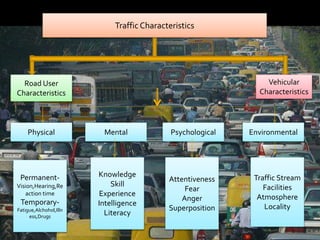
The document is a presentation on traffic engineering, outlining its importance in ensuring safe and efficient traffic flow for both vehicles and pedestrians. It covers various aspects including traffic characteristics, user and vehicle specifics, and the factors influencing driver behavior and vehicle performance. Key components discussed include the perception-reaction time, road user types, and vehicle categories which impact overall traffic management.