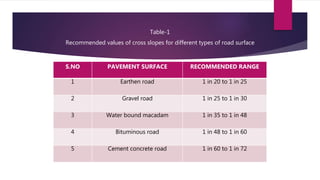
This document discusses the importance and methods of highway drainage systems. It explains that highway drainage aims to remove excess surface water and control subsoil water levels to prevent issues like subgrade failure and pavement deterioration. Surface drainage is achieved through cross slopes, ditches, inlets, storm sewers, and culverts to divert water away. Subsurface drainage uses subsurface drains to intercept groundwater and prevent changes in subgrade moisture content. Proper drainage design is an essential part of highway construction.